Abstract
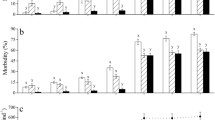
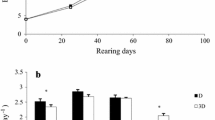
Sea urchins were stocked at a density of 15 (D15), 30 (D30), 45 (D45) and 60 (D60) urchins/cage (0.3 m long × 0.2 m wide × 0.4 m high) in a laboratory culture environment for 16 months. The wet body weight (BW) and test diameter growth were monitored at 2-month intervals during the experiment. At the conclusion of the experiment, the surviving sea urchins were counted and the gonad wet weight (GW) and gonad color were measured. Specific growth rate (SGR) of body weight, survival rate (SR), gonad index (GI), gonad color difference (ΔE 00), coefficients of variation (CV) of BW, GW, GI and ΔE 00, total biomass yield (TY) and total gonad yield (TGY) per cage were calculated. Two marketable yield variables, graded according to gonad index, i.e., marketable biomass yield (MY) and marketable gonad yield (MGY), were also calculated. Coefficient of variation of final body weight (FW) and final test diameter (FTD) of sea urchins increased as the stocking density increased, indicating the existence of adverse social interactions. These adverse social interactions detrimentally affected FW, FTD, SGR, GW and GI (P < 0.01). Although SR decreased with the increasing densities, no statistical significant difference was detected. Sea urchins at D15 had the lowest gonad color difference (ΔE 00) (P < 0.05). However, statistically equal CV of ΔE 00 indicates this density effect was not a result of adverse social interactions. TY and TGY increased with increased density and can be described by the following equations: TY = 84.18X 0.64, R 2 = 0.999 and TGY = 24.16X 0.38, R 2 = 0.979. However, the MY and MGY were not significantly different among stocking densities. The results of this study demonstrate that in intensive culture S. intermedius at low stocking density can achieve high growth rate, gonad index and desirable color without decreasing the marketable yield. Farmers should choose to culture S. intermedius at low stocking densities.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agatsuma Y (2013) Strongylocentrotus intermedius. In: Lawrence JM (ed) Sea urchins: biology and ecology. Elsevier, London, pp 437–447
Bagley MJ, Bentley B, Gall GA (1994) A genetic evaluation of the influence of stocking density on the early growth of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 121:313–326
Chang Y, Wang Z, Wang G (1999) Effect of temperature and algae on feeding and growth in sea urchin, strongylocentrotus intermedius. J Fisheris China 23:69–76 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chang Y, Ding J, Song J, Yang W (2004) Biology and aquaculture of sea cucumbers and sea urchins. Ocean Press, Beijing
Chang Y, Zhang W, Zhao C, Song J (2012) Estimates of heritabilities and genetic correlations for growth and gonad traits in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Aquac Res 43:271–280
Christiansen JS, Siikavuopio SI (2007) The relationship between feed intake and gonad growth of single and stocked green sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis) in a raceway culture. Aquaculture 262:163–167
Chua TE, Teng SK (1979) Relative growth and production of the estuary grouper Epinephelus salmoides under different stocking densities in floating net-cages. Mar Biol 54:363–372
Costas B, Aragão C, Mancera JM, Dinis MT, Conceição LE (2008) High stocking density induces crowding stress and affects amino acid metabolism in Senegalese sole Solea senegalensis (Kaup 1858) juveniles. Aquac Res 39:1–9
de Oliveira EG, Pinheiro AB, de Oliveira VQ, da Silva Júnior ARM, de Moraes MG, Rocha ÍRCB, de Sousa RR, Costa FHF (2012) Effects of stocking density on the performance of juvenile pirarucu (Arapaima gigas) in cages. Aquaculture 370:96–101
Dong S, Liang M, Gao Q, Wang F, Dong Y, Tian X (2010) Intra-specific effects of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) with reference to stocking density and body size. Aquac Res 41:1170–1178
Dunham A, Gurney-Smith H, Plamondon N, Yuan S, Pearce CM (2013) Aquaculture potential of the basket cockle (Clinocardium nuttallii). Part 1: effects of stocking density on first year grow-out performance in intertidal and off-bottom suspended culture. Aquac Res 44:1236–1253
Gilmour KM, DiBattista JD, Thomas JB (2005) Physiological causes and consequences of social status in salmonid fish. Integr Comp Biol 45:263–273
