Abstract
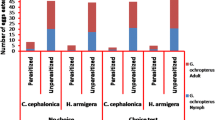
Intraguild predation of Orius majusculus (Reuter) (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae) on Encarsia formosa (Gahan) (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae), both natural enemies of Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae), was studied under laboratory conditions. The experiments quantified prey consumption by 5th instar nymphs and adults of O. majusculus offered unparasitised 3rd, early 4th or 4th instar B. tabaci nymphs or parasitised nymphs containing 2nd or 3rd larval instar or pupal parasitoids. In addition, prey preference of the two stages of O. majusculus for parasitised or unparasitised whitefly nymphs was studied using nine different prey combinations. Both predator stages readily preyed upon on both unparasitised and parasitised B. tabaci. In no-choice experiments, predation on 3rd instar E. formosa by adult predators was the highest, while predator nymphs preyed most on unparasitised 3rd instar B. tabaci and 2nd instar parasitoids. Predation of predator stages was lowest on 4th instar B. tabaci and E. formosa pupae. In all prey combinations, both stages of O. majusculus showed a significant preference for parasitised over unparasitised whitefly nymphs except for the combination of 5th instars of O. majusculus with early 4th instar whiteflies and E. formosa pupae. The results indicate that intraguild interactions between O. majusculus and E. formosa may have negative effects on biological control of B. tabaci.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agekyan NG (1982) Biological features of Encarsia formosa Gahan (Hymenoptera, Aphelinidae). Entomol Obozr (Entomol News) 60:90–94
Al-Zyoud F, Sengonca C (2004) Prey consumption preferences of Serangium parcesetosum Sicard (Col., Coccinellidae) for different prey stages, species and parasitized prey. J Pest Sci 77:197–204
Arno J, Roig J, Riudavets J (2008) Evaluation of Orius majusculus and O. laevigatus as predators of Bemisa tabaci and estimation of their prey preference. Biol Control 44:1–6
Asiimwe P, Ecaat JS, Otim M, Gerling D, Kyamanywa S, Legg JP (2007) Life table analysis of mortality factors affecting populations of Bemisia tabaci on cassava in Uganda. Ent Exp Appl 122:37–44
Brødsgaard HF, Enkegaard A (2005) Intraguild predation between Orius majusculus (Reuter) (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) and Iphiseius degenerans Berlese (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Bull OILB/SROP 28(1):19–22
Christensen RK, Enkegaard A, Brødsgaard HF (2002) Intraspecific interactions among the predators Orius majusculus and Aphidoletes aphidimyza. Bull OILB/SROP 25(1):57–60
Cock MJW (1978) The assessment of preference. J Anim Ecol 47:805–816
Colfer RG, Rosenheim JA (2001) Predation on immature parasitoids and its impact on prey suppression. Oecologia 126:292–304
Fazal S, Xiang RS (2004) Interaction of Serangium japonicum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), an obligate predator of whitefly with immature stages of Eretmocerus sp. (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) within whitefly host (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae). Asian J Plant Sci 3:243–246
Gardiner MM, Landis DA (2007) Impact of intraguild predation by adult Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on Aphis glycines (Hemiptera: Aphididae) biological control in cage studies. Biol Control 40:386–395
Gelman DB, Blackburn MB, Hu JS, Gerling D (2002) The nymphal-adult molt of the silverleaf whitefly (Bemisia argentifolii): timing, regulation, and progress. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 51:67–79
Gerling D (1990) Natural enemies of whiteflies: predators and parasitoids. In: Gerling D (ed) Whiteflies: their bionomics, pest status and management. Intercept, Andover, UK, pp 147–185
Gerling D, Alomar O, Arno J (2001) Biological control of Bemisia tabaci using predators and parasitoids. Crop Prot 20:779–799
Heinz KM, Nelson JM (1996) Interspecific interactions among natural enemies of Bemisia in an inundative biological control program. Biol Control 6:384–393
Heinz KM, Brazzle JR, Pickett CH, Natwick ET, Nelson JM, Parrella MP (1994) Predatory beetle may suppress silverleaf whitefly. Calif Agric 48:35–40
Hoelmer KA, Osborne LS, Yokomi RK (1994) Interactions of the whitefly predator Delphastus pusillus (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) with parasitized sweet potato whitefly (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae). Environ Entomol 23:136–139
Holt RD, Polis GA (1997) A theoretical framework for intraguild predation. Am Nat 149:745–764
Jakobsen L, Enkegaard A, Brødsgaard HF (2004) Interactions between two polyphagous predators, Orius majusculus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) and Macrolophus caliginosus (Heteroptera: Miridae). Biocontrol Sci Technol 14(1):17–24
Janssen A, Montserrat M, HilleRisLambers R, de Roos AM, Pallini A, Sabelis MW (2006) Intraguild predation usually does not disrupt biological control. In: Brodeur J, Boivin G (eds) Trophic and guild interactions in biological control. Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 21–44
Kutuk H, Yigit A, Alaoglu O (2011) Intraguild predation of Serangium parcesetosum Sicard (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), on whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) parasitized by Eretmocerus mundus (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). Biocontrol Sci Technol 21(8):985–989
Manly BFJ (1974) A model for certain types of selection experiments. Biometrics 30:281–294
McGregor RR, Gillespie DR (2005) Intraguild predation by the generalist predator Dicyphus hesperus on the parasitoid Encarsia formosa. Biocontrol Sci Technol 15(3):219–227
