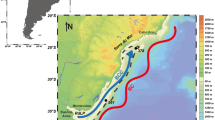
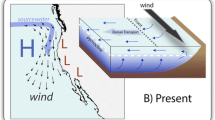
Abstract
Hypoxic conditions in the coastal waters off Texas (USA) were observed since the late 1970s, but little is known about the causes of stratification that contribute to hypoxia formation. Typically, this hypoxia is attributed to downcoast (southwestward) advection of waters from the Mississippi–Atchafalaya River system. Here, we present evidence for a hypoxic event on the inner shelf of Texas coincident with the presence of freshwater linked to high flow of the Brazos River in Texas. These conclusions are based on hydrographic observations and isotopic measurements of waters on the inner shelf near the Brazos River mouth. These data characterize the development, breakdown, and dispersal of a hypoxic event lasting from June through September 2007 off the Texas coast. Oxygen isotope compositions of shelf water indicate that (1) discharge from the Brazos River was the principal source of freshwater and water column stratification during the 2007 event, and (2) during low Brazos River discharge in 2008, freshwater on the Texas shelf was derived mainly from the Mississippi–Atchafalaya River System. Based on these findings, we conclude that the Mississippi–Atchafalaya River System is not the sole cause of hypoxia in the northern Gulf of Mexico; however, more data are needed to determine the relative influence of the Texas versus Mississippi rivers during normal and low flow conditions of Texas rivers.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belabbassi L (2006) Examination of the relationship of river water to occurrences of bottom water with reduced oxygen concentration in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Ph.D. dissertation, Texas A&M University, College Station
Bianchi TS, DiMarco SF, Cowan JH Jr, Hetland RD, Chapman P, Day JW, Allison MA (2010) The science of hypoxia in the northern Gulf of Mexico: a review. Sci Total Environ 408(7):1471–1484
Boesch DF (2002) Challenges and opportunities for science in reducing nutrient over-enrichment of coastal ecosystems. Estuaries 25(4B):886–900
Cho K, Reid RO, Nowlin WD Jr (1998) Objectively mapped stream function fields on the Texas-Louisiana shelf based on 32 months of moored current meter data. J Geophys Res 103(C5):10377–10390
Conley DL, Paerl HW, Howarth RW, Boesch DF, Seitzinger SP, Havens KE, Lancelot C, Likens GE (2009) Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 323(5917):1014–1015
Cooper LW, Benner R, McClelland JW, Peterson BJ, Holmes RM, Raymond PA, Hansell DA, Grebmeier JM, Grebmeier JM, Codispoti LA (2005) Linkages among runoff, dissolved organic carbon, and the stable oxygen isotope composition of seawater and other water mass indicators in the Arctic Ocean. J Geophys Res 110(G2):GO2013. doi:10.1029/2005JG000031
Coplen TB, Kendall C (2000) Stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios for selected sites of the U.S. Geological Survey’s NASQAN and benchmark surface-water networks. Open-file report, USGS
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in precipitation. Science 133:1702–1703
Dale VH et al (2010) Hypoxia in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Springer series on environmental management. Springer, New York
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16(436):468
Diaz RJ, Rosenberg R (1995) Marine benthic hypoxia: a review of its ecological effects and the behavioral responses of benthic macrofauna. Ocean Mar Biol Ann Rev 33:245–303
Diaz RJ, Rosenberg R (2008) Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 321:926–929
DiMarco SF, Howard MK, Reid RO (2000) Seasonal variation of wind-driven diurnal cycling on the Texas-Louisiana continental shelf. Geophys Res Lett 21(7):1017–1020
DiMarco SF, Chapman P, Hetland RD, Walker ND (2010) Does local topography control hypoxia on the Louisiana shelf? J Mar Sci 80(1–2):25–35
Dinnel SP, Wiseman WJ Jr (1986) Fresh water on the Louisiana and Texas Shelf. Cont Shelf Res 6(6):765–784
Etter PC, Howard MK, Cochrane JD (2004) Heat and freshwater budgets of the Texas-Louisiana Shelf. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2003JC001820
Harper DE Jr, McKinney LD, Nance JM, Salzer RR (1991) Recovery responses of two benthic assemblages following an acute hypoxic event on the Texas continental shelf, northwestern Gulf of Mexico. From Tyson RV, Pearson TH (eds) Modern and ancient continental shelf anoxia. Geological Society, London, Special Publication no. 58, pp 49–64
Harper DE, Guillen GJ (1989) Occurrence of a dinoflagellate bloom associated with low salinity water off Galveston, Texas and coincident mortalities of demersal fish and benthic invertebrates. Contrib Mar Sci 31:147–161
Harper DE Jr, Salzer RR, Case RJ (1981) The occurrence of hypoxic bottom water off the upper Texas coast and its effect on the benthic biota. Contrib Mar Sci 24:53–79
Hetland RD, DiMarco SF (2008) The effects of bottom oxygen demand in controlling the structure of hypoxia on the Texas-Louisiana continental shelf. J Mar Syst 70:49–62
Hyeong K, Lawrence JR (2003) Hydrology of the Gulf intra-coastal waterway in the San Bernard-BR estuaries, Texas, USA: Oxygen isotopic ratio and salinity. Geosci J 7(1):27–35
