Abstract
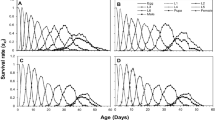
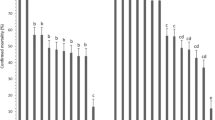
The ectoparasitoid wasp, Habrobracon hebetor Say and the entomopathogenic fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae (Metsch.) Sorokin are biocontrol agents attacking larval stages of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner). Life table parameters of H. hebetor were studied on H. armigera third instar larvae previously (0, 24, 48, and 72 h) infected with a sublethal concentration (LC30) of M. anisopliae (isolate M14). Fungal infection adversely affected life table parameters of H. hebetor depending on the host post-inoculation time for parasitoid release. The entropy values showed the age-specific survivorship (l x ) curves of type 1 at ≤24 h treatments. The highest and lowest intrinsic rates of increase (r m ) were 0.223 and 0.109 for control and 72 h treatment, respectively. Statistically different variations were observed for r m values when post-exposure time was longer than 24 h. Our findings highlight appropriate introduction times of H. hebetor in combination with M. anisopliae (isolate M14) for successful integrated management of H. armigera.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedi Z, Saber M, Gharekhani G, Mehrvar A, Kamita SG (2014) Lethal and sublethal effects of azadirachtin and cypermethrin on Habrobracon hebetor (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). J Econ Entomol 107(2):638–645
Asokan R, Sharath Chandra G, Manamohan M, Krishna Kumar NK, Sita T (2014) Response of various target genes to diet-delivered dsRNA mediated RNA interference in the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera. J Pest Sci 87:163–172
Avilla C, Gonza´lez-Zamora JE (2010) Monitoring resistance of Helicoverpa armigera to different insecticides used in cotton in Spain. Crop Prot 29:100–103
Baskar K, Ignacimuthu S (2012) Antifeedant, larvicidal and growth inhibitory effects of ononitol monohydrate isolated from Cassiatora L. against Helicoverpa armigera (Hub.) and Spodoptera litura (Fab.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Chemosphere 88:384–388
Baverstock J, Clark SJ, Alderson PG, Pell JK (2009) Intraguild interactions between the entomopathogenic fungus Pandora neoaphidis and an aphid predator and parasitoid at the population scale. J Invertebr Pathol 102:167–172
Carey JR (1993) Applied demography for biologists, with special emphasis on insects. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Carey JR (2001) Insect biodemography. Ann Rev Entomol 46:79–110
Chen H, Zhang H, Zhu KY, Throne J (2013) Performance of diapausing parasitoid wasps, Habrobracon hebetor, after cold storage. Biol Control 64:186–194
Desneux N, Decourtye A, Delpuech JM (2007) The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Ann Rev Entomol 52:81–106
Fathipour Y, Sedaratian A (2013) Integrated management of Helicoverpa armigera in soybean cropping systems. In: El-Shemy H (ed) Soybean-pest resistance. InTech Rijeka, Croatia, pp 231–280
Fatiha L, Huang Z, Ren SX, Ali S (2008) Effect of Verticillium lecanii on biological characteristics and life table of Serangium japonicum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), a predator of whiteflies under laboratory conditions. Insect Sci 15:327–333
Goettel MS, Eilenberg J, Glare T (2010) Entomopathogenic fungi and their role in regulation of insect populations. In: Gilbert LI, Gill SS (eds) Insect control: biological and synthetic agents. Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 387–432
Husberg GB, Hokkanen HMT (2001) Effects of Metarhizium anisopliae on the pollen beetle Meligethes aeneus and its parasitoids Phradis morionellus and Diospilus capito. BioControl 46:261–273
Inglis GD, Enkerli J, Goettel MS (2012) Laboratory techniques used for entomopathogenic fungi: Hypocreales. In: Lacey LA (ed) Manual of Techniques in invertebrate pathology. Academic Press, London, pp 189–253
Maia AHN, Luiz AJB, Campanhola C (2000) Statistical inference on associated fertility life table parameters using jackknife technique: computational aspects. J Econ Entomol 93:511–518
Mesquita ALM, Lacey LA (2001) Interactions among the entomopathogenic fungus, Paecilomyces fumosoroseus (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes), the parasitoid, Aphelinus asychis (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae), and their aphid host. Biol Control 22:51–59
Naseri B, Fathipour Y, Moharramipour S, Hosseininaveh V (2009) Comparative life history and fecundity of Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on different soybean varieties. Entomol Sci 12:147–154
Nguyen NTH, Borgemeister C, Poehling HM, Zimmermann G (2007) Laboratory investigations on the potential of entomopathogenic fungi for biocontrol of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae and pupae. Biocontrol Sci Technol 17(8):853–864
Nielsen C, Skovgård H, Steenberg T (2005) Effect of Metarhizium anisopliae (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) on survival and reproduction of the filth fly parasitoid, Spalangia cameroni (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). Environ Entomol 34(1):133–139
Rashki M, Kharazi-pakdel A, Allahyari H, van Alphen JJM (2009) Interactions among the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales), the parasitoid, Aphidius matricariae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), and its host, Myzus persicae (Homoptera: Aphididae). Biol Control 50(3):324–328
Rosa W, Segura HR, Barrera JF, Williams T (2000) Laboratory evaluation of the impact of entomopathogenic fungi on Prorops nasuta (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae), a parasitoid of the Coffee Berry Borer. Environ Entomol 29(1):126–131
Roy HE, Pell JK (2000) Interactions between entomopathogenic fungi and other natural enemies: Implications for biological control. Biocontrol Sci Technol 10:737–752
SAS (2003) A guide to statistical and data analysis, version 9.1. SAS Institute, Cary
Sedaratian A, Fathipour Y, Talaei-Hassanloui R (2013) Deleterious effects of Bacillus thuringiensis on biological parameters of Habrobracon hebetor parasitizing Helicoverpa armigera. BioControl 59(1):89–98
Stark JD, Banks JE, Acheampong S (2004) Estimating susceptibility of biological control agents to pesticides: influence of life history strategies and population structure. Biol Control 29:392–398
Stolz I, Nagel P, Lomer C, Peveling R (2002) Susceptibility of the hymenopteran parasitoids Apoanagyrus (=Epidinocarsis) lopezi (Encyrtidae) and Phanerotoma sp. (Braconidae) to the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae var. acridum (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes). Biocontrol Sci Technol 12:349–360
Surekha Devi V, Sharma HC, Arjuna Rao P (2011) Interaction between host plant resistance and biological activity of Bacillus thuringiensis in managing the pod borer Helicoverpa armigera in chickpea. Crop Prot 30:962–969
Tounou AK, Agboka K, Poehling HM, Raupach K, Langewald J, Zimmermann G, Borgemeister C (2003) Evaluation of the entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and Paecilomyces fumosoroseus (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) for control of the green leafhopper Empoasca decipiens (Homoptera: Cicadellidae) and potential side effects on the egg parasitoid Anagrus atomus (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae). Biocontrol Sci Technol 13(8):879–920
Zimmermann G (2007) Review on safety of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Biocontrol Sci Technol 17(9):715–728
Acknowledgments
This study received financial support from Urmia University, Urmia, Iran, which is greatly appreciated. We also thank Dr. Mark S. Goettel for improving the manuscript by his valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Helen Roy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jarrahi, A., Safavi, S.A. Sublethal effects of Metarhizium anisopliae on life table parameters of Habrobracon hebetor parasitizing Helicoverpa armigera larvae at different time intervals. BioControl 61, 167–175 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-015-9707-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-015-9707-y