Abstract
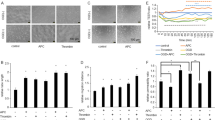
Pigment epithelial-derived factor (PEDF) is a potent anti-angiogenic factor whose effects are partially mediated through the induction of endothelial cell apoptosis. However, the underlying mechanism for PEDF and the functional PEDF peptides 34-mer and 44-mer to inhibit angiogenesis in the heart has not been fully established. In the present study, by constructing adult Sprague–Dawley rat models of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and in vitro myocardial angiogenesis, we showed that PEDF and 34-mer markedly inhibits angiogenesis by selectively inducing tip cells apoptosis rather than quiescent cells. Peptide 44-mer on the other hand exhibits no such effects. Next, we identified Fas death pathway as essential downstream regulators of PEDF and 34-mer activities in inhibiting angiogenesis. By using peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPAR-γ) siRNA and PPAR-γ inhibitor, GW9662, we found the effects of PEDF and 34-mer were extensively blocked. These data suggest that PEDF and 34-mer inhibit angiogenesis via inducing tip cells apoptosis at least by means of up-regulating PPAR-γ to increase surface FasL in the ischemic heart, which might be a novel mechanism to understanding cardiac angiogenesis after AMI.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banai S, Jaklitsch MT, Casscells W, Shou M, Shrivastav S, Correa R et al (1991) Effects of acidic fibroblast growth factor on normal and ischemic myocardium. Circ Res 69:76–85
Pearlman JD, Hibberd MG, Chuang ML, Harada K, Lopez JJ, Gladstone SR et al (1995) Magnetic resonance mapping demonstrates benefits of VEGF-induced myocardial angiogenesis. Nat Med 1:1085–1089
Cai J, Jiang WG, Grant MB, Boulton M (2006) Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits angiogenesis via regulated intracellular proteolysis of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1. J Biol Chem 281:3604–3613
Rychli K, Huber K, Wojta J (2009) Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) as a therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets 13:1295–1302
Kawaguchi T, Yamagishi SI, Sata M (2010) Structure-function relationships of PEDF. Curr Mol Med 10:302–311
Amaral J, Becerra SP (2010) Effects of human recombinant PEDF protein and PEDF-derived peptide 34-mer on choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51:1318–1326
Chuderland D, Ben-Ami I, Kaplan-Kraicer R, Grossman H, Komsky A, Satchi-Fainaro R et al (2013) Hormonal regulation of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) in granulosa cells. Mol Hum Reprod 19:72–81
Ho TC, Chen SL, Yang YC, Liao CL, Cheng HC, Tsao YP (2007) PEDF induces p53-mediated apoptosis through PPAR gamma signaling in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res 76:213–223
Semkova I, Fauser S, Lappas A, Smyth N, Kociok N, Kirchhof B et al (2006) Overexpression of FasL in retinal pigment epithelial cells reduces choroidal neovascularization. FASEB J 20:1689–1691
Weavers H, Skaer H (2013) Tip cells act as dynamic cellular anchors in the morphogenesis of looped renal tubules in Drosophila. Dev Cell 27:331–344
Eichmann A, Thomas JL (2013) Molecular parallels between neural and vascular development. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med 3:a006551
Yao Y, Li L, Huang X, Gu X, Xu Z, Zhang Y et al (2013) SERPINA3K induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells via activating the Fas/FasL/caspase-8 signaling pathway. FEBS J 280:3244–3255
Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM (1995) The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell 83:841–850
Schiffrin EL (2005) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and cardiovascular remodeling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288:H1037–H1043
Wang T, Xu J, Yu X, Yang R, Han ZC (2006) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in malignant diseases. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 58:1–14
Ishibashi Y, Matsui T, Ohta K, Tanoue R, Takeuchi M, Asanuma K et al (2013) PEDF inhibits AGE-induced podocyte apoptosis via PPAR-gamma activation. Microvasc Res 85:54–58
Gao X, Zhang H, Zhuang W, Yuan G, Sun T, Jiang X et al (2014) PEDF and PEDF-derived peptide 44mer protect cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-induced apoptosis and necroptosis via anti-oxidative effect. Sci Rep 4:5637
Zhang H, Wang Z, Feng SJ, Xu L, Shi HX, Chen LL et al (2015) PEDF improves cardiac function in rats with acute myocardial infarction via inhibiting vascular permeability and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci 16:5618–5634
Li TS, Cheng K, Lee ST, Matsushita S, Davis D, Malliaras K et al (2010) Cardiospheres recapitulate a niche-like microenvironment rich in stemness and cell-matrix interactions, rationalizing their enhanced functional potency for myocardial repair. Stem Cells 28:2088–2098
De Smet F, Segura I, De Bock K, Hohensinner PJ, Carmeliet P (2009) Mechanisms of vessel branching: filopodia on endothelial tip cells lead the way. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:639–649
Lu Q, Lu S, Gao X, Luo Y, Tong B, Wei Z et al (2012) Norisoboldine, an alkaloid compound isolated from Radix Linderae, inhibits synovial angiogenesis in adjuvant-induced arthritis rats by moderating Notch1 pathway-related endothelial tip cell phenotype. Exp Biol Med 237:919–932
Bernard A, Gao-Li J, Franco CA, Bouceba T, Huet A, Li Z (2009) Laminin receptor involvement in the anti-angiogenic activity of pigment epithelium-derived factor. J Biol Chem 284:10480–10490
Chen L, Zhang SS, Barnstable CJ, Tombran-Tink J (2006) PEDF induces apoptosis in human endothelial cells by activating p38 MAP kinase dependent cleavage of multiple caspases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348:1288–1295
Li L, Yao YC, Fang SH, Ma CQ, Cen Y, Xu ZM et al (2014) Pigment epithelial-derived factor (PEDF)-triggered lung cancer cell apoptosis relies on p53 protein-driven Fas ligand (Fas-L) up-regulation and Fas protein cell surface translocation. J Biol Chem 289:30785–30799
Bouck N (2002) PEDF: anti-angiogenic guardian of ocular function. Trends Mol Med 8:330–334
Li JK, Liang HL, Li Z, Gu CH, Yi DH, Pei JM (2014) Pigment epithelium-derived factor promotes Fas-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via its receptor phospholipase A2. Life Sci 99:18–23
Bonofiglio D, Gabriele S, Aquila S, Qi H, Belmonte M, Catalano S et al (2009) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activates fas ligand gene promoter inducing apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 113:423–434
Wang X, Huang G, Mei S, Qian J, Ji J, Zhang J (2009) Over-expression of C/EBP-alpha induces apoptosis in cultured rat hepatic stellate cells depending on p53 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 380:286–291
Michailidou Z, Turban S, Miller E, Zou X, Schrader J, Ratcliffe PJ et al (2012) Increased angiogenesis protects against adipose hypoxia and fibrosis in metabolic disease-resistant 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (HSD1)-deficient mice. J Biol Chem 287:4188–4197
Biscetti F, Pecorini G, Arena V, Stigliano E, Angelini F, Ghirlanda G et al (2013) Cilostazol improves the response to ischemia in diabetic mice by a mechanism dependent on PPARgamma. Mol Cell Endocrinol 381:80–87
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (81400227), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (81270173) and Natural Science Foundation for colleges and universities in Jiangsu Province (14KJB320026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Hao Zhang, Tengteng Wei, and Xia Jiang have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Wei, T., Jiang, X. et al. PEDF and 34-mer inhibit angiogenesis in the heart by inducing tip cells apoptosis via up-regulating PPAR-γ to increase surface FasL. Apoptosis 21, 60–68 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1186-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1186-1