Abstract
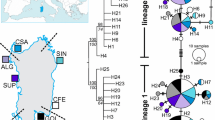
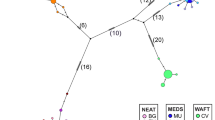
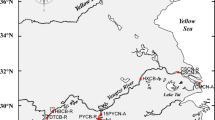
The genetic differentiation among the populations of the European abalone Haliotis tuberculata was investigated using different markers to better understand the evolutionary history and exchanges between populations. Three markers were used: mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I (COI), the sperm lysin nuclear gene, and eight nuclear microsatellites. These markers present different characteristics concerning mutation rate and inheritance, which provided complementary information about abalone history and gene diversity. Genetic diversity and relationships among subspecies were calculated from a sample of approximately 500 individuals, collected from 17 different locations in the north-eastern Atlantic Ocean, Macaronesia, and Mediterranean Sea. COI marker was used to explore the phylogeny of the species with a network analysis and two phylogenetic methods. The analysis revealed 18 major haplotypes grouped into two distinct clades with a pairwise sequence divergence up to 3.5 %. These clades do not correspond to subspecies but revealed many contacts along Atlantic coast during the Pleistocene interglaciations. The sperm lysin gene analysis separated two different subtaxa: one associated to Macaronesian islands, and the other to all other populations. Moreover, a small population of the northern subtaxon was isolated in the Adriatic Sea—probably before the separation of the two lineages—and evolved independently. Microsatellites were analyzed by different genetics methods, including the Bayesian clustering method and migration patterns analysis. It revealed genetically distinct microsatellite patterns among populations from Mediterranean Sea, Brittany and Normandy, Morocco, and Canary and Balearic islands. Gene flow is asymmetric among the regions; the Azores and the Canary Islands are particularly isolated and have low effective population sizes. Our results support the hypothesis that climate changes since the Pleistocene glaciations have played a major role in the geographic distribution of the European abalone. Traces of these events related to maternal inheritance were shown on COI marker.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addison JA, Hart MW (2005) Colonization, dispersal, and hybridization influence phylogeography of North Atlantic Sea urchins (Strongilocentrotus droebachiensis). Evolution 59:532–543
Almada VC, Oliveira RF, Goncalves EJ, Almeida AJ, Santos RS, Wirtz P (2001) Patterns of diversity of the north-eastern Atlantic blenniid fish fauna (Pisces: Blenniidae). Glob Ecol Biogeogr 10:411–422
An HS, Jee YJ, Min KS, Kim BL, Han SJ (2005) Phylogenetic analysis of six species of pacific abalone (Haliotidae) based on DNA sequences of 16 s rRNA and cytochrome oxidase subunit I mitochondrial genes. Marine Biotechnology. Springer, New York, pp 373–380
Ávila SP, Da Silva CM, Schiebel R, Cecca F, Backeljau T, De Frias Martins AM (2009) How did they get here? The biogeography of the marine molluscs of the Azores. Bull Soc Geol Fr 180:295–307
Avise JC (2000) Phylogeography: the history and formation of species. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Azevedo C, Conchas RF, Tajdari J, Montes J (2006a) Ultrastructural description of new Rickettsia-like organisms in the commercial abalone Haliotis tuberculata (Gastropoda: Haliotidae) from the NW of Spain. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 71:233–237
Azevedo C, Balseiro P, Casal G, Gestal C, Aranguren R, Stokes NA, Carnegie RB, Novoa B, Burreson EM, Figueras A (2006b) Ultrastructural and molecular characterization of Haplosporidium montforti n. sp., parasite of the European abalone Haliotis tuberculata. J Invertebr Pathol 92:23–32
Bahri-Sfar L, Lemaire C, Hassine OKB, Bonhomme F (2000) Fragmentation of sea bass populations in the western and eastern Mediterranean as revealed by microsatellite polymorphism. Proc R Soc Lond B 267:929–935
Balseiro P, Aranguren R, Gestal C, Novoa B, Figueras A (2006) Candidatus Xenohaliotis californiensis and Haplosporidium montforti associated with mortalities of abalone Haliotis tuberculata cultured in Europe. Aquaculture 258:63–72
Bandelt HJ, Forster P, RÃhl A (1999) Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 16(1):37–48
Beerli P, Felsenstein J (2001) Maximum likelihood estimation of a migration matrix and effective population sizes in n subpopulations by using a coalescent approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:4563–4568
Belkhir K, Borsa P, Chikhi L, Raufaste N, Bonhomme F (1996–2004) GENETIX 4.05, logiciel sous Windows TM pour la génétique des populations. Laboratoire Génome, Populations, Interactions, CNRS UMR 5171, Université de Montpellier II, Montpellier (France).
