Abstract
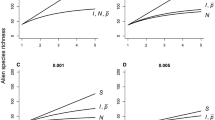
A new species invading a new area may cause a decrease in diversity of the community already present there. Comparison of temporal changes in species diversity of the “new” community (including alien species) with those of the “original” community (including only native species) may clarify our understanding of the effect of alien species. Using a simulation-based modelling approach we considered several scenarios describing the invasion of native communities by alien species and calculated the trends in Shannon-Wiener indices and in the numbers of species of the “original” and “new” communities during the course of the invasion. We found that despite a large increase in the population size of the invasive alien species the diversity of the original community may be little affected. Native species numbers may stay relatively constant for a long time and then suddenly collapse. The results indicate some possibly still concealed consequences of the spread of the invasive ladybird Harmonia axyridis (Pallas).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwala BK, Bhowmik PJ (2011) Effect of resource gradient on age and size at maturity and their influence on early-life fecundity in the predatory Asian lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis. Entomol Exp Appl 141:97–102
Alyokhin A, Sewell G (2004) Changes in a lady beetle community following the establishment of three alien species. Biol Invasion 6:463–471
Bahlai CA, Colunga-Garcia M, Gage SH, Landis DA (2013) Long-term functional dynamics of an aphidophagous coccinellid community remain unchanged despite repeated invasions. PLoS ONE 8(12):e83407
Bahlai CA, Colunga-Garcia M, Gage SH, Landis DA (2015) The role of exotic ladybeetles in the decline of native ladybeetle populations: evidence from long-term monitoring. Biol Invasions 17:1005–1024
Bélanger É, Lucas É (2011) Dominance of the multicoloured Asian lady beetle Harmonia axyridis in an undisturbed wild meadow ecosystem. Eur J Environ Sci 1:7–14
Brown PMJ, Adriaens T, Bathon H, Cuppen J, Goldarazena A, Hägg T, Kenis M, Klausnitzer BEM, Kovar I, Loomans AJM, Majerus MEN, Nedved O, Pedersen J, Rabitsch W, Roy HE, Ternois V, Zakharov IA, Roy BD (2008) Harmonia axyridis in Europe: spread and distribution of a nonnative coccinellid. BioControl 53:5–21
Brown PMJ, Frost R, Doberski J, Harrington R, Roy HE (2011) Decline in native ladybirds in response to the arrival of Harmonia axyridis: early evidence from England. Ecol Entomol 36:231–240
Colunga-Garcia M, Gage SH (1998) Arrival, establishment, and habitat use of the multicolored Asian lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in a Michigan landscape. Environ Entomol 27:1574–1580
Comont RF, Roy HE, Lewis OT, Harrington R, Shortall CR, Purse BV (2012) Using biological traits to explain ladybird distribution patterns. J Biogeogr 39:1772–1781
Crowder DW, Snyder WE (2010) Eating their way to the top? Mechanisms underlying the success of invasive insect generalist predators. Biol Invasions 12:2857–2876
Das BC, Dixon AFG (2011) Assessment of patch quality by aphidophagous ladybirds: laboratory study on the minimum density of aphids required for oviposition. Eur J Environ Sci 1:57–60
Didham RK, Tylianakis JM, Gemmell NJ, Rand TA, Ewers RM (2007) Interactive effects of habitat modification and species invasion on native species decline. Trends Ecol Evol 22:489–496
Diepenbrock LM, Finke DL (2013) Refuge for native lady beetles (Coccinellidae) in perennial grassland habitats. Insect Conserv Divers 6:671–679
Diepenbrock LM, Fothergill K, Tindall KV, Losey JE, Smyth RR, Finke DL (2016) The influence of exotic lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) establishment on the species composition of the native lady beetle community in Missouri. Environ Entomol 45:855–864
Dixon AFG, Honek A (2014) Rate of development of predatory insects is dependent on that of their prey. Eur J Environ Sci 4:87–91
Dixon AFG, Kindlmann P (2012) Cannibalism, optimal egg size and vulnerable developmental stages in insect predators. Eur J Environ Sci 2:84–88