Guillou M, Lumingas L (1999) Variation in the reproductive strategy of the sea urchin Sphaerechinus granularis (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) related to food availability. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 79:131–136
Imsland A, Nilsen T, Folkvord A (1998) Stochastic simulation of size variation in turbot: possible causes analysed with an individual-based model. J Fish Biol 53:237–258
Irwin S, O’halloran J, FitzGerald R (1999) Stocking density, growth and growth variation in juvenile turbot, Scophthalmus maximus (Rafinesque). Aquaculture 178:77–88
Jobling M, Baardvik B (1994) The influence of environmental manipulations on inter—and intra—individual variation in food acquisition and growth performance of Arctic charr, Salvelinus alpinus. J Fish Biol 44:1069–1087
Lawrence JM, Cao X, Chang Y, Wang P, Yu Y, Lawrence AL, Watts SA (2009) Temperature effect on feed consumption, absorption, and assimilation efficiencies and production of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. J Shellfish Res 28:389–395
Lawrence JM, Chang Y, Cao X, Lawrence AL, Watts SA (2011) Potential for production of uni by Strongylocentrotus intermedius using dry formulated feeds. J World Aquacult Soc 42:253–260
Lund I, Steenfeldt SJ, Herrmann B, Pedersen PB (2013) Feed intake as explanation for density related growth differences of common sole Solea solea. Aquac Res 44:367–377
Luo MR, Cui G, Rigg B (2001) The development of the CIE 2000 colour-difference formula: CIEDE2000. Color Res Appl 26:340–350
Luo S, Zhao C, Chang Y, Feng W, Tian X (2014) Banana peel provides a new insight into improving gonad flavor in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Aquacult Int 22:833–841
Matsuno T, Tsushima M (2001) Carotenoids in sea urchins. Dev Aquac Fisheries Sci 32:115–138
Mgaya YD, Mercer JP (1995) The effects of size grading and stocking density on growth performance of juvenile abalone, Haliotis tuberculata Linnaeus. Aquaculture 136:297–312
Onders RJ, Mims SD, Dasgupta S (2011) Effect of size-grading and feeding frequency on growth and size variation of paddlefish, polyodon spathula, juveniles reared in ponds. J World Aquacult Soc 42:127–134
Otero-Villanueva MdM, Kelly MS, Burnell G (2004) How diet influences energy partitioning in the regular echinoid Psammechinus miliaris; constructing an energy budget. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 304:159–181
Pearce CM, Daggett TL, Robinson S (2002) Effect of protein source ratio and protein concentration in prepared diets on gonad yield and quality of the green sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis. Aquaculture 214:307–332
Pearce CM, Daggett TL, Robinson SM (2003) Effects of starch type, macroalgal meal source, and β-carotene on gonad yield and quality of the green sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis (Müller), fed prepared diets. J Shellfish Res 22:505–519
Pearce CM, Daggett TL, Robinson S (2004) Effect of urchin size and diet on gonad yield and quality in the green sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis). Aquaculture 233:337–367
Pei S, Dong S, Wang F, Tian X, Gao Q (2012) Effects of density on variation in individual growth and differentiation in endocrine response of Japanese sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus Selenka). Aquaculture 356:398–403
Robinson S, Castell J, Kennedy E (2002) Developing suitable colour in the gonads of cultured green sea urchins (Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis). Aquaculture 206:289–303
Rowland SJ, Mifsud C, Nixon M, Boyd P (2006) Effects of stocking density on the performance of the Australian freshwater silver perch (Bidyanus bidyanus) in cages. Aquaculture 253:301–308
Sadhu N, Sharma SK, Joseph S, Dube P, Philipose K (2014) Chronic stress due to high stocking density in open sea cage farming induces variation in biochemical and immunological functions in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch). Fish Physiol Biochem 40:1–9
Shpigel M, McBride SC, Marciano S, Ron S, Ben-Amotz A (2005) Improving gonad colour and somatic index in the European sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Aquaculture 245:101–109
Shpigel M, Schlosser SC, Ben-Amotz A, Lawrence AL, Lawrence JM (2006) Effects of dietary carotenoid on the gut and the gonad of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Aquaculture 261:1269–1280
