Abstract
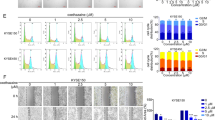
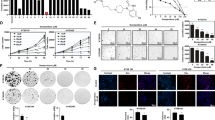
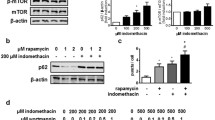
Regular usage of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is associated with reduced incidence of a variety of cancers. The molecular mechanisms underlying these chemopreventive effects remain poorly understood. This current investigation showed that in gastric cancer cells: (1) Indomethacin treatment enhanced the degradation of chromosomal passenger proteins, Survivin and Aurora B kinase; (2) Indomethacin treatment down-regulated Aurora B kinase activity in a cell cycle-independent fashion; (3) siRNA knockdown of Survivin level promoted Aurora B kinase protein degradation, and vice versa; (4) ectopic overexpression of Survivin blocked reduction of Aurora B kinase level and activity by indomethacin treatment, and vice versa; (5) siRNA knockdown of Aurora B kinase level and AZD1152 inhibition of its activity induced apoptosis, and overexpression of Aurora B kinase inhibited indomethacin-induced apoptosis; (6) indomethacin treatment reduced Aurora B kinase level, coinciding with reduction of Survivin level and induction of apoptosis, in KATO III and HT-29 cells, and in mouse gastric mucosa. A role for Aurora B kinase function in NSAID-induced apoptosis was not previously explored. Thus this report provides better understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the anti-cancer effect of NSAIDs by elucidating a significant role for Aurora B kinase in indomethacin-induced apoptosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gurpinar E, Grizzle WE, Piazza GA (2013) COX-independent mechanisms of cancer chemoprevention by anti-inflammatory drugs. Front Oncol 3:181. doi:10.3389/fonc.2013.00181
Farrugia G, Balzan R (2013) The proapoptotic effect of traditional and novel nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in Mammalian and yeast cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:504230. doi:10.1155/2013/504230
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC (1997) A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med 3:917–921
Adida C, Crotty PL, McGrath J, Berrebi D, Diebold J, Altieri DC (1998) Developmentally regulated expression of the novel cancer anti-apoptosis gene survivin in human and mouse differentiation. Am J Pathol 152:43–49
Lehner R, Enomoto T, McGregor JA, Shroyer L, Haugen BR, Pugazhenthi U, Shroyer KR (2002) Correlation of survivin mRNA detection with histologic diagnosis in normal endometrium and endometrial carcinoma. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 81:162–167
Ka H, Hunt JS (2003) Temporal and spatial patterns of expression of inhibitors of apoptosis in human placentas. Am J Pathol 163:413–422
Chiou SK, Moon WS, Jones MK, Tarnawski AS (2003) Survivin expression in the stomach: implications for mucosal integrity and protection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 305:374–379
Velculescu VE, Madden SL, Zhang L, Lash AE, Yu J, Rago C, Lal A, Wang CJ, Beaudry GA, Ciriello KM, Cook BP, Dufault MR, Ferguson AT, Gao Y, He TC, Hermeking H, Hiraldo SK, Hwang PM, Lopez MA, Luderer HF, Mathews B, Petroziello JM, Polyak K et al (1999) Analysis of human transcriptomes. Nat Genet 23:387–388
Lee GH, Joo YE, Koh YS, Chung IJ, Park YK, Lee JH, Kim HS, Choi SK, Rew JS, Park CS, Kim SJ (2006) Expression of survivin in gastric cancer and its relationship with tumor angiogenesis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:957–963
Song KY, Jung CK, Park WS, Park CH (2009) Expression of the antiapoptosis gene Survivin predicts poor prognosis of stage III gastric adenocarcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol 39:290–296
Tu SP, Jiang XH, Lin MC, Cui JT, Yang Y, Lum CT, Zou B, Zhu YB, Jiang SH, Wong WM, Chan AO, Yuen MF, Lam SK, Kung HF, Wong BC (2003) Suppression of survivin expression inhibits in vivo tumorigenicity and angiogenesis in gastric cancer. Cancer Res 63:7724–7732
Deveraux QL, Reed JC (1999) IAP family proteins–suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:239–252
Carmena M, Wheelock M, Funabiki H, Earnshaw WC (2012) The chromosomal passenger complex (CPC): from easy rider to the godfather of mitosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:789–803. doi:10.1038/nrm3474
Vader G, Kauw JJ, Medema RH, Lens SM (2006) Survivin mediates targeting of the chromosomal passenger complex to the centromere and midbody. EMBO Rep 7:85–92
Bolton MA, Lan W, Powers SE, McCleland ML, Kuang J, Stukenberg PT (2002) Aurora B kinase exists in a complex with survivin and INCENP and its kinase activity is stimulated by survivin binding and phosphorylation. Mol Biol Cell 13:3064–3077
