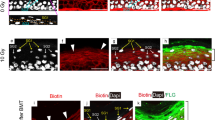
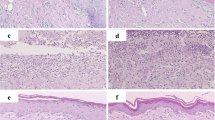
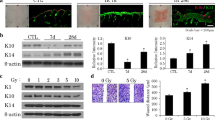
Abstract
In the event of a nuclear disaster, the individuals proximal to the source of radiation will be exposed to combined radiation injury. As irradiation delays cutaneous repair, the purpose of this study was to elucidate the effect of combined radiation and burn injury (CRBI) on apoptosis and inflammation at the site of skin injury. Male C57Bl/6 mice were exposed to no injury, thermal injury only, radiation only (1 and 6 Gy) and CRBI (1 and 6 Gy) and euthanized at various times after for skin collection. TUNEL staining revealed that the CRBI 6 Gy group had a delayed and increased apoptotic response. This correlated with decreased recovery of live cells as compared to the other injuries. Similar response was observed when cleaved-caspase-3 immunohistochemical staining was compared between CRBI 6 Gy and thermal injury. TNFR1, caspase 8, Bax and IL-6 mRNA expression revealed that the higher CRBI group had delayed increase in mRNA expression as compared to thermal injury alone. RIPK1 mRNA expression and necrotic cell counts were delayed in the CRBI 6 Gy group to day 5. TNF-α and NFκB expression peaked in the CRBI 6 Gy group at day 1 and was much higher than the other injuries. Also, inflammatory cell counts in the CRBI 6 Gy group were lower at early time points as compared to thermal injury by itself. These data suggest that CRBI delays and exacerbates apoptosis and inflammation in skin as well as increases necrosis thus resulting in delayed wound healing.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ledney GD, Elliott TB, Moore MM (1992) Modulations of mortality by tissue trauma and sepsis in mice after radiation injury. In: Mossman KL, Mills WA (eds) The biological basis of radiation protection practices. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Kiang JG, Jiao W, Cary LH, Mog SR, Elliott TB, Pellmar TC, Ledney GD (2009) Wound trauma increases radiation-induced mortality by activation of iNOS pathway and elevation of cytokine concentrations and bacterial infection. Radiat Res 173(3):319–332. doi:10.1667/RR1892.1
Ledney GD, Elliott TB (2010) Combined injury: factors with potential to impact radiation dose assessments. Health Phys 98(2):145–152. doi:10.1097/01.HP.0000348466.09978.77
Shah KG, Wu R, Jacob A, Blau SA, Ji Y, Dong W, Marini CP, Ravikumar TS, Coppa GF, Wang P (2009) Human ghrelin ameliorates organ injury and improves survival after radiation injury combined with severe sepsis. Mol Med 15(11–12):407–414. doi:10.2119/molmed.2009.00100
Kiang JG, Ledney GD (2013) Skin injuries reduce survival and modulate corticosterone, C-reactive protein, complement component 3, IgM, and prostaglandin E2 after whole-body reactor-produced mixed field (n + γ-photons) irradiation. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2013:10. doi:10.1155/2013/821541
Alpen EL, Sheline GE (1954) The combined effects of thermal burns and whole body X irradiation on survival time and mortality. Ann Surg 140(1):113–118
Reid JD, Brooks JW, Ham WT, Evans EI (1955) The influence of x-radiation on mortality following thermal flash burns: the site of tissue injury as a factor determining the type of invading bacteria. Ann Surg 142(5):844–850
Baxter H, Drummond JA, Stephens-Newsham LG, Randall RG (1953) Reduction of mortality in swine from combined total body radiation and thermal burns by streptomycin. Ann Surg 137(4):450–455
Jadhav SS, Sharma N, Meeks CJ, Mordwinkin NM, Espinoza TB, Roda NR, DiZerega GS, Hill CK, Louie SG, Rodgers KE (2013) Effects of combined radiation and burn injury on the renin–angiotensin system. Wound Repair Regen 21(1):131–140. doi:10.1111/j.1524-475X.2012.00867.x
Kiang JG, Jiao W, Cary LH, Mog SR, Elliott TB, Pellmar TC, Ledney GD (2010) Wound trauma increases radiation-induced mortality by activation of iNOS pathway and elevation of cytokine concentrations and bacterial infection. Radiat Res 173(3):319–332. doi:10.1667/RR1892.1
