Abstract
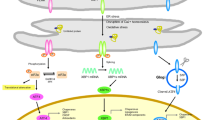
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress has been implicated in the pathophysiology of many diseases including heart disease, cancer and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s. Prolonged or excessive ER stress results in the initiation of signaling pathways resulting in cell death. Over the past decade much research investigating the onset and progression of ER stress-induced cell death has been carried out. Owing to this we now have a better understanding of the signaling pathways leading to ER stress-mediated cell death and have begun to appreciate the importance of ER localized stress sensors, IRE1α, ATF6 and PERK in this process. In this article we provide an overview of the current thinking and concepts concerning the various stages of ER stress-induced cell death, focusing on the role of ER localized proteins in sensing and triggering ER stress-induced death signals with particular emphasis on the contribution of calcium signaling and Bcl-2 family members to the execution phase of this process. We also highlight new and emerging directions in ER stress-induced cell death research particularly the role of microRNAs, ER-mitochondria cross talk and the prospect of mitochondria-independent death signals in ER stress-induced cell death.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Hendershot LM, Harding HP, Ron D (2000) Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell Biol 2(6):326–332
Ye J, Rawson RB, Komuro R, Chen X, Davé UP, Prywes R, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (2000) ER stress induces cleavage of membrane-bound ATF6 by the same proteases that process SREBPs. Mol Cell 6(6):1355–1364. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00133-7
Wang XZ, Harding HP, Zhang Y, Jolicoeur EM, Kuroda M, Ron D (1998) Cloning of mammalian Ire1 reveals diversity in the ER stress responses. EMBO J 17(19):5708–5717
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T, Mori K (2001) XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 107(7):881–891
Lin JH, Li H, Yasumura D, Cohen HR, Zhang C, Panning B, Shokat KM, LaVail MM, Walter P (2007) IRE1 signaling affects cell fate during the unfolded protein response. Science 318(5852):944–949. doi:10.1126/science.1146361
Kurata M, Yamazaki Y, Kanno Y, Ishibashi S, Takahara T, Kitagawa M, Nakamura T (2011) Anti-apoptotic function of Xbp1 as an IL-3 signaling molecule in hematopoietic cells. Cell Death Dis 10(2):e118. doi:10.1038/cddis
Gomez BP, Riggins RB, Shajahan AN, Klimach U, Wang A, Crawford AC, Zhu Y, Zwart A, Wang M, Clarke R (2007) Human X-Box binding protein-1 confers both estrogen independence and antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer cell lines. FASEB J 21(14):4013–4027
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Chung P, Harding HP, Ron D (2000) Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science 287(5453):664–666
Yamamoto K, Ichijo H, Korsmeyer SJ (1999) BCL-2 Is phosphorylated and inactivated by an ASK1/Jun N-terminal protein kinase pathway normally activated at G2/M. Mol Cell Biol 19(12):8469–8478
Donovan N, Becker EBE, Konishi Y, Bonni A (2002) JNK phosphorylation and activation of BAD couples the stress-activated signaling pathway to the cell death machinery. J Biol Chem 277(43):40944–40949. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206113200
Lei K, Davis RJ (2003) JNK phosphorylation of Bim-related members of the Bcl2 family induces Bax-dependent apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(5):2432–2437
Maundrell K, Antonsson B, Magnenat E, Camps M, Muda M, Chabert C, Gillieron C, Boschert U, Vial-Knecht E, Martinou J-C, Arkinstall S (1997) Bcl-2 undergoes phosphorylation by c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinases in the presence of the constitutively active GTP-binding protein Rac1. J Biol Chem 272(40):25238–25242. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.40.25238
