Abstract
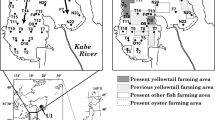
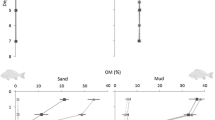
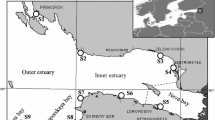
This study aims to compare the impact of oyster cultures on diagenetic processes and the phosphorus cycle in the sediments of the Aber Benoît and the Rivière d’Auray, estuary of Brittany, France. Our results showed clear evidence of the seasonal impact of oyster cultures on sediment characteristics (grain size and organic matter parameters) and the phosphorus cycle, especially in the Aber Benoît. At this site, seasonal variations in sulfide and Fe concentrations in pore waters, as well as Fe–P concentrations in the solid phase, highlighted a shift from a system governed by iron reduction (Reference) to a system governed by sulfate reduction (beneath oyster). This could be partly explained by the increase in labile organic matter (i.e., biodeposits) beneath oysters, whose mineralization by sulfate led to high sulfide concentrations in pore waters (up to 4,475 µmol l−1). In turn, sulfide caused an enhanced release of phosphate in the summer, as adsorption sites for phosphate decreased through the formation of iron–sulfide compounds (FeS and FeS2). In the Aber Benoît, dissolved Fe/PO4 ratios could be used as an indicator of phosphate release into oxic water. Low Fe/PO4 ratios in the summer indicated higher effluxes of phosphate toward the water column (up to 47 µmol m−2 h−1). At other periods, Fe/PO4 ratios higher than 2 mol/mol indicated very low phosphate fluxes. In contrast, in the Rivière d’Auray, the occurrence of macroalgae, stranding regularly all over the site, clearly masked the impact of oyster cultures on sediment properties and the phosphorus cycle and made the use of Fe/PO4 ratios more difficult in terms of indicators of phosphate release.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aminot A, Kérouel R (2004) Hydrologie des écosystèmes marins. Paramètres et anlayses. Ifremer, Plouzané
Aminot A, Kérouel R, Coverly SC (2009) Nutrients in seawater using segmented flow analysis. In: Wurl O (ed) Practical guidelines for the analysis of seawater. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 143–178
Andrieux-Loyer F, Aminot A (2001) Phosphorus forms related to sediment grain size and geochemical characteristics in French coastal areas. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 52:617–629
Andrieux-Loyer F, Philippon X, Bally G, Kérouel R, Youenou A, Le Grand J (2008) Phosphorus dynamics and bioavailability in sediments of the Penzé Estuary (NW France): in relation to annual P-fluxes and occurrences of Alexandrium Minutum. Biogeochemistry 88:213–231
Anschutz P, Zhong A, Sundby B, Mucci A, Gobeil C (1998) Burial efficiency of phosphorus and the geochemistry of iron in continental margin sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 43:53–64
Anschutz P, Chaillou G, Lecroart P (2007) Phosphorus diagenesis in sediment of the Thau lagoon. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 72(3):447–456
Argese E, Cogoni G, Zaggia L, Zonta R, Pini R (1992) Study on Redox state and grain size of sediments in a mud flat of the Venice Lagoon. Environ Geol Water Sci 20:35–42
Aspila KI, Agemian H, Chau AS (1976) A semi-automated method for the determination of inorganic, organic and total phosphate in sediments. Analyst 101:187–197
Azandegbe A (2010) Etude de la structure des communautés bactériennes du sediment et de l’écologie de Vibrio aestuarianus pathogène de l’huître creuse Crassostrea gigas dans deux sites ostréicoles. Thèse de Doctorat, Univ-Brest
Barranget C (1997) The role of microphytobenthic primary production in a Mediterranean mussel culture area. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 44:753–765
Barranget C, Alliot E, Plante-Cuny MP (1994) Benthic microphytic activity at two Mediterranean shellfish cultivation sites with reference to benthic fluxes. Oceanol Acta 17(2):211–221
Berelson WM, Heggie D, Longmorec A, Kilgore T, Nicholsonc G, Skyring G (1998) Benthic nutrient recycling in Port Phillip Bay, Australia. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 46:917–934