Siikavuopio SI, James PJ (2011) Long-term effects of stocking density on somatic growth, gonad index and survival of the juvenile sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis. Aquacult Int 19:741–747
Siikavuopio SI, Dale T, Foss A, Mortensen A (2004) Effects of chronic ammonia exposure on gonad growth and survival in green sea urchin Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis. Aquaculture 242:313–320
Siikavuopio SI, Dale T, Mortensen A (2007a) The effects of stocking density on gonad growth, survival and feed intake of adult green sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis). Aquaculture 262:78–85
Siikavuopio SI, Dale T, Mortensen A, Foss A (2007b) Effects of hypoxia on feed intake and gonad growth in the green sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis. Aquaculture 266:112–116
Siikavuopio SI, Mortensen A, Christiansen JS (2008) Effects of body weight and temperature on feed intake, gonad growth and oxygen consumption in green sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis. Aquaculture 281:77–82
Sookying D, Silva FSD, Davis DA, Hanson TR (2011) Effects of stocking density on the performance of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei cultured under pond and outdoor tank conditions using a high soybean meal diet. Aquaculture 319:232–239
Symonds RC, Kelly MS, Caris-Veyrat C, Young AJ (2007) Carotenoids in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus: Occurrence of 9′- cis-echinenone as the dominant carotenoid in gonad colour determination. Comp Biochem Phys B 148:432–444
Symonds RC, Kelly MS, Suckling CC, Young AJ (2009) Carotenoids in the gonad and gut of the edible sea urchin Psammechinus miliaris. Aquaculture 288:120–125
Tidwell JH, Coyle S, Webel C, Evans J (1999) Effects and interactions of stocking density and added substrate on production and population structure of freshwater prawns Macrobrachiurn rosenbergii. J World Aquacult Soc 30:174–179
Viera MdP, Viçose GC, Fernández-Palacios H, Izquierdo M (2016) Grow-out culture of abalone Haliotis tuberculata coccinea Reeve, fed land-based IMTA produced macroalgae, in a combined fish/abalone offshore mariculture system: effect of stocking density. Aquac Res 47(1):71–81
Wallat G, Tiu L, Wang H, Rapp D, Leighfield C (2005) The effects of size grading on production efficiency and growth performance of yellow perch in earthen ponds. N Am J Aquacult 67:34–41
Wang J, Cheng X, Yang Y, Wang N (2007) Polyculture of juvenile sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus intermedius) with juvenile sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus Selenka) at various stocking densities. J Dalian Fish Univ 22:102–108 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Woods CM, James PJ, Moss GA, Wright J, Siikavuopio S (2008) A comparison of the effect of urchin size and diet on gonad yield and quality in the sea urchin Evechinus chloroticus Valenciennes. Aquacult Int 16:49–68
Zhang W, Zhao C, Chen M, Chang Y, Song J, Luo S (2013) Family growth response to different laboratory culture environments shows genotype–environment interaction in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Aquac Res 44:1706–1714
Zhang W, Chang Y, Luo S, Zhou H, Tian X, Ding J, Chen X (2014) Effects of biofilms as the main and as a supplementary food on the survival, somatic growth and gonad enhancement of sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Aquacult Int 22:925–936
Zhao C, Zhang W, Chang Y, Zhou H, Song J, Luo S (2013) Effects of continuous and diel intermittent feeding regimes on food consumption, growth and gonad production of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius of different size classes. Aquacult Int 21:1–10
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Chinese National 863 project (2012AA10A412). We are greatly grateful to Prof. John M. Lawrence for providing many useful editorial suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shoubing Qi and Weijie Zhang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, S., Zhang, W., Jing, C. et al. Long-term effects of stocking density on survival, growth performance and marketable production of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius . Aquacult Int 24, 1323–1339 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-016-9988-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-016-9988-x