Messelink GJ, van Maanen R, van Steenpal SEF, Janssen A (2008) Biological control of thrips and whiteflies by a shared predator: two pests are better than one. Biol Control 44(3):372–379
Meyling NV, Enkegaard A, Brødsgaard HF (2004) Intraguild predation by Anthocoris nemorum (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae) on the aphid parasitoid Aphidius colemani (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Biocontrol Sci Technol 14(6):627–630
Montserrat M, Albajes R, Castane C (2000) Functional response of four Heteropteran predators preying on greenhouse whitefly (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) and western flower thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Environ Entomol 29:1075–1082
Naranjo SE (2007) Intraguild predation on Eretmocerus sp. nr. emiratus, a parasitoid of Bemisia tabaci, by three generalist predators with implications for estimating the level and impact of parasitism. Biocontrol Sci Technol 17(5/6): 605–622
Naranjo SE, Ellsworth PC (2005) Mortality dynamics and population regulation in Bemisia tabaci. Entomol Exp Appl 116:93–108
Neal JW Jr, Leonhardt BA, Brown JK, Bentz JA, Devilbiss ED (1994) Cuticular lipids of greenhouse whitefly and sweet potato whitefly type A and B (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) pupal exuviae on the same hosts. Ann Entomol Soc Am 87:609–618
Oliveira MRV, Henneberry TJ, Anderson P (2001) History, current status, and collaborative research projects for Bemisia tabaci. Crop Prot 20:709–723
Polis GA, Holt RD (1992) Intraguild predation: the dynamics of complex trophic interactions. Trends Ecol Evol 7:151–154
Polis GA, Myers CA, Holt RD (1989) The ecology and evolution of intraguild predation: potential competitors that eat each other. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 20:297–330
Raymond B, Darby AC, Douglas AE (2000) Intraguild predators and the spatial distribution of a parasitoid. Oecologia 124:367–372
Rees NE, Onsager JA (1982) Influence of predators on the efficiency of the Blaesoxipha spp. parasites of the migratory grasshopper. Environ Entomol 11:426–428
Riudavets J (1995) Predators of Frankliniella occidentalis (Perg.) and Thrips tabaci Lind.: a review. In: van Lenteren JC, Loomans AJM (eds) Biological control of thrips pests. Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, pp 46–78
Rosenheim JA (2005) Intraguild predation of Orius tristicolor by Geocoris spp. and the paradox of irruptive spider mite dynamics in California cotton. Biol Control 32:172–179
Rosenheim JA, Kaya HK, Ehler LE, Marois JJ, Jaffee BA (1995) Intraguild predation among biological control agents: theory and evidence. Biol Control 5:303–335
Sanderson J, Brødsgaard HF, Enkegaard A (2005) Preference assessment of two Orius spp. for Neoseiulus cucumeris vs. Frankliniella occidentalis. IOBC/WPRS Bull 28(1): 221–224
SAS Institute Inc. (2010) SAS/STAT® 9.22 user’s guide. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, USA
Schausberger P, Walzer A (2001) Combined versus single species release of predaceous mites: predator–predator interactions and pest suppression. Biol Control 20:269–278
Sherratt TS, Harvey I (1993) Frequency-dependent food selection by arthropods: a review. Biol J Linn Soc 48:167–186
Shiojiri K, Takabayashi J (2005) Parasitoid preference for host-infested plants is affected by the risk of intraguild predation. J Insect Behav 18(4):567–576
Snyder WE, Ives AR (2001) Generalist predators disrupt biological control by a specialist parasitoid. Ecology 82:705–716
Snyder WE, Ballard SN, Yang S, Clevenger GM, Miller TD, Ahn JJ, Hatten TD, Berryman AA (2004) Complementary biocontrol of aphids by the ladybird beetle Harmonia axyridis and the parasitoid Aphelinus asychis on greenhouse roses. Biol Control 30:229–235
Tommasini MG, van Lenteren JC, Burgio G (2004) Biological traits and predation capacity of four Orius species on two prey species. Bull Insectol 57(2):79–93
Trottin-Caudal Y, Grasselly D, Trapateau M, Dobelin H, Millot P (1991) Biological control of Frankliniella occidentalis with Orius majusculus on cucumber. Bull OILB/SROP 14(5):50–56
Zang LS, Liu TX (2007) Intraguild interactions between an oligophagous predator, Delphastus catalinae (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), and a parasitoid, Encarsia sophia (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae), of Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae). Biol Control 41:142–150
Zhang ZQ (2003) Mites of greenhouses. Identification, biology and control. CABI Publishing, Cambridge, UK
Acknowledgments
This project was carried out in Denmark during a sabbatical leave of the first author. The authors would like to thank the associate editor and two anonymous reviewers for their valuable and helpful comments on earlier drafts of this manuscript. We also thank technician Gitte Christiansen, Dept. of Agroecology, for her kind assistance during the experiments as well as senior scientist Kristian Kristensen, Dept. of Agroecology, for statistical assistance and Kirsten Jensen, Dept. of Agroecology, for editorial and language assistance. Financial support provided by the Research Deputy of the Shahid Chamran University and Aarhus University, Faculty of Science and Technology is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Arne Janssen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sohrabi, F., Enkegaard, A., Shishehbor, P. et al. Intraguild predation by the generalist predator Orius majusculus on the parasitoid Encarsia formosa . BioControl 58, 65–72 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-012-9468-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-012-9468-9