Benzie JAH, Smith-Keune C (2006) Microsatellite variation in Australian and Indonesian pearl oyster Pinctada maxima populations. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 314:197–211
Bester-van der Merwe A (2009) Population genetic structure and demographical history of South African abalone, Haliotis midae, in a conservation context. Stellenbosh University, Stellenbosch
Bierne N, Borsa P, Daguin C, Jollivet D, Viard F, Bonhomme F, David P (2003) Introgression patterns in the mosaic hybrid zone between Mytilus edulis and M. galloprovincialis. Mol Ecol 12:447–461
Borsa P, Blanquer A, Berrebi P (1997) Genetic structure of the flounders Platichthys flesus and P. stellatus at different geographic scales. Mar Biol 129:233–246
Calderón I, Giribet G, Turon X (2008) Two markers and one history: phylogeography of the edible common sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus in the Lusitanian region. Mar Biol 154:137–151
Calvo E, Villanueva J, Grimalt JO, Boelaert A, Labeyrie L (2001) New insights into the glacial latitudinal temperature gradients in the North Atlantic. Results from UK′37 sea surface temperatures and terrigenous inputs. Earth Planet Sci Lett 188:509–519
Chen C, Durand E, Forbes F, François O (2007) Bayesian clustering algorithms ascertaining spatial population structure: a new computer program and a comparison study. Mol Ecol Notes 7:747–756
Clark PU, Mix AC (2002) Ice sheets and sea level of the last glacial maximum. Quatern Sci Rev 21:1–7
Clark NL, Findlay GD, Yi X, MacCoss MJ, Swanson WJ (2007) Duplication and selection on abalone sperm lysin in an allopatric population. Mol Biol Evol 24:2081–2090
Clavier J, Richard O (1986) Growth of juvenile Haliotis tuberculata (Mollusca: Gastropoda) in their natural environment. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 66:497–503
Conod N, Bartlett JP, Evans BS, Elliott NG (2002) Comparison of mitochondrial and nuclear DNA analyses of population structure in the blacklip abalone Haliotis rubra Leach. Mar Freshw Res 53:711–718
Crowley TJ (1981) Temperature and circulation changes in the eastern North Atlantic during the last 150,000 years: evidence from the planktonic foraminiferal record. Mar Micropaleontol 6:97–129
de Vicose GC, Viera MP, Bilbao A, Izquierdo MS (2007) Embryonic and larval development of Haliotis tuberculata coccinea reeve: an indexed micro-photographic sequence. J Shellfish Res 26:847–854
de Viçose GC, Viera M, Bilbao A, Izquierdo M (2010) Larval settlement of Haliotis tuberculata coccinea in response to different inductive cues and the effect of larval density on settlement, early growth, and survival. J Shellfish Res 29:587–591
Domingues VS, Bucciarelli G, Almada VC, Bernardi G (2005) Historical colonization and demography of the Mediterranean damselfish, Chromis chromis. Mol Ecol 14:4051–4063
Domingues VS, Santos RS, Brito A, Almada VC (2006) Historical population dynamics and demography of the eastern Atlantic pomacentrid Chromis limbata (Valenciennes, 1833). Mol Phylogenet Evol 40:139–147
Domingues VS, Santos RS, Brito A, Alexandrou M, Almada VC (2007) Mitochondrial and nuclear markers reveal isolation by distance and effects of Pleistocene glaciations in the northeastern Atlantic and Mediterranean populations of the white seabream (Diplodus sargus L.). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 346:102–113
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochemistry Bulletin 19:11–15
Du Y-R, Guo S-C, Wang Z-F, Ci H-X, Cai Z-Y, Zhang Q, Su J-P, Liu J-Q (2010) Demographic history of the Tibetan antelope Pantholops hodgsoni (chiru). J Syst Evol 48:490–496
Elliott NG, Evans B, Conod N, Bartlett J, Officer R, Sweijd N (2000) Application of molecular genetics to the understanding of abalone population structure–Australian and South African case studies. J Shellfish Res 19:510
Emig CC. (2004) The Mediterranean deep-sea fauna: historical evolution, bathymetric variations and geographical changes. In: Carnets de Géologie/Notebooks on Geology