Carter SR, Zahs A, Palmer JL, Wang L, Ramirez L, Gamelli RL, Kovacs EJ (2013) Intestinal barrier disruption as a cause of mortality in combined radiation and burn injury. Shock 40(4):281–289. doi:10.1097/SHK.0b013e3182a2c5b5
Fliedner TM, Graessle D, Meineke V, Dörr H (2007) Pathophysiological principles underlying the blood cell concentration responses used to assess the severity of effect after accidental whole-body radiation exposure: an essential basis for an evidence-based clinical triage. Exp Hematol 35(4 Suppl):8–16. doi:10.1016/j.exphem.2007.01.006
Monti P, Wysocki J, van der Meeren A, Griffiths NM (2005) The contribution of radiation-induced injury to the gastrointestinal tract in the development of multi-organ dysfunction syndrome or failure. BJR suppl/BIR 27:89–94. doi:10.1259/bjr/53186341
Muller K, Meineke V (2007) Radiation-induced alterations in cytokine production by skin cells. Exp Hematol 35(4 Suppl 1):96–104. doi:10.1016/j.exphem.2007.01.017
Langley RE, Bump EA, Quartuccio SG, Medeiros D, Braunhut SJ (1997) Radiation-induced apoptosis in microvascular endothelial cells. Br J Cancer 75(5):666–672
Peña LA, Fuks Z, Kolesnick RN (2000) Radiation-induced apoptosis of endothelial cells in the murine central nervous system: protection by fibroblast growth factor and sphingomyelinase deficiency. Cancer Res 60(2):321–327
Schildkopf P, Frey B, Mantel F, Ott OJ, Weiss E-M, Sieber R, Janko C, Sauer R, Fietkau R, Gaipl US (2010) Application of hyperthermia in addition to ionizing irradiation fosters necrotic cell death and HMGB1 release of colorectal tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391(1):1014–1020. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.12.008
Mantel F, Frey B, Haslinger S, Schildkopf P, Sieber R, Ott O, Lödermann B, Rödel F, Sauer R, Fietkau R, Gaipl U (2010) Combination of ionising irradiation and hyperthermia activates programmed apoptotic and necrotic cell death pathways in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Strahlenther Onkol 186(11):587–599. doi:10.1007/s00066-010-2154-x
Stone HB, Coleman CN, Anscher MS, McBride WH (2003) Effects of radiation on normal tissue: consequences and mechanisms. Lancet Oncol 4(9):529–536. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(03)01191-4
Zhou Y, Ni H, Balint K, Sanzari JK, Dentchev T, Diffenderfer ES, Wilson JM, Cengel KA, Weissman D (2014) Ionizing radiation selectively reduces skin regulatory T cells and alters immune function. PLoS ONE 9(6):e100800. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0100800
Takikawa M, Sumi Y, Tanaka Y, Nambu M, Doumoto T, Yanagibayashi S, Azuma R, Yamamoto N, Kishimoto S, Ishihara M, Kiyosawa T (2012) Protective effect of prostaglandin E1 on radiation-induced proliferative inhibition and apoptosis in keratinocytes and healing of radiation-induced skin injury in rats. J Radiat Res 53(3):385–394. doi:10.1269/jrr.11193
Fukumoto R, Cary LH, Gorbunov NV, Lombardini ED, Elliott TB, Kiang JG (2013) Ciprofloxacin modulates cytokine/chemokine profile in serum, improves bone marrow repopulation, and limits apoptosis and autophagy in ileum after whole body ionizing irradiation combined with skin-wound trauma. PLoS ONE 8(3):e58389. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058389
Jung E, Perrone EE, Brahmamdan P, McDonough JS, Leathersich AM, Dominguez JA, Clark AT, Fox AC, Dunne WM, Hotchkiss RS, Coopersmith CM (2013) Inhibition of intestinal epithelial apoptosis improves survival in a murine model of radiation combined injury. PLoS ONE 8(10):e77203. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077203
Paris F, Fuks Z, Kang A, Capodieci P, Juan G, Ehleiter D, Haimovitz-Friedman A, Cordon-Cardo C, Kolesnick R (2001) Endothelial apoptosis as the primary lesion initiating intestinal radiation damage in mice. Science 293(5528):293–297. doi:10.1126/science.1060191
Kiang JG, Garrison BR, Burns TM, Zhai M, Dews IC, Ney PH, Cary LH, Fukumoto R, Elliott TB, Ledney GD (2012) Wound trauma alters ionizing radiation dose assessment. Cell Biosci 2(1):20. doi:10.1186/2045-3701-2-20