Hu P, Han Z, Couvillon AD, Kaufman RJ, Exton JH (2006) Autocrine tumor necrosis factor alpha links endoplasmic reticulum stress to the membrane death receptor pathway through IRE1α-mediated NF-κB activation and down-regulation of TRAF2 expression. Mol Cell Biol 26(8):3071–3084. doi:10.1128/mcb.26.8.3071-3084.2006
Yang Q, Kim YS, Lin Y, Lewis J, Neckers L, Liu ZG (2006) Tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced activation of the MAP kinase JNK. EMBO Rep 7(6):622–627
Hollien J, Weissman JS (2006) Decay of endoplasmic reticulum-localized mRNAs during the unfolded protein response. Science 313(5783):104–107. doi:10.1126/science.1129631
Han D, Lerner AG, Walle LV, Upton JP, Xu W, Hagen A, Backes BJ, Oakes SA, Papa FR (2009) IRE1α kinase activation modes control alternate endoribonuclease outputs to determine divergent cell fates. Cell 138(3):562–575
Woehlbier U, Hetz C (2011) Modulating stress responses by the UPRosome: a matter of life and death. Trends Biochem Sci 36(6):329–337
Hetz C, Bernasconi P, Fisher J, Lee AH, Bassik MC, Antonsson B, Brandt GS, Iwakoshi NN, Schrinzel A, Glimcher LH, Korsmeyer SJ (2006) Proapoptotic BAX and BAK modulate the unfolded protein response by a direct interaction with IRE1α. Science 312(5773):572–576
Rong J, Chen L, Toth JI, Tcherpakov M, Petroski MD, Reed JC (2011) Bifunctional apoptosis regulator (BAR), an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated E3 ubiquitin ligase, modulates BI-1 protein stability and function in ER stress. J Biol Chem 286(2):1453–1463. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.175232
Rodriguez DA, Zamorano S, Lisbona F, Rojas-Rivera D, Urra H, Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Armisen R, Henriquez DR, Cheng HE, Letek M, Vaisar T, Irrazabal T, Gonzalez-Billault C, Letai A, Pimentel-Muinos FX, Kroemer G, Hetz C (2012) BH3-only proteins are part of a regulatory network that control the sustained signalling of the unfolded protein response sensor IRE1[alpha]. EMBO J 31(10):2322–2335
Gupta S, Deepti A, Deegan S, Lisbona F, Hetz C, Samali A (2010) HSP72 protects cells from ER stress-induced apoptosis via enhancement of IRE1α-XBP1 signaling through a physical interaction. PLoS Biol 8(7):e1000410. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000410
Harding HP, Zhang Y, Ron D (1999) Protein translation and folding are coupled by an endoplasmic-reticulum-resident kinase. Nature 397(6716):271–274
Harding HP, Novoa I, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Wek R, Schapira M, Ron D (2000) Regulated translation initiation controls stress-induced gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell 6(5):1099–1108
Scheuner D, Song B, McEwen E, Liu C, Laybutt R, Gillespie P, Saunders T, Bonner-Weir S, Kaufman RJ (2001) Translational control is required for the unfolded protein response and in vivo glucose homeostasis. Mol Cell 7(6):1165–1176
Lu PD, Harding HP, Ron D (2004) Translation reinitiation at alternative open reading frames regulates gene expression in an integrated stress response. J Cell Biol 167(1):27–33. doi:10.1083/jcb.200408003
Harding HP, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Novoa I, Lu PD, Calfon M, Sadri N, Yun C, Popko B, Paules R, Stojdl DF, Bell JC, Hettmann T, Leiden JM, Ron D (2003) An integrated stress response regulates amino acid metabolism and resistance to oxidative stress. Mol Cell 11(3):619–633. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00105-9
Oyadomari S, Mori M (2003) Roles of CHOP//GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ 11(4):381–389
Puthalakath H, O’Reilly LA, Gunn P, Lee L, Kelly PN, Huntington ND, Hughes PD, Michalak EM, McKimm-Breschkin J, Motoyama N, Gotoh T, Akira S, Bouillet P, Strasser A (2007) ER stress triggers apoptosis by activating BH3-only protein BIM. Cell 129(7):1337–1349. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.027
Ghosh AP, Klocke BJ, Ballestas ME, Roth KA (2012) CHOP potentially co-operates with FOXO3a in neuronal cells to regulate PUMA and BIM expression in response to ER stress. PLoS ONE 7(6):e39586. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039586