Evans EW (2016) Biodiversity, ecosystem functioning, and classical biological control. Appl Entomol Zool 51:173–184
Evans EW, Soares AO, Yasuda H (2011) Invasions by ladybugs, ladybirds, and other predatory beetles. BioControl 56:597–611
Fothergill K, Tindall KV (2010) Lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae: Coccinellinae) occurrences in southeastern Missouri agricultural systems: differences between 1966 and present. The Coleopt Bull 64:379–382
Gardiner MM, O’Neal ME, Landis DA (2011) Intraguild predation and native lady beetle decline. PLoS ONE 6(9):e23576
Gardiner MM, Smith CA, Gardiner MM (2013) Biodiversity loss following the introduction of exotic competitors: does intraguild predation explain the decline of native lady beetles? PLoS ONE 8(12):e84448
Gardiner MM, Prajzner SP, Burkman CE, Albro S, Grewal PS (2014) Vacant land conversion to community gardens: influences on generalist arthropod predators and biocontrol services in urban greenspaces. Urban Ecosyst 17:101–122
Gidoin C, Roques L, Boivin T (2015) Linking niche theory to ecological impacts of successful invaders: insights from resource fluctuation-specialist herbivore interactions. J Anim Ecol 84:396–406
Gillespie RG, Roderick GK (2002) Arthropods on islands: colonization, speciation, and conservation. Annu Rev Entomol 47:595–632
Grez AA, Zaviezo T, Roy HE, Brown PMJ, Bizama G (2016) Rapid spread of Harmonia axyridis in Chile and its effects on local coccinellid biodiversity. Divers Distrib 22:982–994
Guedes CFC, Almeida LM, Penteado SRC, Moura MO (2016) Effect of different diets on biology, reproductive variables and life and fertility tables of Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae). Rev Bras Entomol 60:260–266
Harmon JP, Stephens E, Losey J (2007) The decline of native coccinellids (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in the United States and Canada. J Insect Conserv 11:85–94
Hautier L, San Martin G, de Biseau JC, Gregoire JC (2011) Alkaloids provide evidence of intraguild predation on native coccinellids by Harmonia axyridis in the field. Biol Invasions 13:1805–1814
Hemptinne JL, Magro A, Saladin C, Dixon AFG (2012) Role of intraguild predation in aphidophagous guilds. J Appl Entomol 136:161–170
Hodek I, Evans EW (2012) Food relations. In: Hodek I, van Emden HF, Honek A (eds) Ecology and behaviour of the ladybird beetles (Coccinellidae). Wiley, Chichester, pp 141–274
Honek A, Martinkova Z, Kindlmann P, Ameixa OMCC, Dixon AFG (2013) Long-term trends in the composition of aphidophagous coccinellid communities in Central Europe. Insect Conserv Divers 7:55–63
Honek A, Martinkova Z, Dixon AFG, Roy HE, Pekar S (2016) Long-term changes in communities of native coccinellids: population fluctuations and the effect of competition from an invasive non-native species. Insect Conserv Divers 9:202–209
Kindlmann P, Ameixa OMCC, Dixon AFG (2011) Ecological effects of invasive alien species on native communities, with particular emphasis on the interactions between aphids and ladybirds. BioControl 56:469–476
Koch R, Costamagna A (2016) Reaping benefits from an invasive species: role of Harmonia axyridis in natural biological control of Aphis glycines in North America. BioControl. doi:10.1007/s10526-016-9749-9
LaMana ML, Miller JC (1996) Field observations on Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Oregon. Biol Control 6:232–237
Lockwood JL, Hoopes MF, Marchetti MP (2007) Invasion ecology. Blackwell, Malden
Lombaert E, Guillemaud T, Cornuet JM, Malausa T, Facon B, Estoup A (2010) Bridgehead effect in the worldwide invasion of the biocontrol harlequin ladybird. PLoS ONE 5(3):e9743
Lombaert E, Guillemaud T, Thomas CE, Handley LJL, Wang S, Pang H, Goryacheva I, Zakharov IA, Jousselin E, Poland RL, Migeon A, van Lenteren J, De Clercq R (2011) Inferring the origin of populations introduced from a genetically structured native range by approximate Bayesian computation: case study of the invasive ladybird Harmonia axyridis. Mol Ecol 20:4654–4670
