Abstract
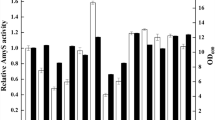
α-Amylase was used as a heterologous model protein to investigate the effects of promoters, signal peptides and over-expression of an extra-cytoplasmic molecular chaperone, PrsA lipoprotein, on enhancing the secretion of α-amylase in Bacillus subtilis. Four promoters and six signal peptides were compared, successively, and the highest yield of α-amylase was achieved under the promotion mediated by PAprE, a strong constitutive promoter, and secretion by SPnprE, a signal peptide from B. subtilis. Moreover, under conditions of overexpressed PrsA lipoprotein, the secretion production and activity of α-amylase increased to 2.5-fold. The performance of the recombinant B. subtilis 1A751PL31 was evaluated with a fed-batch fermentation in a 7.5 l fermentor. Optimization of regulatory elements and over-expression of PrsA lipoprotein had a significant effect on enhancing the production of α-amylase in B. subtilis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brockmeier U, Caspers M, Freudl R, Jockwer A, Noll T, Eggert T (2006) Systematic screening of all signal peptides from Bacillus subtilis: a powerful strategy in optimizing heterologous protein secretion in Gram-positive bacteria. J Mol Biol 362:393–402
Caspers M, Brockmeier U, Degering C, Eggert T, Freudl R (2010) Improvement of Sec-dependent secretion of a heterologous model protein in Bacillus subtilis by saturation mutagenesis of the N-domain of the AmyE signal peptide. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1877–1885
Degering C, Eggert T, Puls M, Bongaerts J, Evers S, Maurer KH, Jaeger KE (2010) Optimization of protease secretion in Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis by screening of homologous and heterologous signal peptides. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6370–6376
Harwood CR, Cranenburgh R (2008) Bacillus protein secretion: an unfolding story. Trends Microbiol 16:73–79
Jan J, Valle F, Bolivar F, Merino E (2001) Construction of protein overproducer strains in Bacillus subtilis by an integrative approach. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55:69–75
Kakeshita H, Kageyama Y, Endo K, Tohata M, Ara K, Ozaki K, Nakamura K (2011) Secretion of biologically-active human interferon-beta by Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Lett 33:1847–1852
Kontinen VP, Sarvas M (1993) The PrsA lipoprotein is essential for protein secretion in Bacillus subtilis and sets a limit for high-level secretion. Mol Microbiol 8:727–737
Leloup L, Driessen AJM, Freudl R (1999) Differential dependence of levansucrase and α-amylase secretion on SecA (Div) during the exponential phase of growth of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 181:1820–1826
Li W, Zhou X, Lu P (2004) Bottlenecks in the expression and secretion of heterologous proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Res Microbiol 155:605–610
Liu YH, Lu FP, Li Y, Wang JL, Gao C (2008) Acid stabilization of Bacillus licheniformis alpha amylase through introduction of mutations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:795–803
Nakamura K, Fujita Y, Itoh Y, Yamane K (1989) Modification of length, hydrophobic properties and electric charge of Bacillus subtilis alpha-amylase signal peptide and their different effects on the production of secretory proteins in B. subtilis and Escherichia coli cells. Mol Genet Genomics 216:1–9
Rahfeld J-U, Rücknagel KP, Schelbert B, Ludwig B (1994) Comfirmation of the existence of a third family among peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerases amino acid sequence and recombinant production of parvulin. FEBS Lett 352:180–184
Simonen M, Palva I (1993) Protein secretion in Bacillus species. Microbiol Rev 57:109–137
Vitikainen M, Pummi T, Airaksinen U, Wahlstrom E, Wu H, Sarvas M, Kontinen VP (2001) Quantitation of the capacity of the secretion apparatus and requirement for PrsA in growth and secretion of alpha-amylase in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 183:1881–1890
Westers L, Westers H, Quax WJ (2004) Bacillus subtilis as cell factory for pharmaceutical proteins: a biotechnological approach to optimize the host organism. Biochim Biophys Acta 1694:299–310
Westers L, Dijkstra DS, Westers H, van Dijl JM, Quax WJ (2006) Secretion of functional human interleukin-3 from Bacillus subtilis. J Biotechnol 123:211–224
You C, Zhang XZ, Zhang YH (2012) Simple cloning via direct transformation of PCR product (DNA Multimer) to Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:1593–1595
Zanen G, Houben EN, Meima R, Tjalsma H, Jongbloed JD, Westers H, Oudega B, Luirink J, van Dijl JM, Quax WJ (2005) Signal peptide hydrophobicity is critical for early stages in protein export by Bacillus subtilis. FEBS J 272:4617–4630
Zhang J, Kang Z, Ling Z, Cao W, Liu L, Wang M, Du G, Chen J (2013) High-level extracellular production of alkaline polygalacturonate lyase in Bacillus subtilis with optimized regulatory elements. Biores Technol 146:543–548
Zhang H, Fu G, Zhang D (2014) Cloning, characterization, and production of a novel lysozyme by different expression hosts. J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1405–1412
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from National Nature Science Foundation of China (31200036, 31370089), the State Key Development Program for Basic Research of China (973 Program, 2013CB733600), and the Key Projects in the Tianjin Science & Technology Pillar Program (14ZCZDSY00065).
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—Strains and plasmids used in this study.
Supplementary Table 2—Primers used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Gai, Y., Fu, G. et al. Enhanced extracellular production of α-amylase in Bacillus subtilis by optimization of regulatory elements and over-expression of PrsA lipoprotein. Biotechnol Lett 37, 899–906 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1755-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1755-3