Kendall C, Coplen TB (2001) Distribution of 18O and deuterium in river waters across the United States. Hydrol Process 15:1363–1393
Kiselkova V (2008) Effects of instabilities in the buoyancy-driven flow on the bottom oxygen: applications to the Louisiana Shelf. Ph.D., dissertation. Texas A&M University, College Station
Lee DH, Veizer J (2003) Water and carbon cycles in the Mississippi River basin: potential implications for the Northern Hemisphere residual terrestrial sink. Glob Biogeochem Cycle 17(2):1037
Mackenzie FT, Mucci A, Luther III, GW (2011) Preface to John W. Morse special issue of aquatic geochemistry. Aquat Geochem 17:307–310
McInnes A, Quigg AS (2011) Near-annual fish kills in small embayments: casual vs. causal factors. Journal of Coastal Research (in press)
Mullins, RL, DiMarco SF, Guinasso NL Jr (2010) Innovative environmental sampling during the summer of 2010 in the western Gulf of Mexico. OCEANS 2010, Washington State Conference and Trade Center (WSCTC), 20–23 Sept 2010, Seattle. OCEANS-IEEE, 2010
Mullins RL, DiMarco SF, Walpert J, Guinasso NL Jr (Sept 2009) Real-time environmental monitoring from a wind farm platform in the Texas hypoxia zone. In: Proceedings of oceans 2009 marine technology society. 11 pp
Mullins RL, DiMarco SF, Walpert J, Guinasso NL Jr (2011) Interdisciplinary ocean observing on the Texas Coast. Marine Tech Soc J 45(1):98–111
Nowlin WD Jr, Jochens AE, DiMarco SF, Reid RO, Howard MK (2005) Low-frequency circulation over the Texas-Louisiana continental shelf. In: Sturges W, Lugo-Fernandez A (ed) Circulation in the Gulf of Mexico: Observations and Models. American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, pp 219–240
Osterman LE (2003) Benthic foraminifers from the continental shelf and slope of the Gulf of Mexico: an indicator of shelf hypoxia. Estuar Coastal Shelf Sci 58:17–35
Pokryfki L, Randall RE (1987) Nearshore hypoxia in the bottom water of the northwestern Gulf of Mexico from 1981 to 1984. Mar Environ Res 22(1):75–90
Rabalais NN, Turner RE, Scavia D (2002) Beyond science into policy: Gulf of Mexico hypoxia and the Mississippi River. Bioscience 52:129–142
Rabalais NN, Turner RE, Sen Gupta BK, Boesch DF, Chapman P, Murrell MC (2007) Characterization and long-term trends of hypoxia in the northern Gulf of Mexico: does the science support the action plan? Estuar Coasts 30:753–772
Rabalais NN, Turner RE, Wiseman WJ Jr (2001) Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico. J Environ Qual 30(320):329
Strauss J (2010) Stable isotope geochemistry of Gulf of Mexico hypoxia: modern processes and paleontological proxies. Ph.D. dissertation, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, 119 pp
Thronson A, Quigg AS (2008) Fifty-five years of fish kills in Coastal Texas. Estuar Coasts 31:802–813
Torgersen T (1979) Isotopic composition of river runoff on the US East Coast: evaluation of stable isotope versus salinity plots for coastal water mass identification. J Geophys Res 84:3773–3775
Wagner AJ, Slowey NC (2011) Oxygen isotopes in seawater from the Texas-Louisiana shelf. Bull Mar Sci 87. doi:10.5343/bms.2010.1004
Wiseman WJ, Rabalais NN, Turner RE, Dinnel SP, MacNaughton A (1997) Seasonal and interannual variability within the Louisiana coastal current: stratification and hypoxia. J Mar Sys 12:237–248
Yankovsky AE, Chapman DC (1997) A simple theory for the fate of buoyant coastal discharge. J Phys Oceanogr 27(7):1386–1401
Zerai B (2001) Spatial and temperature variability in the stable isotope compositions of waters of the Gulf of Mexico: Louisiana-Texas Shelf and upper slope. M.S. thesis, University of Akron, Akron. 160 pp
Zhang X, DiMarco SF, Smith DC, Howard MK, Jochens AE, Hetland RD (2009) Near-resonant ocean response to sea breeze on a stratified continental shelf. J Phys Oceanogr 39:2137–2155. doi:10.1175/2009JPO4054.1
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a Rapid Response Award by Texas Sea Grant College Program (No. 404538). Partial funding was through a grant to S. DiMarco (NOAA-CSCOR NA06NOS4780198), contribution number NGOMEX-132, and the TAMU Department of Oceanography. Support for the stable isotope analyses was provided by a grant from Texas’ Norman Hackerman Advanced Research Program (No. 010366-0053-2007). The authors thank the dedication of Drs. Matthew Howard, Timothy Dellapena, GERG Marine Technicians, high school students, Scott Hall, Nathaniel Weidner, Josh Andrews, and the cohort of TAMU and TAMUG graduate students for their fortitude and dedication during the August 7, 2007 small boat armada to collect the ocean samples. The authors also thank T. S. Bianchi (TAMU), N. Walker (LSU), A. Quigg (TAMUG), R. Smith (Yale), and M. Fisher (Texas Parks and Wildlife Division) for useful discussions related to this work. The thoughtful comments of four reviewers greatly helped to focus this manuscript. This work is dedicated to the memory of our friend and colleague Professor John W. Morse (Mackenzie et al. 2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DiMarco, S.F., Strauss, J., May, N. et al. Texas Coastal Hypoxia Linked to Brazos River Discharge as Revealed by Oxygen Isotopes. Aquat Geochem 18, 159–181 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-011-9156-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-011-9156-x