Evans B, Sweijd N, Bowie RCK, Cook PA, Elliott NG (2004) Population genetic structure of the perlemoen Haliotis midae in South Africa: evidence of range expansion and founder events. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 270:163–172
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin (version 3.0): an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evolut Bioinform Online 1:47–50
Eynaud F, de Abreu L, Voelker A, Schönfeld J, Salgueiro E, Turon JL, Penaud A, Toucanne S, Naughton F, Sánchez Goñi MF, Malaizé B, Cacho I (2009) Position of the Polar Front along the western Iberian margin during key cold episodes of the last 45 ka. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 10(7):Q07U05
Fernandez R, Lemer S, McIntyre E, Giribet G (2015) Comparative phylogeography and population genetic structure of three widespread mollusc species in the Mediterranean and near Atlantic. Mar Ecol 36:701–715
Geiger DL (1999) A total evidence cladistic analysis of the Haliotideae (Gastropoda: Vetigastropoda). University of Southern California, Los Angeles
Geiger DL (2000) Distribution and biogeography of the Haliotidae (Gastropoda: Vetigastropoda) world-wide. Boll Malacologico 35:57–120
Geiger DL, Groves LT (1999) Review of Fossil Abalone (Gastropoda: Vetigastropoda: Haliotidae) with Comparison to Recent Species. J Paleontol 73:872–885
Girard A (1972) La reproduction de l’ormeau Haliotis tuberculata L. Rev Trav Inst Pêches Marit 36:163–184
Giribet G, Wheeler W (2002) On bivalve phylogeny: a high-level analysis of the Bivalvia (Mollusca) based on combined morphology and DNA sequence data. Invertebr Biol 121:271–324
Gow JL, Noble LR, Rollinson D, Jones CS (2005) A high incidence of clustered microsatellite mutations revealed by parent-offspring analysis in the African freshwater snail, Bulinus forskalii (Gastropoda, Pulmonata). Genetica. Springer, Netherlands, pp 77–83
Gruenthal KM, Burton RS (2005) Genetic diversity and species identification in the endangered white abalone (Haliotis sorenseni). Conservation Genetics. Springer, Netherlands, pp 929–939
Gruenthal KM, Burton RS (2008) Genetic structure of natural populations of the California black abalone (Haliotis cracherodii Leach, 1814), a candidate for endangered species status. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 355:47–58
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hamm DE, Burton RS (2000) Population genetics of black abalone, Haliotis cracherodii, along the central California coast. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 254:235–247
Hardy E (2007) Hardy’s internet guide for marine gastropods: a virtual encyclopedy of sea snails. http://www.gastropods.com.
Hellberg ME (2009) Gene flow and isolation among populations of marine animals. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 40:291–310
Huchette S, Clavier J (2004) Status of the ormer (Haliotis tuberculata L.) industry in Europe. J Shellfish Res 23:951–955
Imron JB, Hale P, Degnan BM, Degnan SM (2007) Pleistocene isolation and recent gene flow in Haliotis asinina, an Indo-Pacific vetigastropod with limited dispersal capacity. Mol Ecol 16:289–304
Jiang L, Wu WL, Huang PC (1995) The mitochondrial DNA of Taiwan abalone Haliotis diversicolor Reeve, 1846 (Gastropoda: Archaeogastropoda: Haliotidae). Mol Mar Biol Biotech 4:353–364
Jolly MT, Jollivet D, Gentil F, Thiebaut E, Viard F (2005) Sharp genetic break between Atlantic and English Channel populations of the polychaete Pectinaria koreni, along the North coast of France. Heredity 94:23–32
Jolly M, Viard F, Gentil F, Thiébaut E, Jollivet D (2006) Comparative phylogeography of two coastal polychaete tubeworms in the Northeast Atlantic supports shared history and vicariant events. Mol Ecol 15:1841–1855
Keane T, Creevey C, Pentony M, Naughton T, Mclnerney J (2006) Assessment of methods for amino acid matrix selection and their use on empirical data shows that ad hoc assumptions for choice of matrix are not justified. BMC Evol Biol 6:29
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. Journal of molecular evolution. Springer, New York, pp 111–120
