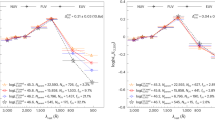
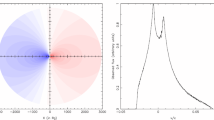
Abstract
The UV spectral range (1100–3000 Å) contains the strongest resonance lines observed in active galactic nuclei (AGN). Analysis of UV line intensity ratios and profile shapes in quasar spectra provide diagnostics of physical and dynamical conditions in the broad line emitting region. This paper discusses properties of UV lines in type-1 AGN spectra, and how they lead an estimate of ionizing photon flux, chemical abundances, radius of the broad line emitting region and central black hole mass. These estimates are meaningfully contextualised through the 4D “eigenvector-1” (4DE1) formalism.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachev, R., Marziani, P., Sulentic, J.W., Zamanov, R., Calvani, M., Dultzin-Hacyan, D.: Astrophys. J. 617, 171 (2004). doi:10.1086/425210. arXiv:astro-ph/0408334
Baldwin, J.A., Ferland, G.J., Korista, K.T., Carswell, R.F., et al.: Astrophys. J. 461, 664 (1996). doi:10.1086/177093
Bentz, M.C., Denney, K.D., Grier, C.J., Barth, A.J., Peterson, B.M., et al.: Astrophys. J. 767, 149 (2013). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/767/2/149. arXiv:1303.1742
Boroson, T.A.: Astrophys. J. 565, 78 (2002). doi:10.1086/324486. arXiv:astro-ph/0109317
Boroson, T.A., Green, R.F.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. 80, 109 (1992). doi:10.1086/191661
Brotherton, M.S., Wills, B.J., Steidel, C.C., Sargent, W.L.W.: Astrophys. J. 423, 131 (1994). doi:10.1086/1737194
Brühweiler, F., Verner, E.: Astrophys. J. 675, 83 (2008). doi:10.1086/525557
Collin, S., Kawaguchi, T., Peterson, B.M., Vestergaard, M.: Astron. Astrophys. 456, 75 (2006). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20064878. arXiv:astro-ph/0603460
Davidson, K., Netzer, H.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 51, 715 (1979). doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.51.715
D’Onofrio, M., Marziani, P., Sulentic, J.W. (eds.): Fifty Years of Quasars from Early Observations and Ideas to Future Research. Astrophysics and Space Science Library, vol. 386. Springer, Berlin (2012). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-27564-7
Ferland, G.J., Baldwin, J.A., Korista, K.T., Hamann, F., et al.: Astrophys. J. 461, 683 (1996). doi:10.1086/177094
Ferland, G.J., Hu, C., Wang, J., Baldwin, J.A., et al.: Astrophys. J. Lett. 707, 82 (2009). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/707/1/L82. arXiv:0911.1173
Ferland, G.J., Porter, R.L., van Hoof, P.A.M., Williams, R.J.R., et al.: Rev. Mex. Astron. Astrofís. 49, 137 (2013). arXiv:1302.4485
Fine, S., Croom, S.M., Bland-Hawthorn, J., Pimbblet, K.A., et al.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 409, 591 (2010). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17107.x. arXiv:1005.5287
Gaskell, C.M.: Astrophys. J. 263, 79 (1982). doi:10.1086/160481
Gaskell, C.M.: ArXiv e-prints (2009). arXiv:0903.4447
Green, R.F., Schmidt, M., Liebert, J.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. 61, 305 (1986). doi:10.1086/191115
Grier, C.J., Peterson, B.M., Horne, K., Bentz, M.C., Pogge, R.W., Denney, K.D., et al.: Astrophys. J. 764, 47 (2013). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/764/1/47. arXiv:1210.2397
Hu, C., Wang, J.-M., Ho, L.C., Ferland, G.J., Baldwin, J.A., Wang, Y.: Astrophys. J. 760, 126 (2012). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/760/2/126. arXiv:1210.4187
Juarez, Y., Maiolino, R., Mujica, R., Pedani, M., Marinoni, S., Nagao, T., Marconi, A., Oliva, E.: Astron. Astrophys. 494, 25 (2009). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200811415. arXiv:0901.0974
Kaspi, S., Smith, P.S., Netzer, H., Maoz, D., Jannuzi, B.T., Giveon, U.: Astrophys. J. 533, 631 (2000). doi:10.1086/308704. arXiv:astro-ph/9911476
Kollatschny, W., Zetzl, M., Dietrich, M.: Astron. Astrophys. 454, 459 (2006). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054357
Kruczek, N.E., Richards, G.T., Gallagher, S.C., Deo, R.P., et al.: Astron. J. 142, 130 (2011). doi:10.1088/0004-6256/142/4/130. arXiv:1109.1515
Kuraszkiewicz, J., Wilkes, B.J., Schmidt, G., Smith, P.S., Cutri, R., Czerny, B.: Astrophys. J. 692, 1180 (2009). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/692/2/1180
Maiolino, R., Risaliti, G., Salvati, M., Pietrini, P., et al.: Astron. Astrophys. 517, 47 (2010). doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200913985. arXiv:1005.3365
Marziani, P., Sulentic, J.W., Dultzin-Hacyan, D., Calvani, M., Moles, M.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. 104, 37 (1996). doi:10.1086/192291
Marziani, P., Sulentic, J.W., Zwitter, T., Dultzin-Hacyan, D., Calvani, M.: Astrophys. J. 558, 553 (2001). doi:10.1086/322286. arXiv:astro-ph/0105343
Marziani, P., Sulentic, J.W., Plauchu-Frayn, I., del Olmo, A.: Astron. Astrophys. 555, 89 (2013). doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201321374. arXiv:1305.1096