Kishi HS (2000) Effects of the “special bomb”: recollections of a neurosurgeon in Hiroshima, August 8–15, 1945. Neurosurgery 47(2):441–445 (discussion 445–446)
Nagata M, Takenaka H, Shibagaki R, Kishimoto S (1999) Apoptosis and p53 protein expression increase in the process of burn wound healing in guinea-pig skin. Br J Dermatol 140(5):829–838. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.1999.02811.x
McNamara AR, Zamba KD, Sokolich JC, Jaskille AD, Light TD, Griffin MA, Meyerholz DK (2010) Apoptosis is differentially regulated by burn severity and dermal location. J Surg Res 162(2):258–263. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2009.01.038
Hsu Y-L, Yu H-S, Lin H-C, Wu K-Y, Yang R-C, Kuo P-L (2011) Heat shock induces apoptosis through reactive oxygen species involving mitochondrial and death receptor pathways in corneal cells. Exp Eye Res 93(4):405–412. doi:10.1016/j.exer.2011.06.005
Mirzaie-Joniani H, Eriksson D, Sheikholvaezin A, Johansson A, Löfroth P-O, Johansson L, Stigbrand T (2002) Apoptosis induced by low-dose and low-dose-rate radiation. Cancer 94(S4):1210–1214. doi:10.1002/cncr.10287
Ding L-H, Shingyoji M, Chen F, Hwang J-J, Burma S, Lee C, Cheng J-F, Chen DJ (2005) Gene expression profiles of normal human fibroblasts after exposure to ionizing radiation: a comparative study of low and high doses. Radiat Res 164(1):17–26. doi:10.1667/RR3354
Goldberg Z, Rocke DM, Schwietert C, Berglund SR, Santana A, Jones A, Lehmann J, Stern R, Lu R, Hartmann Siantar C (2006) Human in vivo dose-response to controlled, low-dose low linear energy transfer ionizing radiation exposure. Clin Cancer Res 12(12):3723–3729. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-05-2625
Otani A, Kojima H, Guo C, Oishi A, Yoshimura N (2012) Low-dose-rate, low-dose irradiation delays neurodegeneration in a model of Retinitis Pigmentosa. Am J Pathol 180(1):328–336. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.09.025
Xing X, Zhang C, Shao M, Tong Q, Zhang G, Li C, Cheng J, Jin S, Ma J, Wang G, Li X, Cai L (2012) Low-dose radiation activates Akt and Nrf2 in the kidney of diabetic mice: a potential mechanism to prevent diabetic nephropathy. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2012:12. doi:10.1155/2012/291087
Calabrese EJ, Calabrese V (2013) Low dose radiation therapy (LD-RT) is effective in the treatment of arthritis: animal model findings. Int J Radiat Biol 89(4):287–294. doi:10.3109/09553002.2013.752595
Mitchel REJ, Hasu M, Bugden M, Wyatt H, Hildebrandt G, Chen YX, Priest ND, Whitman SC (2013) Low-dose radiation exposure and protection against atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− mice: the influence of P53 heterozygosity. Radiat Res 179(2):190–199. doi:10.1667/RR3140.1
Jouan-Lanhouet S, Arshad MI, Piquet-Pellorce C, Martin-Chouly C, Le Moigne-Muller G, Van Herreweghe F, Takahashi N, Sergent O, Lagadic-Gossmann D, Vandenabeele P, Samson M, Dimanche-Boitrel MT (2012) TRAIL induces necroptosis involving RIPK1/RIPK3-dependent PARP-1 activation. Cell Death Differ 19(12):2003–2014. doi:10.1038/cdd.2012.90
Blankenbecler R (2010) Low-dose pretreatment for radiation therapy. Dose-Response 8(4):534–542. doi:10.2203/dose-response.10-033.Blankenbecler
Darby IA, Bisucci T, Hewitson TD, MacLellan DG (1997) Apoptosis is increased in a model of diabetes-impaired wound healing in genetically diabetic mice. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 29(1):191–200. doi:10.1016/S1357-2725(96)00131-8
Brown DL, Kao WWY, Greenhalgh DG (1997) Apoptosis down-regulates inflammation under the advancing epithelial wound edge: delayed patterns in diabetes and improvement with topical growth factors. Surgery 121(4):372–380. doi:10.1016/S0039-6060(97)90306-8
Li F, Huang Q, Chen J, Peng Y, Roop DR, Bedford JS, Li C-Y (2010) Apoptotic cells activate the “Phoenix Rising” pathway to promote wound healing and tissue regeneration. Sci Signal 3(110):ra13. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2000634