Klinbunga S, Pripue P, Khamnamtong N, Puanglarp N, Tassanakajon A, Jarayabhand P, Hirono I, Aoki T, Menasveta P (2003) Genetic diversity and molecular markers of the tropical abalone (Haliotis asinina) in Thailand. Mar Biotechnol 5:505–517
Knowlton N, Weigt LA (1998) New dates and new rates for divergence across the Isthmus of Panama. Proc Royal Soc Lond Ser B 265:2257–2263
Koike Y (1978) Biological and ecological studies in the propagation of the ormer Haliotis tuberculata Linnaeus. Larval dispersion and growth of juveniles. La Mer 16:124–136
Kresge N, Vacquier VD, Stout CD (2001) Abalone lysin: the dissolving and evolving sperm protein. BioEssays 23:95–103
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Ladoukakis ED, Zouros E (2001) Direct evidence for homologous recombination in mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) mitochondrial DNA. Mol Biol Evol 18:1168–1175
Lee Y-H, Vacquier VD (1992) The divergence of species-specific abalone sperm lysins is promoted by positive Darwinian selection. Biol Bull 182:97–104
Lee Y-H, Vacquier VD (1995) Evolution and systematics in Haliotidae (Mollusca: Gastropoda): inferences from DNA sequences of sperm lysin. Mar Biol 124:267–278
Lessios HA, Kane J, Robertson DR, Wallis G (2003) Phylogeography of the pantropical sea urchin Tripneustes: contrasting patterns of population structure between oceans. Evolution 57:2026–2036
Lo Brutto S, Arculeo M, Parrinello N (2004) Congruence in genetic markers used to describe Mediterranean and Atlantic populations of European hake (Merluccius merluccius L. 1758). J Appl Ichthyol 20:81–86
Loget N, Van Den Driessche J (2006) On the origin of the Strait of Gibraltar. Sed Geol 188:341–356
Maggs CA, Castilho R, Foltz D, Henzler C, Jolly MT, Kelly J, Olsen J, Perez KE, Stam W, Vainola R, Viard F, Wares J (2008) Evaluating signatures of glacial refugia for North Atlantic benthic marine taxa. Ecology 89:S108–S122
McCartney MA, Keller G, Lessios HA (2000) Dispersal barriers in tropical oceans and speciation in Atlantic and eastern Pacific sea urchins of the genus Echinometra. Mol Ecol 9:1391–1400
Metz EC, Robles-Sikisaka R, Vacquier VD (1998) Nonsynonymous substitution in abalone sperm fertilization genes exceeds substitution in introns and mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:10676–10681
Mgaya YD, Gosling EM, Mercer JP, Donlon J (1995) Genetic variation at three polymorphic loci in wild and hatchery stocks of the abalone, Haliotis tuberculata Linnaeus. Aquaculture 136:71–80
Nei M (1972) Genetic distance between populations. Am Nat 106:283–292
Nicolas JL, Basuyaux O, Mazurié J, Thébault A (2002) Vibrio carchariae, a pathogen of the abalone Haliotis tuberculata. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 50:35–43
Nikula R, Vainola R (2003) Phylogeography of Cerastoderma glaucum (Bivalvia: Cardiidae) across Europe: a major break in the Eastern Mediterranean. Mar Biol 143:339–350
Nilsson T (1983) Chapter 21: systematic review of quaternary mammals. The Pleistocene: geology and life in the quaternary ice age. D. Reidel Publishing Company, Boston, pp 469–503
Ohta T, Kimura M (1973) A model of mutation appropriate to estimate the number of electrophoretically detectable alleles in a finite population. Genet Res 22:201–204
Passamonti M, Boore JL, Scali V (2003) Molecular evolution and recombination in gender-associated mitochondrial DNAs of the Manila clam Tapes philippinarum. Genetics 164:603–611
Petersen JL, Ibarra AM, Ramirez JL, May B (2008) An induced mass spawn of the Hermaphroditic Lion-Paw Scallop, Nodipecten subnodosus: genetic assignment of maternal and paternal parentage. J Hered 99:337–348
Pou-Royo A (1989) La erosion. Ministerio de Obras Públicas y Urbanismo, Centro de Publicaciones
Reuschel S, Cuesta JA, Schubart CD (2010) Marine biogeographic boundaries and human introduction along the European coast revealed by phylogeography of the prawn Palaemon elegans. Mol Phylogenet Evol 55:765–775
Reynolds J, Weir BS, Cockerham CC (1983) Estimation of the coancestry coefficient: basis for a short-term genetic distance. Genetics 105:767–779
Rios C, Sanz S, Saavedra C, Pena JB (2002) Allozyme variation in populations of scallops, Pecten jacobaeus (L.) and P. maximus (L.) (Bivalvia: Pectinidae), across the Almeria-Oran front. Elsevier, Kidlington, ROYAUME-UNI