Lucas E, Rosenheim JA (2011) Influence of extraguild prey density on intraguild predation by heteropteran predators: a review of the evidence and a case study. Biol Control 59:61–67
Orlova-Bienkowskaja MJ, Ukrainsky AS, Brown PMJ (2015) Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Asia: a re-examination of the native range and invasion to southeastern Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan. Biol Invasions 17:1941–1948
Osawa N (2011) Ecology of Harmonia axyridis in natural habitats within its native range. BioControl 56:613–621
Panigaj L, Zach P, Honek A, Nedved O, Kulfan J, Martinkova Z, Selyemova D, Viglasova S, Roy HE (2014) The invasion history, distribution and colour pattern forms of the harlequin ladybird beetle Harmonia axyridis (Pall.) (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae) in Slovakia, Central Europe. Zookeys 412:89–102
Pell JK, Baverstock J, Roy HE, Ware RL, Majerus MEN (2008) Intraguild predation involving Harmonia axyridis: a review of current knowledge and future perspectives. BioControl 53:147–168
Poutsma J, Loomans AJM, Aukema B, Heijerman T (2008) Predicting the potential geographical distribution of the harlequin ladybird, Harmonia axyridis, using the CLIMEX model. BioControl 53:103–125
Reznik SY, Dolgovskaya MY, Ovchinnikov AN, Belyakova NA (2015) Weak photoperiodic response facilitates the biological invasion of the harlequin ladybird Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J Appl Entomol 139:241–249
Roy HE, Brown PMJ (2015) Ten years of invasion: Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Britain. Ecol Entomol 40:336–348
Roy HE, Adriaens T, Isaac NJB, Kenis M, Onkelinx T, San Martin G, Brown PMJ, Hautier L, Poland R, Roy DB, Comont R, Eschen R, Frost R, Zindel R, van Vlaenderen J, Nedved O, Ravn HP, Gregoire JC, de Biseau JC, Maes D (2012) Invasive alien predator causes rapid declines of native European ladybirds. Divers Distrib 18:717–725
Roy HE, Brown PMJ, Adriaens T, Berkvens N, Borges I, Clusella Trullas S, Comont R, De Clercq P, Eschen R, Estoup A, Evans EW, Facon B, Gardiner MM, Gil A, Grez AA, Guillemaud T, Haelewaters D, Herz A, Honek A, Howe AG, Hui C, Hutchinson WD, Kenis M, Koch RL, Kulfan J, Lawson Handley L, Lombaert E, Loomans A, Losey J, Lukashuk AO, Maes D, Magro A, Murray KM, San Martin G, Martinkova Z, Minnaar IA, Nedved O, Orlova-Bienkowskaja MJ, Osawa N, Rabitsch W, Ravn HP, Rondoni G, Rorke SL, Ryndevich SK, Saethre MG, Sloggett JJ, Soares AO, Stals R, Tinsley MC, Vandereycken A, van Wielink P, Viglasova S, Zach P, Zakharov IA, Zaviezo T, Zhao Z (2016) The harlequin ladybird, Harmonia axyridis: global perspectives on invasion history and ecology. Biol Invasions 18:997–1044
Sloggett JJ, Honek A (2012) Genetic studies. In: Hodek I, van Emden HF, Honek A (eds) Ecology and behaviour of the ladybird beetles (Coccinellidae). Wiley, Chichester, pp 13–53
Snyder WE, Evans EW (2006) Ecological effects of invasive arthropod generalist predators. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 37:95–122
Toda Y, Sakuratani Y (2006) Expansion of the geographical distribution of an exotic ladybird beetle, Adalia bipunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), and its interspecific relationships with native ladybird beetles in Japan. Ecol Res 21:292–300
With KA, Pavuk DM, Worchuck JL, Oates RK, Fisher JL (2002) Threshold effects of landscape structure on biological control in agroecosystems. Ecol Appl 12:52–65
Zakharov IA, Goryacheva II, Suvorov A (2011) Mitochondrial DNA polymorphism in invasive and native populations of Harmonia axyridis. Eur J Environ Sci 1:15–18
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Grant No. 14-26561S of the GA CR and by the MSMT within the National Sustainability Program I (NPU I), Grant No. LO1415.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Helen Roy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kindlmann, P., Honěk, A. & Martinková, Z. Spreading of alien species and diversity of communities. BioControl 62, 397–407 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-017-9787-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-017-9787-y