Abstract
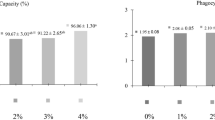
Effect of dietary supplementation of a Gram-positive, aerobic, probiotic bacterium Bacillus subtilis on the immunohaematological indices during pre- and post-challenge in Indian major carp, catla (Catla catla), was studied. The B. subtilis was administered orally at four different doses 1.0 × 106 (T1), 1.0 × 107 (T2), 1.0 × 108 (T3), and 1.0 × 109 (T4) cfu g−1 feed to C. catla for 90 days. The positive control (Cp) and negative control (Cn) were fed with feed without B. subtilis for the same period. On the 60th day, blood and serum were sampled to determine various haematological and serum parameters. Fish were challenged intraperitoneally with Aeromonas hydrophila after 60 days in all the treatment groups and Cp, while the Cn was challenged with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.2) only. Dietary supplementation of B. subtilis leads to the rise of various immunological and haematological parameters in catla during the pre- and post-challenge. During pre-challenge, the highest TEC (1.30 ± 0.02 × 106 cells mm−3), haemoglobin (7.43 ± 0.25 g %), total serum protein (3.89 ± 0.08 g dL−1), and serum lysozyme activity (8.39 ± 0.01 µg ml−1) were recorded in fishes fed feed containing B. subtilis at 1 × 109 cfu/g feed (T4). The highest survival percentage (86.33 %) was also observed in T4 group. The significantly increased survival percentage (P < 0.05) of B. subtilis-treated groups in comparison with control group (Cp) suggests that dietary supplementation of this probiotic bacterium can protect catla from A. hydrophila infection by enhancing innate immunity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aly SM, Abdel-Galil AY, Abdel-Aziz GA, Mohamed MF (2008) Studies on Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, as potential probiotics, on the immune response and resistance of Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus) to challenge infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:128–136
Bagheri T, Hedayati SA, Yavari V, Alizade M, Farzanfar A (2008) Growth, survival and gut microbial load of rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss) fry given diet supplemented with probiotic during the two months of first feeding. Turk J Fish Aqua Sci 8:43–48
Brenden RA, Huizinga HW (1986) Pathophysiology of experimental Aeromonas hydrophila infection in goldfish, Carassius auratus (L.). J Fish Dis 9:163–167
Dalmo RA, Ingebrigtsen K, Bøgwald J (1997) Non-specific defence mechanisms in fish, with particular reference to the reticuloendothelial system (RES). J Fish Dis 20:241–273
Dautiny A, Prager EM, Pham-Dhin D, Jolles J, Pakdel F, Grinde B (1991) cDNA and amino acid sequences of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) lysozymes and their implications for the evolution of lysozyme and lactalbumin. J Mol Evol 32:187–198
Díaz-Rosales P, Arijo S, Chabrillón M, Alarcón FJ, Tapia-Paniagua ST, Martínez-Manzanares E, Balebona MC, Morinigo MA (2009) Effects of two closely related probiotics on respiratory burst activity of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis, Kaup) phagocytes, and protection against Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida. Aquaculture 293:16–21
Dimitroglou A, Merrifield DL, Carnevali O, Picchietti S, Avella M, Daniels C, Guroy D, Davies SJ (2011) Microbial manipulations to improve fish health and production: mediterranean perspective. Fish Shellfish Immunol 30:1–16
EL-Dakar AY, Shalaby SM, Saoud IP (2007) Assessing the use of a dietary probiotic/prebiotic as an enhancer of spinefoot rabbit fish Siganus rivulatus survival and growth. Aquac Nutr 13:407–412
Ellis AE (1999) Immunity to bacteria in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol 9:291–308
Ellis AE (2001) Innate host defense mechanisms of fish against viruses and bacteria. Dev Comp Immunol 25:827–839
Ellis AE, Hastings TS, Munro ALS (1981) The role of Aeromonas salmonicida extracellular products in the pathology of furunculosis. J Fish Dis 4:41–51
FAO (2006) Cultured aquatic species information programme. Catla catla (Hamilton 1822), pp1–11
Fujiki K, Shin D, Nakao M, Yano T (2000) Molecular cloning of carp (Cyprinus carpio) leucocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2, glia maturation factor, CD45 and lysozyme C by use of suppression subtractive hybridization. Fish Shellfish Immunol 10:643–650
