Abstract
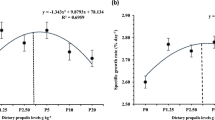
The objective of this study is to investigate the effects of dietary protein and lipid levels on the growth performance and bioeconomic benefits of two-banded seabream (Diplodus vulgaris) juveniles, a candidate species for aquaculture sector. Eight experimental diets were formulated with four protein (50, 45, 40 and 35 %) levels for each of the two lipid levels (15 and 10 %). Triplicate groups of juvenile fish with an average initial body weight of ~3.64 g were reared in a recirculating aquaculture system and hand fed twice a day until satiation for a period of 60 days. In the experiment, no difference in survival rate was found between the different groups. Relative growth rate (RGR), specific growth rate (SGR), feed conversion ratio (FCR) and daily feed intake were not significantly affected by increasing protein and/or lipid treatments in this present study. However, the RGR, SGR and FCR values showed slightly better efficiency in the experimental group (35/15) fed with lower protein content (35 %) and higher lipid level (15 %) compared with those fed other diets. According to bioeconomic analyses results, the diet with the 35 % protein and 15 % lipid generated the best profit. The results suggest that two-banded seabream can be accepted as a promising alternative species for the aquaculture industry and optimum growth of two-banded seabream fingerlings can be obtained when they are fed a diet containing 35 % crude protein and 15 % crude lipid.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JL (1988) Residues of benzocaine in rainbow trout, largemouth bass and fish meal. Progress Fish Cult 50:59–60
Allen JL, Vang G, Steege S, Xtong S (1994) Solubility of benzocaine in freshwater. Progress Fish Cult 56:145–146
AOAC (2000) Official methods of analysis, 17th edn. Assoc Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, VA
Atienza MT, Chatzifotis S, Divanach P (2004) Macronutrient selection by sharp snout sea bream (Diplodus puntazzo). Aquaculture 232:481–491
Brunty J, Bucklin R, Davis J, Baird C, Nordstedt R (1997) The influence of feed protein intake on tilapia ammonia production. Aquacult Eng 16:161–166
Coutinho F, Peres H, Guerreiro I, Pousão-Ferreira P, Oliva-Teles A (2012) Dietary protein requirement of sharpsnout sea bream (Diplodus puntazzo, Cetti 1777) juveniles. Aquaculture 356:391–397
De La Higuera M, García Gallego M, Sanz A, Hidalgo MC, Suárez MD (1989) Utilization of dietary protein by the eel (Anguilla anguilla): optimum dietary protein levels. Aquaculture 79:53–61
Espinós FJ, Tomás A, Pérez LM, Balasch J, Jover M (2003) Growth of dentex fingerlings (Dentex dentex) fed diets containing different levels of protein and lipid. Aquaculture 218:479–490
Guidetti P (2004) Consumers of sea urchins, Paracentrotus lividus and Arbacia lixula, in shallow Mediterranean rocky reefs. Helgol Mar Res 58:110–116
Hidalgo F, Alliot E (1988) Influence of water temperature on protein requirement and protein utilization in juvenile sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax. Aquaculture 72:115–129
Horta M, Costa MJ, Cabral H (2004) Spatial and trophic niche overlap between Diplodus bellottii and Diplodus vulgaris in the Tagus estuary, Portugal. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 84:837–842
Jover M, García-Gómez A, Tomás A, De la Gándara F, Pérez L (1999) Growth of Mediterranean yellowtail (Seriola dumerilii) fed extruded diets containing different levels of protein and lipid. Aquaculture 79:25–33
Jug-Dujakovic J, Glamuzina B (1988) Preliminary studies of reproduction and early life history of Diplodus vulgaris (E. Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire 1817) in captivity. Aquaculture 69:361–377
Kim K, Kayes BT, Amundson HC (1991) Purified diet development and re-evaluation of the dietary protein requirement of fingerling rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 96:57–67
Lupatsch I, Kissil GW, Sklan D (2003) Defining energy and protein requirements of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) to optimize feeds and feeding regimes. Isr J Aquac Bamidgeh 55(4):243–257
Maldonado-García M, Rodríguez-Romero J, Reyes-Becerril M, Álvarez-González CA, Civera-Cerecedo R, Spanopoulos M (2012) Effect of varying dietary protein levels on growth, feeding efficiency, and proximate composition of yellow snapper Lutjanus argentiventris (Peters, 1869). Lat Am J Aquat Res 40(4):1017–1025
NRC (National Research Council) (1993) Nutrient requirements of fish. National Academy Press, Washington, DC 114
Ozório ROA, Valente LMP, Correia S, Pousao-Ferreira P, Damasceno-Oliveira A, Escorcio C, Olivia-Teles A (2009) Protein requirement for maintenance and maximum growth of two-banded seabream (Diplodus vulgaris) juveniles. Aquac Nutr 15:85–93
Pallaoro A, Santic M, Jardas I (2006) Feeding habits of the common two-banded sea bream, Diplodus vulgaris (Sparidae), in the eastern Adriatic Sea. Cybium 30:19–25
Pérez L, Gonzalez M, Jover M, Fernández-Carmona J (1997) Growth of European sea bass fingerlings (Dicentrarchus labrax) fed extruded diets containing varying levels of protein, lipid and carbohydrate. Aquaculture 156:183–193
Sá R, Pousáo-Ferreira P, Olive-Teles A (2008) Dietary protein requirement of White sea bream (Diplodus sargus) juveniles. Aquac Nutr 14:309–317
Sabaut JJ, Luquet P (1973) Nutritional requirements of the gilthead bream Chrysophrys aurata. Quantitative protein requirements. Mar Biol 18:50–54
Schuchardt D, Vergara JM, Fernández-Palacios H, Kalinowski CT, Hernández-Cruz CM, Izquierdo MS, Robaina L (2008) Effects of different dietary protein and lipid levels on growth, feed utilization and body composition of the red porgy (Pagrus pagrus) fingerlings. Aquac Nutr 14:1–9
Wagner E, Miller S, Bosakowski T (1995) Ammonia excretion by rainbow trout over a 24-hour period at two densities during oxygen injection. Progress Fish Cult 57:199–205
Wilson R (1989) Amino acids and proteins. In: Halver JE (ed) Fish nutrition. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp 112–153
Yigit M, Yardim Ö, Koshio S (2002) The protein sparing effects of high lipid levels in diets for Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, W. 1792) with special reference to reduction of total nitrogen excretion. Isr J Aquac 54(2):79–88
Yigit M, Koshio S, Teshima S, Ishikawa M (2004) Dietary protein and energy requirements of juvenile Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. J Appl Sci 4(3):486–492
Yiğit M, Bulut M, Ergün S, Güroy D, Karga M, Kesbiç OS, Yılmaz S, Acar Ü, Güroy B (2012) Utilization of corn gluten meal as a protein source in diets for gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) juveniles. J FisheriesSciences.com 6(1):63–73
Zhang J, Zhou F, Wang L, Shao Q, Xu Z (2010) Dietary protein requirement of juvenile sea bream, Sparus macrocephalus. J World Aquac Soc 41(2):151–162
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bulut, M., Yiğit, M., Ergün, S. et al. Evaluation of dietary protein and lipid requirements of two-banded seabream (Diplodus vulgaris) cultured in a recirculating aquaculture system. Aquacult Int 22, 965–973 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-013-9720-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-013-9720-z