Abstract
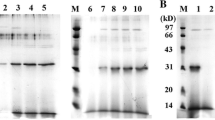
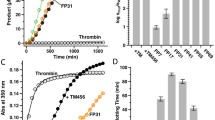
Recombinant plasminogen activator (r-PA, reteplase) is an engineered variant of alteplase. When expressed in E. coli, it appears as inclusion bodies that require refolding to recover its biological activity. An important step following refolding is to determine the activity of refolded protein. Current methods for enzymatic activity of thrombolytic drugs are costly and complex. Here a straightforward and low-cost clot lysis assay was developed. It quantitatively measures the activity of the commercial reteplase and is also capable of screening refolding conditions. As evidence for adequate accuracy and sensitivity of the current assay, r-PA activity measurements are shown to be comparable to those obtained from chromogenic substrate assay.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkjaersig N, Fletcher AP, Sherry S (1959) The mechanism of clot dissolution by plasmin. J Clin Invest 38:1086–1095
Apte-Deshpnade A, Mandal G, Soorapaneni S, Prasad B, Kumar J, Padmanabhan S (2009) High-level expression of non-glycosylated and active staphylokinase from Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Lett 31:811–817
Astrup T, Mullertz S (1952) The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys 40:346–351
Beebe DP, Aronson DL (1987) An automated fibrinolytic assay performed in microtiter plates. Thromb Res 47:123–128
Cylwik D, Mogielnicki A, Kramkowski K, Stokowski J, Buczko W (2004) Antithrombotic effect of l-arginine in hypertensive rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 55:563–574
De Bernardez Clark E, Schwarz E, Rudolph R (1999) Inhibition of aggregation side reactions during in vitro protein folding. Method Enzymol 309:217–236
Fazeli A, Shojaosadati SA, Fazeli MR, Ilka H (2011) Effect of parallel feeding of oxidizing agent and protein on fed-batch refolding process of recombinant IFNβ-1b. Process Biochem 46:796–800
Jones AJS, Meunier AM (1990) A precise and rapid microtiter plate clot lysis assay: methodology, kinetic modelling and measurement of catalytic constants for plasminogen activation during fibrinolysis. Thromb Haemost 64:455–463
Kessner A, Troll W (1976) Fluorometric microassay of plasminogen activators. Arch Biochem Biophys 176:411–416
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lewis ML, Nachtwey DS, Damron KL (1991) A miniaturized fibrinolytic assay for plasminogen activators. Thromb Res 64:223–234
Nordt TK, Bode C (2003) Thrombolysis: newer thrombolytic agents and their role in clinical medicine. Heart 89:1358–1362
Okuda M, Yamamoto Y (2004) Usefulness of synthetic phospholipid in measurement of activated partial thromboplastin time: a new preparation procedure to reduce batch difference. Clin Lab Haematol 26:215–233
Prasad S, Kashyap RS, Deopujari JY, Purohit HJ, Taori GM, Daginawala HF (2006) Development of an in vitro model to study clot lysis activity of thrombolytic drugs. Thromb J 4:14
Rijken DC, Lijnen HR (2009) New insights into the molecular mechanisms of the fibrinolytic system. J Thromb Haemost 7:4–13
Saito Y, Ishii Y, Sasaki H, Hayashi M, Fujimura T, Imai Y, Nakamura S, Suzuki S, Notani J, Asada T (1994) Production and characterization of a novel tissue-type plasminogen activator derivative in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Prog 10:472–479
Sherry S, Alkjaersig N, Fletcher AP (1966) Activity of plasmin and streptokinase-activator on substituted arginine and lysine esters. Thromb Diath Haemorrh 16:18–31
Sidelmann J, Jespersen J, Gram J (1995) Plasminogen activator activity and plasma-coagulum lysis measured by use of optimized fibrin gel structure preformed in microtiter plates. Clin Chem 41:979–985
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Zistdaru Danesh Company for their generous gift of r-PA inclusion bodies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamialahmadi, O., Fazeli, A., Hashemi-Najafabadi, S. et al. A novel clot lysis assay for recombinant plasminogen activator. Biotechnol Lett 37, 593–600 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1711-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1711-2