Berner RA (1980) Early diagenesis: a theoretical approach. Princeton University Press, Princeton, pp 9–14
Boesen C, Postma D (1988) Pyrite formation in anoxic environments of the Baltic. Am J Sci 288:575–603
Boon AR, Duineveld GCA (1998) Chlorophyll a as a marker for bioturbation and carbon flux in Southern and Central North Sea sediments. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 162:33–43
Boudreau BP (1996) The diffusive tortuosity of fine-grained unlithified sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:3139–3142
Bühring SI, Ehrenhauss S, Kamp A, Moodley L, Witte U (2006) Enhanced benthic activity in sandy sublittoral sediments: evidence from C-13 tracer experimetns. Mar Biol Res 2:120–129
Cauwet G (1975) Optimisation d’une technique de dosage du carbone organique des sediments. Chem Geol 16:59–63
Dyers K (1989) Estuarine flow interaction with topography—lateral and longitudinal effects in Estuarine circulation. In: Neilson B, Kuo A, Brubaker J (eds) Estuarine circulation. Humana, Louisville
Ekholm P, Lehtoranta J (2012) Does control of soil erosion inhibit aquatic eutrophication? J Environ Manag 93:140–146
Fonselius S, Dyrssen D, Yhlen B (1999) Determination of hydrogen sulfide. In: Grasshoff K, Kremling K, Ehrhardt M (eds) Methods of seawater analysis, 3rd extended edn. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 91–100
Forrest BM, Creese RG (2006) Benthic impacts of intertidal oyster culture, with consideration of taxonomic sufficiency. Environ Monit Assess 112:159–176
Gaertner-Mazouni N, Lacoste E, Bodoy A, Peacock L, Rodier M, Langlade M, Orempuller J, Charpy L (2012) Nutrient fluxes between water column and sediments: potential influence of the pearl oyster culture. Mar Pollut Bull 65(10–12):500–505
Gagnaire B, Soletchnik P, Madec P, Geairon P, Le Moine O, Renault T (2006) Diploid and triploid oysters, Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg), reared at two heights above sediment in Marennes-Oleron Basin, France: difference in mortality, sexual maturation and hemocyte parameters. Aquaculture 254:606–616
Gardner WS, Mc Carthy MJ, An S, Soboleo D, Sell KS, Brock D (2006) Nitrogen fixation and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) support nitrogen dynamics in Texas estuaires. Limnol Oceanogr 51(1, part 2):558–568
Geurts JJM, Smolders AJP, Verhoeven JTA, Roelofs JGM, Lamers LPM (2008) Sediment Fe:PO4 ratio as a diagnostic and prognostic tool for the restoration of macrophyte biodiversity in fen waters. Freshw Biol 53:2101–2116
Giles H, Pilditch CA (2006) Effects of mussel (Perna canaliculus) biodeposit decomposition on benthic respiration and nutrient fluxes. Mar Biol 150:261–271
Giles H, Pilditch CA, Bell DG (2006) Sedimentation from mussel (Perna canaliculus) culture in the Firth of Thames, New Zealand: impact on sediment oxygen and nutrient fluxes. Aquaculture 261(1):125–140
Golterman HL (1995) Theorical aspects of the adsorption of ortho-phosphate onto iron hydroxide. Hydrobiologia 315:59–68
Golterman HL (1998) The distribution of phosphate over ironbound and calcium-bound phosphate in stratified sediments. Hydrobiologia 364:75–81
Gunnars A, Blomqvist S (1997) Phosphate exchange across the sediment-water interface when shifting from anoxic to oxic conditions-an experimental comparison of freshwater and brackish-marine systems. Biogeochemistry 37:203–226
Heijs SK, Azzoni R, Giordani G, Jonkers HM, Nizzoli D, Viaroli P, van Gemerden H (2000) Sulfide-induced release of phosphate from sediments of coastal lagoons and the possible relation to the disappearance of Ruppia sp. Aquat Microb Ecol 23:85–95
Hupfer M, Lewandowski J (2008) Oxygen controls the phosphorus release from lake sediments—a long-lasting paradigm in limnology. Int Rev Hydrobiol 93(4/5):415–432
Hyun J, Kim S, Mok J, Lee JS, An S, Lee W, Jung R (2013) Impacts of long-line aquaculture of pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas) on sulfate reduction and diffusive nutrient flux in the coastal sediments of jinhae–tongyeong, Korea. Mar Pollut Bull 74(1):187–198