Martin P (1997) Wound healing-aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science 276(5309):75–81. doi:10.2307/2892601
Miyamoto Y, Hosotani R, Doi R, Wada M, Ida J, Tsuji S, Kawaguchi M, Nakajima S, Kobayashi H, Masui T, Imamura M (2001) Interleukin-6 inhibits radiation induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Anticancer Res 21(4A):2449–2456
Dent P, Yacoub A, Contessa J, Caron R, Amorino G, Valerie K, Hagan MP, Grant S, Schmidt-Ullrich R (2003) Stress and radiation-induced activation of multiple intracellular signaling pathways. Radiat Res 159(3):283–300
Zhou D, Brown SA, Yu T, Chen G, Barve S, Kang BC, Thompson JS (1999) A high dose of ionizing radiation induces tissue-specific activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in vivo. Radiat Res 151(6):703–709
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2004) Signaling to NF-κB. Genes Dev 18(18):2195–2224. doi:10.1101/gad.1228704
Kim JJ, Lee SB, Park JK, Yoo YD (2010) TNF-[alpha]-induced ROS production triggering apoptosis is directly linked to Romo1 and Bcl-XL. Cell Death Differ 17(9):1420–1434. http://www.nature.com/cdd/journal/v17/n9/suppinfo/cdd201019s1.html
Gu Q, Wang D, Wang X, Peng R, Liu J, Jiang T, Wang Z, Wang S, Deng H (2004) Basic fibroblast growth factor inhibits radiation-induced apoptosis of HUVECs. I. The PI3K/AKT pathway and induction of phosphorylation of BAD. Radiat Res 161(6):692–702. doi:10.1667/RR3158
Epperly MW, Sikora CA, DeFilippi SJ, Gretton JA, Zhan Q, Kufe DW, Greenberger JS (2002) Manganese superoxide dismutase (SOD2) inhibits radiation-induced apoptosis by stabilization of the mitochondrial membrane. Radiat Res 157(5):568–577. doi:10.1667/0033-7587(2002)157[0568:MSDSIR]2.0.CO;2
Vorotnikova E, Rosenthal RA, Tries M, Doctrow SR, Braunhut SJ (2010) Novel synthetic SOD/catalase mimetics can mitigate capillary endothelial cell apoptosis caused by ionizing radiation. Radiat Res 173(6):748–759. doi:10.1667/RR1948.1
Abrahamson S, Bender MA, Conger AD, Wolff S (1973) Uniformity of radiation-induced mutation rates among different species. Nature 245(5426):460–462. doi:10.1038/245460a0
Zawaski JA, Yates CR, Miller DD, Kaffes CC, Sabek OM, Afshar SF, Young DA, Yang Y, Gaber MW (2014) Radiation combined injury models to study the effects of interventions and wound biomechanics. Radiat Res 182(6):640–652. doi:10.1667/RR13751.1
Ran X, Cheng T, Shi C, Xu H, Qu J, Yan G, Su Y, Wang W, Xu R (2004) The effects of total-body irradiation on the survival and skin wound healing of rats with combined radiation-wound injury. J Trauma-Injury Infect Crit Care 57(5):1087–1093
Qu J, Cheng T, Shi C, Yuan Ran X (2004) A study on the activity of fibroblast cells in connection with tissue recovery in the wounds of skin injury after whole-body irradiation. J Radiat Res 45(2):341–344. doi:10.1269/jrr.45.341
Belyakov OV, Prise KM, Trott KR, Michael BD (1999) Delayed lethality, apoptosis and micronucleus formation in human fibroblasts irradiated with X-rays or alpha-particles. Int J Radiat Biol 75(8):985–993. doi:10.1080/095530099139746
Mendonca MS, Mayhugh BM, McDowell B, Chin-Sinex H, Smith ML, Dynlacht JR, Spandau DF, Lewis DA (2005) A radiation-induced acute apoptosis involving TP53 and BAX precedes the delayed apoptosis and neoplastic transformation of CGL1 human hybrid cells. Radiat Res 163(6):614–622. doi:10.1667/RR3387
Moretti L, Cha YI, Niermann KJ, Lu B (2007) Switch between apoptosis and autophagy: radiation-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress? Cell Cycle 6(7):793–798
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health (RC1AI080976). Norma Roda and Rachel Livingston are thanked for their help with tissue processing.
Compliance with ethical standards
This study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jadhav, S.S., Meeks, C.J., Mordwinkin, N.M. et al. Effect of combined radiation injury on cell death and inflammation in skin. Apoptosis 20, 892–906 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1116-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1116-2