Cazanave SC, Elmi NA, Akazawa Y, Bronk SF, Mott JL, Gores GJ (2010) CHOP and AP-1 cooperatively mediate PUMA expression during lipoapoptosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 299(1):G236–G243. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00091.2010
McCullough KD, Martindale JL, Klotz LO, Aw TY, Holbrook NJ (2001) Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress by down-regulating Bcl2 and perturbing the cellular redox state. Mol Cell Biol 21(4):1249–1259
Marciniak SJ, Yun CY, Oyadomari S, Novoa I, Zhang Y, Jungreis R, Nagata K, Harding HP, Ron D (2004) CHOP induces death by promoting protein synthesis and oxidation in the stressed endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev 18(24):3066–3077
Li G, Mongillo M, Chin KT, Harding H, Ron D, Marks AR, Tabas I (2009) Role of ERO1-α-mediated stimulation of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor activity in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biol 186(6):783–792
Ohoka N, Yoshii S, Hattori T, Onozaki K, Hayashi H (2005) TRB3, a novel ER stress-inducible gene, is induced via ATF4-CHOP pathway and is involved in cell death. EMBO J 24(6):1243–1255
Du K, Herzig S, Kulkarni RN, Montminy M (2003) TRB3: a tribbles homolog that inhibits Akt/PKB activation by insulin in liver. Science 300(5625):1574–1577
Zou CG, Cao XZ, Zhao YS, Gao SY, Li SD, Liu XY, Zhang Y, Zhang KQ (2009) The molecular mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in PC-12 neuronal cells: the protective effect of insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology 150(1):277–285
Novoa I, Zeng H, Harding HP, Ron D (2001) Feedback inhibition of the unfolded protein response by GADD34-mediated dephosphorylation of eIF2α. J Cell Biol 153(5):1011–1021
Boyce M, Bryant KF, Jousse C, Long K, Harding HP, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Ma D, Coen DM, Ron D, Yuan J (2005) A selective inhibitor of elF2α dephosphorylation protects cells from ER stress. Science 307(5711):935–939
Adachi Y, Yamamoto K, Okada T, Yoshida H, Harada A, Mori K (2008) ATF6 is a transcription factor specializing in the regulation of quality control proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Struct Funct 33(1):75–89
Yoshida H, Okada T, Haze K, Yanagi H, Yura T, Negishi M, Mori K (2000) ATF6 activated by proteolysis binds in the presence of NF-Y (CBF) directly to the cis-acting element responsible for the mammalian unfolded protein response. Mol Cell Biol 20(18):6755–6767
Morishima N, Nakanishi K, Nakano A (2011) Activating transcription factor-6 (ATF6) mediates apoptosis with reduction of myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1 (Mcl-1) protein via induction of WW domain binding protein. J Biol Chem 286(40):35227–35235
Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, Smith BJ, Fletcher JI, Hinds MG, Colman PM, Day CL, Adams JM, Huang DCS (2005) Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Mol Cell 17(3):393–403
Letai A, Bassik MC, Walensky LD, Sorcinelli MD, Weiler S, Korsmeyer SJ (2002) Distinct BH3 domains either sensitize or activate mitochondrial apoptosis, serving as prototype cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell 2(3):183–192. doi:10.1016/s1535-6108(02)00127-7
Li J, Lee B, Lee AS (2006) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis: multiple pathways and activation of p53-UP-regulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) and NOXA by p53. J Biol Chem 281(11):7260–7270
Lin W-C, Chuang Y-C, Chang Y-S, Lai M-D, Teng Y-N, Su I-J, Wang CCC, Lee K-H, Hung J-H (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum stress stimulates p53 expression through NF-κB activation. PLoS ONE 7(7):e39120. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039120
Deng J, Lu PD, Zhang Y, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Sonenberg N, Harding HP, Ron D (2004) Translational repression mediates activation of nuclear factor kappa B by phosphorylated translation initiation factor 2. Mol Cell Biol 24(23):10161–10168