Matsuoka, K., Nagao, T., Marconi, A., Maiolino, R., Taniguchi, Y.: Astron. Astrophys. 527, 100 (2011). doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201015584. arXiv:1011.5811
Nagao, T., Maiolino, R., Marconi, A.: Astron. Astrophys. 447, 863 (2006). doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054127. arXiv:astro-ph/0508652
Negrete, A., Dultzin, D., Marziani, P., Sulentic, J.: Astrophys. J. 757, 62 (2012). arXiv:1107.3188
Negrete, C.A., Dultzin, D., Marziani, P., Sulentic, J.W.: Astrophys. J. 771, 31 (2013). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/771/1/31. arXiv:1305.4574
Negrete, C.A., Dultzin, D., Marziani, P., Sulentic, J.W.: Adv. Space Res. 54, 1355 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.asr.2013.11.037
Netzer, H.: The Physics and Evolution of Active Galactic Nuclei. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2013)
Netzer, H., Lira, P., Trakhtenbrot, B., Shemmer, O., Cury, I.: Astrophys. J. 671, 1256 (2007). doi:10.1086/523035. arXiv:0708.3787
Padovani, P., Burg, R., Edelson, R.A.: Astrophys. J. 353, 438 (1990). doi:10.1086/168631
Peterson, B.M., Wandel, A.: Astrophys. J. Lett. 521, 95 (1999). doi:10.1086/312190. arXiv:astro-ph/9905382
Peterson, B.M., Ferrarese, L., Gilbert, K.M., Kaspi, S., et al.: Astrophys. J. 613, 682 (2004). doi:10.1086/423269. arXiv:astro-ph/0407299
Popović, L.Č., Kovačević, J.: Astrophys. J. 738, 68 (2011). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/738/1/68. arXiv:1106.3021
Punsly, B.: Astrophys. J. 713, 232 (2010). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/713/1/232. arXiv:1002.4681
Richards, G.T., Kruczek, N.E., Gallagher, S.C., Hall, P.B., et al.: Astron. J. 141, 167 (2011). doi:10.1088/0004-6256/141/5/167. arXiv:1011.2282
Roig, B., Blanton, M.R., Ross, N.P.: Astrophys. J. 781, 72 (2014). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/781/2/72
Sameshima, H., Kawara, K., Matsuoka, Y., Oyabu, S., Asami, N., Ienaka, N.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 410, 1018 (2011). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17498.x. arXiv:1008.2405
Shen, Y., Ho, L.C.: Nature 513, 210 (2014). doi:10.1038/nature13712. arXiv:1409.2887
Shen, Y., Liu, X.: Astrophys. J. 753, 125 (2012). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/753/2/125. arXiv:1203.0601
Shin, J., Woo, J.-H., Nagao, T., Kim, S.C.: Astrophys. J. 763, 58 (2013). doi:10.1088/0004-637X/763/1/58. arXiv:1211.6749
Sigut, T.A.A., Pradhan, A.K.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. 145, 15 (2003). doi:10.1086/345498. arXiv:astro-ph/0206096
Steinhardt, C.L., Silverman, J.D.: Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 65, 82 (2013). doi:10.1093/pasj/65.4.82
Sulentic, J.W., Marziani, P., Zwitter, T., Dultzin-Hacyan, D., Calvani, M.: Astrophys. J. Lett. 545, 15 (2000). doi:10.1086/317330. arXiv:astro-ph/0009326
Sulentic, J.W., Marziani, P., Zamanov, R., Bachev, R., Calvani, M., Dultzin-Hacyan, D.: Astrophys. J. Lett. 566, 71 (2002). doi:10.1086/339594. arXiv:astro-ph/0201362
Sulentic, J.W., Bachev, R., Marziani, P., Negrete, C.A., Dultzin, D.: Astrophys. J. 666, 757 (2007). doi:10.1086/519916. arXiv:0705.1895
Sulentic, J.W., Marziani, P., del Olmo, A., Dultzin, D., et al.: ArXiv e-prints (2014). arXiv:1406.5920
Tang, B., Shang, Z., Gu, Q., Brotherton, M.S., Runnoe, J.C.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. 201, 38 (2012). doi:10.1088/0067-0049/201/2/38. arXiv:1207.2539
Trakhtenbrot, B., Netzer, H.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 427, 3081 (2012). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.22056.x. arXiv:1209.1096
Tytler, D., Fan, X.-M.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. 79, 1 (1992). doi:10.1086/191642
Vanden Berk, D.E., Richards, G.T., Bauer, A., Strauss, M.A., et al.: Astron. J. 122, 549 (2001). doi:10.1086/321167. arXiv:astro-ph/0105231
Vestergaard, M., Wilkes, B.J.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. 134, 1 (2001). doi:10.1086/320357. arXiv:astro-ph/0104320
Wandel, A., Peterson, B.M., Malkan, M.A.: Astrophys. J. 526, 579 (1999). doi:10.1086/308017. arXiv:astro-ph/9905224
Willott, C.J., Delorme, P., Reylé, C., Albert, L., et al.: Astron. J. 139, 906 (2010). doi:10.1088/0004-6256/139/3/906. arXiv:0912.0281
Wills, B.J., Laor, A., Brotherton, M.S., Wills, D., Wilkes, B.J., Ferland, G.J., Shang, Z.: Astrophys. J. Lett. 515, 53 (1999). doi:10.1086/311980
Zamfir, S., Sulentic, J.W., Marziani, P., Dultzin, D.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 403, 1759 (2010). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.16236.x. arXiv:0912.4306
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marziani, P., Sulentic, J.W., Negrete, C.A. et al. UV spectral diagnostics for low redshift quasars: estimating physical conditions and radius of the broad line region. Astrophys Space Sci 356, 339–346 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-014-2136-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-014-2136-z