Green DH, Wakeley PR, Page A, Barnes A, Baccigalupi L, Ricca E, Cutting SM (1999) Characterization of two Bacillus probiotics. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4288–4291
He S, Liu W, Zhou Z, Mao W, Ren P, Marubashi T, Ringo E (2011) Evaluation of probiotic strain Bacillus subtilis C-3102 as a feed supplement for koi carp (Cyprinus carpio). J Aquac Res Dev 1:005
Hikima J, Hirono T, Aoki T (1997) Characterization and expression of C-type lysozyme cDNA from Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 6:339–344
Hikima J, Minagawa S, Hirono I, Aoki T (2001) Molecular cloning, expression and evolution of Japanese flounder goose-type lysozyme gene, and lytic activity of its recombinant protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1520:35–44
Ikeda Y, Ozaki H, Hayama K, Ikeda S, Minami T (1976) Diagnostic study on blood constituents in the yellow tail inoculated with Nocardia kampachi. Bull Jap Soc Sci Fish 42:1055–1064
Ingram GA (1980) Substances involved in the natural resistance of fish to infection-a review. J Fish Biol 16:23–60
Irianto A, Austin B (2002) Use of probiotics to control furunculosis in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 25:333–342
Kamgar M, Ghane M (2012) Evaluation of Bacillus subtilis effect as probiotic on hematological parameters of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum) following experimental infection with Streptococcus iniae. J Fish Aquat Sci 7:1–9
Kim JY, Kwon JH, Ahn SH, Lee SI, Han YS, Choi YO, Lee SY, Ahn KM, Ji GE (2010) Effect of probiotic mix (Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bifidobacterium lactis, Lactobacillus acidophilus) in the primary prevention of eczema: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Pediatr Allery Immunol 21:386–393
Kumar R, Mukherjee SC, Prasad KP, Pal AK (2006) Evaluation of Bacillus subtilis as a probiotic to Indian major carp Labeo rohita (Ham.). Aquac Res 37:1215–1221
Kumar R, Mukherjee SC, Ranjan R, Nayak SK (2008) Enhanced innate immune parameters in Labeo rohita (Ham.) following oral administration of Bacillus subtilis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 24:168–172
Larsen AN, Solstad T, Svineng G, Seppola M, Jørgensen TØ (2009) Molecular characterization of a goose-type lysozyme gene in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 26:122–132
Liu CH, Chiu CH, Wang SW, Cheng W (2012) Dietary administration of the probiotic, Bacillus subtilis E20, enhances the growth, innate immune responses, and disease resistance of the grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol 33:699–706
Merrifield DL, Dimitroglou A, Bradley G, Baker RTM, Davies SJ (2010a) Probiotic applications for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum I). Effects on growth performance, feed utilization, intestinal microbiota and related health criteria. Aquac Nutr 16:504–510
Merrifield DL, Dimitroglou A, Foey A, Davies SJ, Baker R, Bøgwald J, Castex M, Ringo E (2010b) The current status and future focus of probiotic and prebiotic applications for salmonids. Aquaculture 302:1–18
Mock A, Peters G (1990) Lysozyme activity in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), stressed by handling, transport and water pollution. J Fish Biol 37:873–885
Nayak SK (2010) Probiotics and immunity: a fish perspective. Fish Shellfish Immunol 29:2–14
Nayak SK, Swain P, Mukherjee SC (2007) Effect of dietary supplementation of probiotic and vitamin C on the immune response of Indian major carp, Labeo rohita (Ham). Fish Shellfish Immunol 23:892–896
Nikoskelainen S, Ouwehand AC, Bylund G, Salminen S, Lilius EM (2003) Immune enhancement in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) by potential probiotic bacteria (Lactobacillus rhamnosus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 15:443–452
Olivier G, Lallier R, Lariviere S (1981) A toxigenic profile of Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas sobria isolated from fish. Can J Microbiol 27:330–333
Paulsen SM, Engstad RE, Robertsen B (2001) Enhanced lysozyme production in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) macrophages treated with yeast ß-glucan and bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Fish Shellfish Immunol 11:23–37
Purwandari AR, Chen HY (2013) Effects of probiotic Bacillus subtilis on intestinal microbial diversity and immunity of orange spotted grouper Epinephelus coioides. J Appl Biotechnol 1:25–36