Jensen HS, Thamdrup Bo (1993) Iron-bound phosphorus in marine sediments as measured by bicarbonate-dithionite extraction. Hydrobiologia 253:47–59
Jensen HS, Kristensen P, Jeppesen E, Skytthe A (1992) Iron:phosphorus ratio in surface sediment as an indicator of phosphate release from aerobic sediments in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 235(236):731–743
Kervella Y, Germain G, Gaurier B, Facq JV, Cayocca F, Lesueur P (2010) Experimental study of the near-field impact of an oyster table on the flow. Eur J Mech B/Fluids 29(1):32–42
Krom MD, Berner RA (1980) Adsorption of phosphate in anoxic marine sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 25:797–806
Krom MD, Berner RA (1981) The diagenesis of phosphorus in a nearshore marine sediment. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:207–216
Larsonneur C (1971) Manche Centrale et Baie de Seine: géologie du substratum et des dépôts meubles. Thèse d’Etat de l’université de Caen, n° A.O. 5404
Lehtoranta J, Heiskanen AS (2003) Dissolved iron:phosphate ratio as an indicator of phosphate release to oxic water of the inner and outer coastal Baltic sea. Hydrobiologia 492:69–84
Lehtoranta J, Ekholm P, Pitkänen H (2009) Coastal eutrophication threshold: a matter of sediment microbial processes. Ambio 38(6):303–308
Li YH, Gregory S (1974) Diffusion of ions in sea water and in deep-sea sediments. Geochemi Cosmochim Acta 33:703–714
Lorenzen CJ (1967) Determination of chlorophyll and pheopigments: spectrophotometric equations. Limnol Oceanogr 12:343–346
Mallet AL, Carver CE, Landry T (2006) Impact of suspended and off-bottom eastern oyster culture on the benthic environment in eastern Canada. Aquaculture 255:362–373
Matijevic S, Grozdan K, Kljakovic-Gaspic Z, Bogner D (2008) Impact of fish farming on the distribution of phosphorus in sediments in the Middle Adriatic area. Mar Pollut Bull 56:535–548
Mazouni N (2004) Influence of suspended oyster cultures on nitrogen regeneration in a coastal lagoon (Thau, France). Mar Ecol Progr Ser 276:103–113
Mesnage V, Ogier S, Bally G, Disnar JR, Lottier N, Dedieu K, Rabouille C, Copard Y (2007) Nutrient dynamics at the sediment water-interface in a Mediterranean lagoon (Thau, France): influence of biodeposition by shellfish farming activities. Mar Environ Res 63:257–277
Mudroch A, Azcue JM (1995) Manuel of aquatic sediment sampling. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Nizzoli D, Welsh DT, Fano EA, Viaroli P (2006) Impact of clam and mussel farming on benthic metabolism and nitrogen cycling, with emphasis on nitrate reduction pathways. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 315:151–165
Nugues MM, Kaiser MJ, Spencer BE, Edwards DB (1996) Benthic community changes associated with intertidal oyster cultivation. Aquat Resour 27:913–924
Pietros JM, Rice MA (2003) The impacts of aquacultured oysters, Crassostrea virginica (Gmelin, 1791) on water column nitrogen and sedimentation: results of a mesocosm study. Aquaculture 220:407–422
Piriou JY, Chapron V, Annezo JP (1995) Mesure des flux nutritifs et inventaire d’algues vertes en 1995. Précontrat baie «Golfe du Morbihan». Ifremer-DEL-n° 95-19
Psenner R, Boström B, Dinka M, Petterson K, Puckso R, Sager M (1988) Fractionation of phosphorus in suspended matter and sediment. Archiv Für Hydrobiologie Beiheft Ergebnis Limnologie 30:98–103
Raimonet M, Andrieux-Loyer F, Ragueneau O, Michaud E, Kerouel R, Philippon X, Nonent M, Mémery L (2013) Strong gradients of benthic biogeochemical processes along a macrotidal temperate estuary: focus on P and Si cycles. Biogeochemistry 115(1–3):399–417
Resing JA, Mottl MJ (1992) Determination of manganese in seawater using flow injection analysis with on-line preconcentration and spectrophotometric detection. Anal Chem 64:2682–2687
