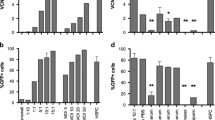
Abstract
Lentivirus-based vectors have the potential to transduce non-dividing primary stem cells. However, primary cells tend to be less susceptible to manipulation and require a high concentration of virus inoculum. Furthermore, increasing the concentration of the lentivirus inoculum may raise safety risks. Therefore, to develop a technique that allows high transduction efficiency at low multiplicities of infection (MOIs), we optimized a lentivirus-based system for cell lines and primary cells by determining the best condition using various parameters. When progenitor cell assays were conducted using human CD34+ bone marrow and mononuclear cells, the transduction condition yielded a great number of eGFP+ colonies with lower-dose viral inocula compared to that of current lentivirus-based transduction technologies. In conclusion, this system is anticipated to produce stable expression of a gene introduced into primary cells for preclinical studies with lower safety risks.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiuti A, Biasco L, Scaramuzza S, Ferrua F, Cicalese MP, Baricordi C, Dionisio F, Calabria A, Giannelli S, Castiello MC et al (2013) Lentiviral hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy in patients with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Science 341:1233151
Buchschacher GL Jr, Wong-Staal F (2000) Development of lentiviral vectors for gene therapy for human diseases. Blood 95:2499–2504
Case S, Price M, Jordan C, Yu X, Wang L, Bauer G, Haas DL, Xu D, Stripecke R, Naldini L et al (1999) Stable transduction of quiescent CD34(+)CD38(−) human hematopoietic cells by HIV-1-based lentiviral vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:2988–2993
Chen M, Li W, Fan J, Kasahara N, Woodley D (2003) An efficient gene transduction system for studying gene function in primary human dermal fibroblasts and epidermal keratinocytes. Clin Exp Dermatol 28:193–199
Guenechea G, Gan OI, Inamitsu T, Dorrell C, Pereira DS, Kelly M, Naldini L, Dick JE (2000) Transduction of human CD34+ CD38− bone marrow and cord blood-derived SCID-repopulating cells with third-generation lentiviral vectors. Mol Ther 1:566–573
Hofmann W, Schubert D, LaBonte J, Munson L, Gibson S, Scammell J, Ferrigno P, Sodroski J (1999) Species-specific, postentry barriers to primate immunodeficiency virus infection. J Virol 73:10020–10028
Kutner RH, Puthli S, Marino MP, Reiser J (2009) Simplified production and concentration of HIV-1-based lentiviral vectors using HYPERFlask vessels and anion exchange membrane chromatography. BMC Biotechnol 9:10–15
Kwon YJ, Peng CA (2005) High-yield retroviral production using a temperature-modulated two-stage operation. Biotechnol Bioeng 90:365–372
Leuci V, Gammaitoni L, Capellero S, Sangiolo D, Mesuraca M, Bond HM, Migliardi G, Cammarata C, Aglietta M, Morrone G et al (2009) Efficient transcriptional targeting of human hematopoietic stem cells and blood cell lineages by lentiviral vectors containing the regulatory element of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome gene. Stem Cells 27:2815–2823
Noort WA, Kruisselbrink AB, Anker PS, Kruger M, van Bezooijen RL, de Paus RA, Heemskerk MH, Löwik CW, Falkenburg JH, Willemze R et al (2002) Mesenchymal stem cells promote engraftment of human umbilical cord blood-derived CD34+ cells in NOD/SCID mice. Exp Hematol 30:870–878
O’Connor TP, Crystal RG (2006) Genetic medicines: treatment strategies for hereditary disorders. Nat Rev Genet 7:261–276
Sarkis C, Philippe S, Mallet J, Serguera C (2008) Non-integrating lentiviral vectors. Curr Gene Ther 8:430–437
Sloan RD, Wainberg MA (2011) The role of unintegrated DNA in HIV infection. Retrovirology 8(52):1–15
Sutton RE, Wu HT, Rigg R, Bohnlein E, Brown PO (1998) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vectors efficiently transduce human hematopoietic stem cells. J Virol 72:5781–5788
Yi Y, Noh MJ, Lee KH (2011) Current advances in retroviral gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther 11:218–228
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant (KRF08-C00557) and a Grant of the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project of the Ministry for Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (A091007).
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S.W., Pyo, CW. & Choi, SY. High-efficiency lentiviral transduction of primary human CD34+ hematopoietic cells with low-dose viral inocula. Biotechnol Lett 37, 281–288 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1678-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1678-z