Kaneko M, Niinuma Y, Nomura Y (2003) Activation signal of nuclear factor-κB in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress is transduced via IRE1 and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2. Biol Pharm Bull 26(7):931–935
Yamazaki H, Hiramatsu N, Hayakawa K, Tagawa Y, Okamura M, Ogata R, Huang T, Nakajima S, Yao J, Paton AW, Paton JC, Kitamura M (2009) Activation of the Akt-NF-κB pathway by subtilase cytotoxin through the ATF6 branch of the unfolded protein response. J Immunol 183(2):1480–1487
Futami T, Miyagishi M, Taira K (2005) Identification of a network involved in thapsigargin-induced apoptosis using a library of small interfering RNA expression vectors. J Biol Chem 280(1):826–831
Heath-Engel HM, Chang NC, Shore GC (2008) The endoplasmic reticulum in apoptosis and autophagy: role of the BCL-2 protein family. Oncogene 27(50):6419–6433
Szegezdi E, MacDonald DC, Chonghaile TN, Gupta S, Samali A (2009) Bcl-2 family on guard at the ER. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296(5):C941–C953
Gaut JR, Hendershot LM (1993) The modification and assembly of proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Curr Opin Cell Biol 5(4):589–595
Chen R, Valencia I, Zhong F, McColl KS, Roderick HL, Bootman MD, Berridge MJ, Conway SJ, Holmes AB, Mignery GA, Velez P, Distelhorst CW (2004) Bcl-2 functionally interacts with inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors to regulate calcium release from the ER in response to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. J Cell Biol 166(2):193–203
White C, Li C, Yang J, Petrenko NB, Madesh M, Thompson CB, Foskett JK (2005) The endoplasmic reticulum gateway to apoptosis by Bcl-XL modulation of the InsP3R. Nat Cell Biol 7(10):1021–1028
Zong WX, Li C, Hatzivassiliou G, Lindsten T, Yu QC, Yuan J, Thompson CB (2003) Bax and Bak can localize to the endoplasmic reticulum to initiate apoptosis. J Cell Biol 162(1):59–69
Pinton P, Ferrari D, Magalhaes P, Schulze-Osthoff K, Di Virgilio F, Pozzan T, Rizzuto R (2000) Reduced loading of intracellular Ca2 + stores and downregulation of capacitative Ca2 + influx in Bcl-2-overexpressing cells. J Cell Biol 148(5):857–862
Bassik MC, Scorrano L, Oakes SA, Pozzan T, Korsmeyer SJ (2004) Phosphorylation of BCL-2 regulates ER Ca2 + homeostasis and apoptosis. EMBO J 23(5):1207–1216
Chae HJ, Kim HR, Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B, Krajewska M, Krajewski S, Banares S, Cui J, Digicaylioglu M, Ke N, Kitada S, Monosov E, Thomas M, Kress CL, Babendure JR, Tsien RY, Lipton SA, Reed JC (2004) BI-1 regulates an apoptosis pathway linked to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell 15(3):355–366
Bailly-Maitre B, Fondevila C, Kaldas F, Droin N, Luciano F, Ricci JE, Croxton R, Krajewska M, Zapata JM, Kupiec-Weglinski JW, Farmer D, Reed JC (2006) Cytoprotective gene bi-1 is required for intrinsic protection from endoplasmic reticulum stress and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(8):2809–2814
Oakes SA, Scorrano L, Opferman JT, Bassik MC, Nishino M, Pozzan T, Korsmeyer SJ (2005) Proapoptotic BAX and BAK regulate the type 1 inositol trisphosphate receptor and calcium leak from the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(1):105–110
Wang X, Olberding KE, White C, Li C (2011) Bcl-2 proteins regulate ER membrane permeability to luminal proteins during ER stress-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 18(1):38–47
Mathai JP, Germain M, Shore GC (2005) BH3-only BIK regulates BAX, BAK-dependent release of Ca2 + from endoplasmic reticulum stores and mitochondrial apoptosis during stress-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 280(25):23829–23836
Reimertz C, Kögel D, Rami A, Chittenden T, Prehn JHM (2003) Gene expression during ER stress-induced apoptosis in neurons: induction of the BH3-only protein Bbc3/PUMA and activation of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. J Cell Biol 162(4):587–597