Richard P, Riera P, Galois R (1997) Temporal variations in the chemical and carbon isotop compositions of marine and terrestrial organic inputs in the Bay of Marennes-Oléron, France. J Coastal Res 13:879–889
Rozan TF, Taillefert M, Trouwborst RE, Glazer BT, Ma S (2002) Iron–sulfur–phosphorus cycling in the sediments of a shallow coastal bay: implications for sediment nutrient release and benthic macroalgal blooms. Limnol Oceanogr 47(5):1346–1354
Ruttenberg KC (1990) Diagenesis and burial of phosphorus in marine sediments: implications for the marine phosphorus budget. Ph.D. thesis, Yale Ubiversity, 375 pp
Ruttenberg KC, Berner RA (1993) Authigenic apatite formation and burial in sediments from non-upwelling, continental margin environments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57:991–1007
Ruttenberg KC, Turnewitsch R, Witte U, Graf G (1992) Development of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 37(7):1460–1482
Sahling H, Rickert D, Lee RW, Linke P, Suess E (2002) Macrofaunal community structure and sulfife flux at gas hydrate deposits from the Cascadia convergent margin, NE Pacific. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 231:121–138
Samain JF, McCombie H (eds) (2007) Summer mortalities of Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas, the Morest project. Ifremer/Quae, Plouzané
Sarradin PM, Le Bris N, Le Gall C, Rodier O (2005) Fe analysis by the ferrozine method: adaptation to FIA towards in situ analysis in hydrothermal environment. Talanta 66:1131–1138
Schuffert JD, Jahnke RA, Kastner M, Leather J, Sturz A, Wing MR (1994) Rates of formation of modern phosphorites off western Mexico. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:5001–5010
Slomp CP, Epping EHG, Helder W, Van Raaphorst W (1996) A key role for iron-bound phosphorus in authigenic apatite formation in North Atlantic continental platform sediments. J Mar Res 54:1179–1205
Smolder AJP, Lamers LPM, Moonen M, Zwaga K, Roelofs JGM (2001) Controlling phosphate release from phosphate-enriched sediments by adding various iron compounds. Biogeochemistry 54:219–228
Soletchnik P, Lambert C, Costil K (2005) Summer mortality of Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg) in relation to environmental rearing conditions. J Shellfish Res 24:197–207
Sornin JM (1984) Rôle et consequences de la biodéposition à l’interface eau-sédiment. Journal De Recherche Océanographique 9:38–40
Spagnoli F, Bergamini MC (1997) Water-sediment exchange of nutrients during early diagenesis and resuspension of anoxic sediments from the Northern Adriatic Sea Shelf. Water Air Soil Pollut 99:541–556
Stumm W (1992) Chemistry of the solid–water interface. In: Processes at the mineral-water and particle-water interface in natural systems. Wiley Interscience, New York
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1970) Aquatic Chemistry. An introduction emphasizing chemical equilibria in natural waters. Wiley Intersciences, New York
Sugawara K, Koyama T, Kamata E (1957) Recovery of precipitated phosphate from lake muds related to sulfate reduction. Chem Inst Fac. Sci Nagoya Univ 5:60–67
Sundby B, Gobeil C, Silverberg N, Mucci A (1992) The phosphorus cycle in coastal marine sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 37:1129–1145
Zak D, Kleeberg A, Hupfer M (2006) Sulphate-mediated phosphorus mobilization in reverine sediments at increasing sulphate concentrations, River Spree, NE Germany. Biogeochemistry 80:109–119
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Brittany Region and the French Research Institute for Exploitation of the Sea (IFREMER). We sincerely thank two anonymous reviewers for their insightful critical comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
See Table 5.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andrieux-Loyer, F., Azandegbé, A., Caradec, F. et al. Impact of Oyster Farming on Diagenetic Processes and the Phosphorus Cycle in Two Estuaries (Brittany, France). Aquat Geochem 20, 573–611 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-014-9238-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-014-9238-7