Chu Y, Yao PY, Wang W, Wang D, Wang Z, Zhang L, Huang Y, Ke Y, Ding X, Yao X (2011) Aurora B kinase activation requires survivin priming phosphorylation by PLK1. J Mol Cell Biol 3:260–267. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjq037
Crosio C, Fimia GM, Loury R, Kimura M, Okano Y, Zhou H, Sen S, Allis CD, Sassone-Corsi P (2002) Mitotic phosphorylation of histone H3: spatio-temporal regulation by mammalian Aurora kinases. Mol Cell Biol 22:874–885
Wheatley SP, Henzing AJ, Dodson H, Khaled W, Earnshaw WC (2004) Aurora-B phosphorylation in vitro identifies a residue of survivin that is essential for its localization and binding to inner centromere protein (INCENP) in vivo. J Biol Chem 279:5655–5660
Bishop JD, Schumacher JM (2002) Phosphorylation of the carboxyl terminus of inner centromere protein (INCENP) by the Aurora B kinase stimulates Aurora B kinase activity. J Biol Chem 277:27577–27580
Ban R, Matsuzaki H, Akashi T, Sakashita G, Taniguchi H, Park SY, Tanaka H, Furukawa K, Urano T (2009) Mitotic regulation of the stability of microtubule plus-end tracking protein EB3 by ubiquitin ligase SIAH-1 and Aurora mitotic kinases. J Biol Chem 284:28367–28381. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.000273
Portella G, Passaro C, Chieffi P (2011) Aurora B: a new prognostic marker and therapeutic target in cancer. Curr Med Chem 18:482–496
Diaz RJ, Golbourn B, Shekarforoush M, Smith CA, Rutka JT (2012) Aurora kinase B/C inhibition impairs malignant glioma growth in vivo. J Neurooncol 108:349–360. doi:10.1007/s11060-012-0835-2
Chiou SK, Tanigawa T, Akahoshi T, Abdelkarim B, Jones MK, Tarnawski AS (2005) Survivin: a novel target for indomethacin-induced gastric injury. Gastroenterology 128:63–73
Chiou SK, Mandayam S (2007) NSAIDs enhance proteasomic degradation of survivin, a mechanism of gastric epithelial cell injury and apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 74:1485–1495
Chiou SK, Hodges A, Hoa N (2010) Suppression of growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible 45alpha expression confers resistance to sulindac and indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 334:693–702
Mima S, Tsutsumi S, Ushijima H, Takeda M, Fukuda I, Yokomizo K, Suzuki K, Sano K, Nakanishi T, Tomisato W, Tsuchiya T, Mizushima T (2005) Induction of claudin-4 by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and its contribution to their chemopreventive effect. Cancer Res 65:1868–1876
Bonin AM, Yáñez JA, Fukuda C, Teng XW, Dillon CT, Hambley TW, Lay PA, Davies NM (2010) Inhibition of experimental colorectal cancer and reduction in renal and gastrointestinal toxicities by copper-indomethacin in rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 66:755–764
Chiou SK, Hoa N, Hodges A (2011) Sulindac sulfide induces autophagic death in gastric epithelial cells via survivin down-regulation: a mechanism of NSAIDs-induced gastric injury. Biochem Pharmacol 81:1317–1323
Tarnawski A, Pai R, Chiou SK, Chai J, Chu EC (2005) Rebamipide inhibits gastric cancer growth by targeting survivin and Aurora-B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334:207–212
Mortlock AA, Foote KM, Heron NM, Jung FH, Pasquet G, Lohmann JJ, Warin N, Renaud F, De Savi C, Roberts NJ, Johnson T, Dousson CB, Hill GB, Perkins D, Hatter G, Wilkinson RW, Wedge SR, Heaton SP, Odedra R, Keen NJ, Crafter C, Brown E, Thompson K, Brightwell S, Khatri L, Brady MC, Kearney S, McKillop D, Rhead S, Parry T, Green S (2007) Discovery, synthesis, and in vivo activity of a new class of pyrazoloquinazolines as selective inhibitors of aurora B kinase. J Med Chem 50:2213–2224
Hadj-Slimane R, Pamonsinlapatham P, Herbeuval JP, Garbay C, Lepelletier Y, Raynaud F (2010) RasV12 induces Survivin/Aurora B pathway conferring tumor cell apoptosis resistance. Cell Signal 22:1214–1221
van der Waal MS, Hengeveld RC, van der Horst A, Lens SM (2012) Cell division control by the chromosomal passenger complex. Exp Cell Res 318:1407–1420
Cimini D, Wan X, Hirel CB, Salmon ED (2006) Aurora kinase promotes turnover of kinetochore microtubules to reduce chromosome segregation errors. Curr Biol 16:1711–1718
Lampson MA, Renduchitala K, Khodjakov A, Kapoor TM (2004) Correcting improper chromosome-spindle attachments during cell division. Nat Cell Biol 6:232–237
Manchado E, Guillamot M, Malumbres M (2012) Killing cells by targeting mitosis. Cell Death Differ 19:369–377
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by a Department of Veterans Administration Merit Review Grant, and by SCIRE Small grant to S.-K.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiou, SK., Hoa, N., Hodges, A. et al. Indomethacin promotes apoptosis in gastric cancer cells through concomitant degradation of Survivin and Aurora B kinase proteins. Apoptosis 19, 1378–1388 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1002-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1002-3