Abstract
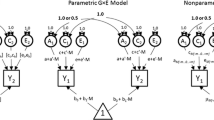
To extend Purcell’s well known ACE model in testing gene by measured environment interactions (GxM) in behavior genetic designs, Rathouz et al. considered a broader class of models for quantifying and testing such interactions. Only a sub-group of these extended models have been investigated for their statistical operating characteristics by Van Hulle et al. due to lack of closed form likelihood. With an estimation procedure developed using numerical techniques in a companion paper, we study statistical operating characteristics of these extended models, especially those with non-linear effects. Type I error analysis shows the likelihood ratio test for GxM to be conservative in testing models extended from the bivariate Cholesky model, and to be liberal for models extended from the bivariate correlated factors model. Parameter estimation for all models is very good, with little bias exhibited for most models and parameters. Comparisons among alternative models under various simulated conditions show that it is relatively more difficult to confirm the existence of gene by environment interactions versus to detect non-linear effects which exclude such interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Jinks JL, Fulker DW (1970) Comparison of the biometrical genetical, mava, and classical approaches to the analysis of the human behavior. Psychol Bull 73(5):311–349
Johnson W (2007) Genetic and environmental influences on behavior: capturing all the interplay. Psychol Rev 114(2):423–440
Loehlin J (1996) The Cholesky approach: a cautionary note. Behav Genet 26(1):65–69
Neale MC, Cardon LR (1992) Methodology for genetic studies of twins and families. Springer, Berlin
Purcell S (2002) Variance components models for gene-environment interaction in twin analysis. Twin Res 5(6):554–571
R Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing [Computer software manual]. Retrieved from http://www.R-project.org/
Raftery AE (1995) Bayesian model selection in social research. Sociol Methodol 25:111–164
Rathouz PJ, Van Hulle CA, Rodgers JL, Waldman ID, Lahey BB (2008) Specification, testing, and interpretation of gene-by-measured-environment interaction models in the presence of gene-environment correlation. Behav Genet 38(3):301–315
Van Hulle CA, Lahey BB, Rathouz PJ (2013) Operating characteristics of alternative statistical methods for detecting gene-by-measured environment interaction in the presence of gene-environment correlation in twin and sibling studies. Behav Genet 43(1):71–84
Zheng H, Rathouz PJ (2013) GxM: maximum likelihood estimation for gene-by-measured environment interaction models [Computer software manual]. Retrieved from http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/GxM/index.html
Zheng H, Rathouz PJ (2015) Fitting procedures for novel gene-by-measured environment interaction models in behavior genetic designs. Behav Genet. doi:10.1007/s10519-015-9707-9
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the NIH Grant R21 MH086099 from the National Institute for Mental Health.
Conflict of Interest
Hao Zheng, Carol A. Van Hulle, and Paul J. Rathouz declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
There are no animals and humans used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by Gitta Lubke.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H., Van Hulle, C.A. & Rathouz, P.J. Comparing Alternative Biometric Models with and without Gene-by-Measured Environment Interaction in Behavior Genetic Designs: Statistical Operating Characteristics. Behav Genet 45, 480–491 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-015-9710-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-015-9710-1