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Roussel V, Huchette S, Van Wormhoudt A (2010) Isolation and characterization of eight microsatellite loci in the European abalone, Haliotis tuberculata. Molecular Ecol Resour 10:751–754
Rozas J, Sanchez-DelBarrio JC, Messeguer X, Rozas R (2003) DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods. Bioinformatics 19:2496–2497
Ruggiero MV, Turk R, Procaccini G (2002) Genetic identity and homozygosity in North-Adriatic populations of Posidonia oceanica: an ancient, post-glacial clone? Conserv Genet 3:69–72
Saavedra C, Peña JB (2005) Nucleotide diversity and Pleistocene population expansion in Atlantic and Mediterranean scallops (Pecten maximus and P. jacobaeus) as revealed by the mitochondrial 16S ribosomal RNA gene. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 323:138–150
Schmidt D, Pool J (2002) The effect of population history on the distribution of the Tajima’s D statistic. http://www.cam.cornell.edu/~deena/TajimasD.pdf
Slatkin M (1995) A measure of population subdivision based on microsatellite allele frequencies. Genetics 139:457–462
Swanson WJ, Aquadro CF, Vacquier VD (2001) Polymorphism in abalone fertilization proteins is consistent with the neutral evolution of the egg’s receptor for lysin (VERL) and positive Darwinian selection of sperm lysin. Mol Biol Evol 18:376–383
Tajima F (1989) The effect of change in population size on DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123:597–601
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tintore J, La Violette PE, Blade I, Cruzado A (1988) A study of an intense density front in the eastern Alboran Sea: the Almeria-Oran Front. J Phys Oceanogr 18:1384–1397
Van Wormhoudt A, Roussel V, Courtois G, Huchette S (2011a) Mitochondrial DNA introgression in the European Abalone Haliotis tuberculata tuberculata: evidence for experimental mtDNA paternal inheritance and a natural hybrid sequence. Mar Biotechnol 13:563–574
Van Wormhoudt A, Gaume B, Le Bras Y, Roussel V, Huchette S (2011b) Two different and functional nuclear rDNA genes in the abalone Haliotis tuberculata: tissue differential expression. Genetica 139:1217–1227
Wang ZY, Ho KC, Yu DH, Ke CH, Mak WY, Chu KH (2004) Lack of genetic divergence in nuclear and mitochondrial DNA between subspecies of two Haliotis species. J Shellfish Res 23:1143–1146
Wares JP, Cunningham CW (2001) Phylogeography and historical ecology of the North Atlantic intertidal. Evolution 55:2455–2469
Yokoyama Y, Lambeck K, De Deckker P, Johnston P, Fifield LK (2000) Timing of the last glacial maximum from observed sea-level minima. Nature 406:713–716
Zulliger D, Tanner S, Ruch M, Ribi G (2009) Genetic structure of the high dispersal Atlanto-Mediterreanean sea star Astropecten aranciacus revealed by mitochondrial DNA sequences and microsatellite loci. Mar Biol 156:597–610
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the EEC (SUDEVAB no 222156 program for SMEs). Sylvain Huchette (France Haliotis) supplied Northern Brittany samples. Olivier Basuyaux from the S.M.E.L. supplied samples from Normandy collected in 2007. Galicia and Asturias samples were collected by Susana Soto and Carmen Rodríguez (Facultad Ciencas del mar, Universidad Vigo, Spain). Banyuls samples were provided by Jean Michel Amouroux (CNRS), Croatia samples by Andrej Jaklin (Rovinj), Balearic samples by Samuel Iglesias (MNHN), Carthagen samples by Nuria Garcia Bueno (University of Nantes), Morocco samples by Bhaby Sanaa (Faculty of Ain Chock, Casablanca), and Canary Islands samples by Gercende Courtois (Grupo de Investigación en Acuicultura (GIA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roussel, V., Van Wormhoudt, A. The Effect of Pleistocene Climate Fluctuations on Distribution of European Abalone (Haliotis tuberculata), Revealed by Combined Mitochondrial and Nuclear Marker Analyses. Biochem Genet 55, 124–154 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-016-9778-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-016-9778-1