Abstract
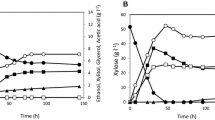
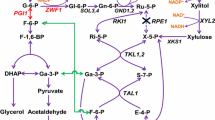
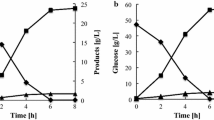
Simultaneous co-utilization of xylose and glucose is a key issue in engineering microbes for cellulosic ethanol production. We coupled xylose utilization with glucose metabolism by deletion of d-ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase (RPE1) through pentose phosphate pathway flux. Simultaneous utilization of xylose and glucose then occurred in the engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with the xylose utilization pathway. Xylose consumption occurred at the beginning of glucose consumption by the engineered yeast without RPE1 in a mixed sugar fermentation. About 3.2 g xylose l−1 was utilized simultaneously with consumption of 40.2 g glucose l−1 under O2-limited conditions. In addition, an approximate ratio (~1:10) for xylose and glucose consumption was observed in the fermentation with different sugar concentration by the engineered strain without RPE1. Simultaneous utilization of xylose is realized by the coupling of glucose metabolism and xylose utilization through RPE1 deletion in xylose-utilizing S. cerevisiae.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Diao L, Liu Y, Qian F, Yang J, Jiang Y, Yang S (2013) Construction of fast xylose-fermenting yeast based on industrial ethanol-producing diploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae by rational design and adaptive evolution. BMC Biotechnol 13:110
Gawand P, Hyland P, Ekins A, Martin VJ, Mahadevan R (2013) Novel approach to engineer strains for simultaneous sugar utilization. Metab Eng 20:63–72
Gombert AK, dos Santos MM, Christensen B, Nielsen J (2001) Network identification and flux quantification in the central metabolism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under different conditions of glucose repression. J Bacteriol 183:1441–1451
Gonçalves DL, Matsushika A, de Sales BB, Goshima T, Bon EP, Stambuk BU (2014) Xylose and xylose/glucose co-fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing individual hexose transporters. Enzyme Microb Technol 63:13–20
Ha SJ, Galazka JM, Kim SR et al (2011) Engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of simultaneous cellobiose and xylose fermentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:504–509
He Y, Fang Z, Zhang J, Li X, Bao J (2014) De-ashing treatment of corn stover improves the efficiencies of enzymatic hydrolysis and consequent ethanol fermentation. Bioresour Technol 169:552–558
Kim JH, Block DE, Mills DA (2010) Simultaneous consumption of pentose and hexose sugars: an optimal microbial phenotype for efficient fermentation of lignocellulosic biomass. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88:1077–1085
Lee SM, Jellison T, Alper HS (2014) Systematic and evolutionary engineering of a xylose isomerase-based pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient conversion yields. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:122
Li BZ, Balan V, Yuan YJ, Dale BE (2010) Process optimization to convert forage and sweet sorghum bagasse to ethanol based on ammonia fiber expansion (AFEX) pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 101:1285–1292
Lin Q, Jia B, Mitchell LA, Luo J, Yang K, Zeller KI, Zhang W, Xu Z, Stracquadanio G, Bader JS, Boeke JD, Yuan YJ (2014) RADOM, an efficient in vivo method for assembling designed DNA fragments up to 10 kb long in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. ACS Synth Biol. doi:10.1021/sb500241e
Liu L, Zhang L, Tang W, Gu Y, Hua Q, Yang S, Jiang W, Yang C (2012) Phosphoketolase pathway for xylose catabolism in Clostridium acetobutylicum revealed by 13C metabolic flux analysis. J Bacteriol 194:5413–5422
Liu ZH, Qin L, Jin MJ, Pang F, Li BZ, Kang Y, Dale BE, Yuan YJ (2013) Evaluation of storage methods for the conversion of corn stover biomass to sugars based on steam explosion pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 132:5–15
Miosga T, Zimmermann FK (1996) Cloning and characterization of the first two genes of the non-oxidative part of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae pentose-phosphate pathway. Curr Genet 30:404–409
Qin L, Liu ZH, Jin M, Li BZ, Yuan YJ (2013) High temperature aqueous ammonia pretreatment and post-washing enhance the high solids enzymatic hydrolysis of corn stover. Bioresour Technol 146:504–511
Saitoh S, Hasunuma T, Tanaka T, Kondo A (2010) Co-fermentation of cellobiose and xylose using beta-glucosidase displaying diploid industrial yeast strain OC-2. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1975–1982
Shen Y, Chen X, Peng B, Chen L, Hou J, Bao X (2012) An efficient xylose-fermenting recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain obtained through adaptive evolution and its global transcription profile. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:1079–1091
Subtil T, Boles E (2012) Competition between pentoses and glucose during uptake and catabolism in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Biofuels 5:14
Zha J, Hu ML, Shen MH, Li BZ, Wang JY, Yuan YJ (2012) Balance of XYL1 and XYL2 expression in different yeast chassis for improved xylose fermentation. Front Microbiol 3:355
Zha J, Li BZ, Shen MH, Hu ML, Song H, Yuan YJ (2013) Optimization of CDT-1 and XYL1 expression for balanced co-production of ethanol and xylitol from cellobiose and xylose by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS One 8:e68317
Zha J, Shen MH, Hu ML, Song H, Yuan YJ (2014) Enhanced expression of genes involved in initial xylose metabolism and the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway in the improved xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae through evolutionary engineering. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41:27–39
Zhu JQ, Qin L, Li BZ, Yuan YJ (2014) Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation of aqueous ammonia pretreated corn stover with an engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae SyBE005. Bioresour Technol 169:9–18
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21390203) and Ministry of Science and Technology of China (“973” Program: 2013CB733600).
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1 – Primers used in the study.
Supplementary Figure 1 - Fermentation performance of SyBE_Sc17002 in medium containing 40 g glucose l−1 and 10 g xylose l-1. The initial cell density was adjusted to OD600 = 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, MH., Song, H., Li, BZ. et al. Deletion of d-ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase (RPE1) induces simultaneous utilization of xylose and glucose in xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Biotechnol Lett 37, 1031–1036 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1759-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1759-z