Luo X, He Q, Huang Y, Sheikh MS (2005) Transcriptional upregulation of PUMA modulates endoplasmic reticulum calcium pool depletion-induced apoptosis via Bax activation. Cell Death Differ 12(10):1310–1318
Grimm S (2012) The ER-mitochondria interface: the social network of cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta 1823(2):327–334
Szabadkai G, Bianchi K, Várnai P, De Stefani D, Wieckowski MR, Cavagna D, Nagy AI, Balla T, Rizzuto R (2006) Chaperone-mediated coupling of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial Ca2 + channels. J Cell Biol 175(6):901–911
Hayashi T, Su TP (2007) Sigma-1 receptor chaperones at the ER-mitochondrion interface regulate Ca2 + signaling and cell survival. Cell 131(3):596–610
Chami M, Oulès B, Szabadkai G, Tacine R, Rizzuto R, Paterlini-Bréchot P (2008) Role of SERCA1 truncated isoform in the proapoptotic calcium transfer from ER to mitochondria during ER stress. Mol Cell 32(5):641–651. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.11.014
Verfaillie T, Rubio N, Garg AD, Bultynck G, Rizzuto R, Decuypere JP, Piette J, Linehan C, Gupta S, Samali A, Agostinis P (2012) PERK is required at the ER-mitochondrial contact sites to convey apoptosis after ROS-based ER stress. Cell Death Differ 11:1880–1891. doi:10.1038/cdd.2012.74
Samali A, Gupta S, Cuffe L, Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Neary C, Healy S (2010) Mechanisms of ER stress-mediated mitochondrial membrane permeabilization. Int J Cell Biol 2010:830307–830318. doi:10.1155/2010/830307
Shimizu S, Kanaseki T, Mizushima N, Mizuta T, Arakawa-Kobayashi S, Thompson CB, Tsujimoto Y (2004) Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in a non-apoptopic programmed cell death dependent on autophagy genes. Nat Cell Biol 6(12):1221–1228
Buytaert E, Callewaert G, Vandenheede JR, Agostinis P (2006) Deficiency in apoptotic effectors Bax and Bak reveals an autophagic cell death pathway initiated by photodamage to the endoplasmic reticulum. Autophagy 2(3):238–240
Ullman E, Fan Y, Stawowczyk M, Chen HM, Yue Z, Zong WX (2008) Autophagy promotes necrosis in apoptosis-deficient cells in response to ER stress. Cell Death Differ 15(2):422–425
Yang F, Zhang L, Wang F, Wang Y, Huo X, Yin Y, Sun SH (2011) Modulation of the unfolded protein response is the core of microRNA-122-involved sensitivity to chemotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma 1,2. Neoplasia 13(7):590–600
Dai R, Li J, Liu Y, Yan D, Chen S, Duan C, Liu X, He T, Li H (2010) MiR-221/222 suppression protects against endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis via p27 Kip1- and MEK/ERK-mediated cell cycle regulation. Biol Chem 391(7):791–801
Byrd AE, Aragon IV, Brewer JW (2012) MicroRNA-30c-2* limits expression of proadaptive factor XBP1 in the unfolded protein response. J Cell Biol 196(6):689–698
Gupta S, Read DE, Deepti A, Cawley K, Gupta A, Oommen D, Verfaillie T, Matus S, Smith MA, Mott JL, Agostinis P, Hetz C, Samali A (2012) Perk-dependent repression of miR-106b-25 cluster is required for ER stress-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Dis 3:e333. doi:10.1038/cddis.2012.74
Chitnis NS, Pytel D, Bobrovnikova-Marjon E, Pant D, Zheng H, Maas NL, Frederick B, Kushner J, Chodosh L, Koumenis C, Fuchs S, Diehl J (2012) miR-211 Is a prosurvival MicroRNA that regulates chop expression in a PERK-dependent manner. Mol Cell 48(3):353–364. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2012.08.025
Acknowledgments
Our research is supported by grants from Science Foundation Ireland (09/RFP/BIC2371), Breast Cancer Campaign (2010NovPR13). P Cleary is funded by an Irish Cancer Society Scholarship (CRS11CLE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Logue, S.E., Cleary, P., Saveljeva, S. et al. New directions in ER stress-induced cell death. Apoptosis 18, 537–546 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0818-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0818-6