Qi Z, Zhang XH, Boon N, Bossier P (2009) Probiotics in aquaculture of China-current state, problems and prospect. Aquaculture 290:15–21
Quade MJ, Roth JA (1997) A rapid, direct assay to measure degranulation of bovine neutrophil primary granules. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 58:239–248
Rainger GE, Rowley AF (1993) Antibacterial activity in the serum and mucus of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, following immunization with Aeromonas salmonicida. Fish Shellfish Immunol 3:475–482
Ranjan R, Prasad KP, Vani T, Kumar R (2012) Effect of dietary chitosan on haematology, innate immunity and disease resistance of Asian seabass Lates calcarifer (Bloch). Aquac Res 45(6):983–993
Roberts RJ (1989) Nutritional pathology of teleosts. In: Roberts RJ (ed) Fish pathology. Bailliere Tindall, London, pp 337–362
Sahoo PK, Kumari J, Mishra BK (2005) Non-specific immune responses in juveniles of Indian major carps. J Appl Ichthyol 21:151–155
Salinas I, Cuesta A, Esteban MA, Meseguer J (2005) Dietary administration of Lactobacillus delbrueckii and Bacillus subtilis, single or combined, on gilthead seabream cellular innate immune responses. Fish Shellfish Immunol 19:67–77
Sankaran K, Gurnani S (1972) On the variation in the catalytic activity of lysozyme in fishes. Indian J Biochem Biophys 9:62–165
Savan R, Sakai M (2002) Analysis of expressed sequence tags (EST) obtained from common carp Cyprinus carpio L head kidney cells after stimulation by two mitogens, lipopolysaccharide and concanavalin-A. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B Biochem Mol Biol 131:71–82
Savan R, Amanb A, Sakaib M (2003) Molecular cloning of G type lysozyme cDNA in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 15:263–268
Schaperclaus W, Kulow H, Schreckenbach K (1991) Haematological and serological technique. Fish Dis 1:71–108
Secombes CJ (1990) Isolation of salmonid macrophages and analysis of their killing activity. In: Stolen JS, Feltcher TC, Anderson DP, Robertson BS, Van Muiswinkel WB (eds) Techniques in fish immunology. SOS Publication, Fair Haven, pp 137–154
Stasiak SA, Baumann PC (1996) Neutrophil activity as a potential bioindicator for contaminant analysis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 6:537–539
Wei S, Huang Y, Huang X, Cai J, Wei J, Li P, Qin Q (2014) Molecular cloning and characterization of a new G-type lysozyme gene (Ec-lysG) in orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Dev Comp Immunol 46:401–412
Weissmann G (2010) It’s complicated: inflammation from Metchnikoff to Meryl Streep. FASEB J 24:4129–4132
Wiegertjes GF, Bongers AB, Voorthuis P, Zandieh DB, Groeneveld A, Muiswinkel WB, Stet RJM (1996) Characterization of isogenic carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) lines with a genetically determined high or low antibody production. Anim Genet 27:313–319
Wimalawickrama ND, Pathiratne A (2005) Evaluation of the effects of infestation by trematodes and copepodes on Catla catla an Indian carp cultured in Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka J Aquat Sci 10:85–96
Xie Y, Liu D, Zou J, Li G, Zhu Z (1993) Gene transfer via electroporation in fish. Aquaculture 111:207–213
Ye X, Zhang L, Tian Y, Tan A, Bai J, Li S (2010) Identification and expression analysis of the g-type and c-type lysozymes in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella. Dev Comp Immunol 34:501–509
Zheng W, Tian C, Chen X (2007) Molecular characterization of goose-type lysozyme homologue of large yellow croaker and its involvement in immune response induced by trivalent bacterial vaccine as an acute-phase protein. Immunol Lett 113:107–116
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the University Grant Commission, New Delhi, for awarding the first author with CSIR-UGC Junior Research Fellowship and Director, and to Central Institute of Fisheries Education, Mumbai, for providing the facilities to carry out the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R., Mukherjee, S.C., Ranjan, R. et al. Effect of dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis on haematological and immunological parameters of Catla catla (Hamilton). Aquacult Int 23, 1275–1292 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-015-9883-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-015-9883-x