Abstract
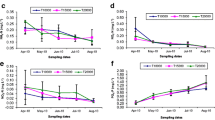
The effect of cattle organic fertilizer on plankton primary production and related variables was tested in six Bulgarian fish ponds situated close to the town of Plovdiv in Bulgaria. At the beginning of the experiment (16th of May 2004, about 10 days after filling with water) a suppression of plankton metabolism was observed and after that the ponds treated with manure demonstrated significantly higher productivity than the controls, especially during the transition to the autumn season when the water column was more regularly mixed. The other measured variables (Secchi disk readings, plankton chlorophyll-a and respiration, assimilation number per unit chlorophyll-a) did not show significant differences between the treated and control ponds.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abakoumov V (ed) (1983) A manual on methods for aquatic biology analysis of surface waters and sediments. Leningrad, Gidrometeoizdat Publisher, p 239 (in Russian)
Arfi R, Guiral D, Torreton J-P (1991) Natural recolonization of a productive tropical pond: day to day variations in the photosynthetic parameters. Aquat Sci 53:39–54
Barthelmes D (1981) Hydrobiologische Grundlagen der Binnenfischerei. VEB Gustav Fischer Verlag Jena, 1-ste Auflage, p 251
Bíró P, Vörös L (1990) Trophic relationships between primary producers and fish yields in Lake Balaton. Hydrobiologia 191:213–221
Boyd C (1973) Summer algal communities and primary productivity in fish ponds. Hydrobiologia 41:357–390
Culver D, Geddes M (1993) Limnology of rearing ponds for Australian fish larvae: relationships among water quality, phytoplankton, zooplankton, and growth of larval fish. Aust J Mar Freshwater Res 44:537–551
Dhawan A, Kaur S (2002) Effect of pig dung on water quality and polyculture of carp species during winter and summer. Aquac Int 10:297–307
Dimitrov M (1983) Intensive polycultured rearing of Carp (Cyprinus carpio (L.)), Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix (Val.)) and White Amur (Ctenopharyngodon idelia (Val.)) in a Mean Large pond. In: Freshwater Fisheries Research Institute Plovdiv (A Jubilee book): 131–142 (in Bulgarian)
Dimitrov M (1987) Intensive polyculture of common carp, Cyprinus carpio (L.), silver carp, Hypophthalmichthys molitrix (Val.) and black buffalo, Ictiobus niger (Raf.). Aquac–Netherlands 65:119–125
Green B, Teichert-Coddington DR, Phelips RP (1990) Response of tilapia yield and economics to varying rates of organic fertilization and season in two Central American countries. Aquaculture 90(3–4):279–290
Grozev G (1997) Effect of reared fish on development of zooplankton in fishery ponds. Bulg J Agric Sci 3:635–646
Grozev G, Paskaleva E, Yoshev L (2001) A methodic for fertilizing and manuring in pond fisheries in dependence of environmental conditions and applied polyculture. Agricultural University Plovdiv (Bulgaria). Fifth Scientific and Practical Conference “Ecological Problems of Agriculture”, XI, VI (1):159–164, (in Bulgarian)
Kalchev R, Terziyski D, Stoeva A, Grozev G (2006) Nutrients and other chemical variables, related to plankton primary production in fertilized and control fish ponds. Bulg J Agric Sci 12:226–235
Kwei Lin C, Yang Y, Kabir Chowdhury MA, Shivappa RB, Diana JS (1999) Effect of mud turbidity on fertilization, and an analysis of techniques to mitigate turbidity problem. In: McElwee K, Burke D, Niles M, Egna H (eds) Sixteenth Annual Technical Report. Pond Dynamics, Aquaculture CRSP, Oregon State University, Corvallis, Oregon, pp 1–6
Mourin V (1972) Intensification of fish farming. Ourozhai Publishing, Kiev, p 116
Qin J, Culver D, Yu N (1995a) Effect of organic fertilizer on heterotrophs and autotrophs: implications for water quality management. Aquac Res 26:911–920
Qin J, Sharook P, David A (1995b) Effect of larval walleye (Stixostedion vitreun) and fertilization on the plankton community: implication for larval fish culture. Aquaculture 130:51–65
Sakovskaya V, Voroshlina Z, Syrov V, Chrustalev E (1991) Manual of fishpond farming. Agropromizdat Publishing, Moskva, p 174 (in Russian)
Paskaleva E, Vodenicharov D (1984) The effect of fertilizing on phytoplankton abundance in some fish ponds of Institute for freshwater fisheries. Hydrobiology (Sofia) 22:39–50 (in Bulgarian)
Vollenweider R, (ed) (1969) A manual on methods for measuring primary production in aquatic environments, IBP, Handbook No. 12. Blackwell Scientific Publications Oxford and Edinburgh, p 212
Zhu Y, Yang Y, Wan J, Hua D, Mathias J (1990) The effect of manure application rate and frequency upon fish yield in integrated fish farm ponds. Aquaculture 91(3–4):233–251
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terziyski, D., Grozev, G., Kalchev, R. et al. Effect of organic fertilizer on plankton primary productivity in fish ponds. Aquacult Int 15, 181–190 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-007-9086-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-007-9086-1