Abstract
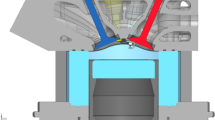
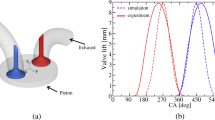
The dynamics and evolution of the turbulent flow inside an experimentally investigated engine-like geometry consisting of a flat-top cylinder head with a fixed, axis-centered valve and low-speed piston were studied numerically by means of Direct Numerical Simulation (DNS) and Large Eddy Simulation (LES), with a particular focus on Cycle-to-Cycle Variability (CCV). DNS was performed by the spectral element code nek5000 on a 58M points grid, whereas LES was carried out by the finite volume software OpenFOAM on a 4.6M hexahedral mesh. Results obtained by DNS and LES are compared with respect to the velocity means and fluctuations, as well with other derived quantities, achieving good agreement between simulations and experiments. The cyclic variability and complex unsteady flow features like the laminar-to-turbulent transition and the evolution of the tumble vortices were studied by time-resolved analysis and Proper Orthogonal Decomposition (POD). Simulations show that during the first half of the intake stroke the flow field is dominated by the dynamics of the incoming jet and the vortex rings it creates. With decreasing piston speed, the large central ring becomes the dominant flow feature until the top dead center. The flow field at the end of the previous cycle is found to have a strong effect on the jet breakup process and the dynamics of the vortex ring below the valve of the subsequent cycle as well as on the observed significant cyclic variations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amsden, A., O’Rourke, P., Butler, T.: KIVA-II: A Computer Program for Chemically Reactive Flows with Sprays. LA 11560-MS. Los Alamos National Laboratory (1989)
Berkooz, G., Holmes, P., Lumley, J.L.: The proper orthogonal decomposition in the analysis of turbulent flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 25(16), 539–575 (1993)
Brusiani, F., Forte, C., Bianchi, G.: Assessment of a Numerical Methodology for Large Eddy Simulation of ICE Wall Bounded Non-Reactive Flows. In: SAE Technical Paper 2007-01-4145 (2007). doi:10.4271/2007-01-4145
Cubit: Cubit. Sandia National Laboratories, Meshing Software (2012)
Deville, M., Fischer, P., Mund, E.: High-order methods for incompressible fluid flow. Cambridge University Press, New York (2002)
Fischer, P.F., Lottes, J.W., Kerkemeier, S.G.: nek5000 web page (2008). http://nek5000.mcs.anl.gov
Fogleman, A.A., Lumley, K., Rempfer, D., Haworth, D.C.: Application of the proper orthogonal decomposition to datasets of internal combustion engine flows. J. Turbul. 5(23), 1–18 (2004)
Garnier, E., Nikolaus, A., Sagaut, P.: Large Eddy Simulation for Compressible Flows, 2009 edn. Springer (2009)
Hasse, C., Sohm, V., Durst, B.: Numerical investigation of cyclic variations in gasoline engines using a hybrid URANS/LES modeling approach. Comput. Fluids 39(1), 25–48 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.compfluid.2009.07.001
Haworth, D.C., Jansen, K.: Large-eddy simulation on unstructured deforming meshes: towards reciprocating IC engines. Comput. Fluids 29, 493–524 (2000)
Liu, K., Haworth, D.C.: Large-eddy simulation for an axisymmetric piston-cylinder assembly with and without swirl. Flow Turbul. Combust. 85, 297–307 (2010). doi:10.1007/s10494-010-9292-1
Liu, K., Haworth, D.C.: Development and assessment of POD for analysis of turbulent flow in piston engines. SAE technical paper 2011-01-0830 (2011)
Montorfano, A., Piscaglia, F., Ferrari, G.: Inlet Boundary Conditions for Incompressible LES: a Comparative Study. Mathematical and Computer Modelling (2011). doi:10.1016/j.mcm.2011.10.077
Montorfano, A., Piscaglia, F., Onorati, A.: An extension of the dynamic mesh handling with topological changes for LES of ICE in OpenFOAM. SAE World Congress & Exhibition 2015, paper n. 2015-01-0384 (2015)
Montorfano, A., Piscaglia, F., Onorati, A.: A LES Study on the Evolution of Turbulent Structures in Moving Engine Geometries by an Open-Source CFD Code. SAE World Congress & Exhibition 2014, paper n. 2014-01-1147 (2014)
Morse, A.P., Whitelaw, J.H., Yanneskis, M.: Turbulent flow measurements by laser-doppler anemometry in motored piston-cylinder assemblies. J. Fluids Eng. 101, 208–216 (1979)
Nicoud, F., Ducros, F.: Subgrid-scale stress modelling based on the square of the velocity gradient tensor. Flow Turbul. Combust. 62, 183–200 (1999). doi:10.1023/A:1009995426001
Piscaglia, F., Montorfano, A., Onorati, A.: A scale adaptive filtering technique for turbulence modeling of unsteady flows in IC engines. SAE Int. J. Engines 8(2), 426–436 (2015). doi:10.4271/2015-01-0395
Piscaglia, F., Montorfano, A., Onorati, A.: Improving the Simulation of the Acoustic Performance of Complex Silencers for ICE by a Multi-Dimensional Non-Linear Approach. SAE Int. J. Engines 2(5), 633–648 (2012). doi:10.4271/2012-01-0828
Piscaglia, F., Montorfano, A., Onorati, A.: Development of a Non-Reflecting Boundary Condition for Multidimensional Nonlinear Duct Acoustic Computation. J. Sound Vib. 332(4), 922–935 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2012.09.030
Piscaglia, F., Montorfano, A., Onorati, A.: Development of Fully-Automatic Parallel Algorithms for Mesh Handling in the OpenFOAM-2.2.x Technology. SAE Technical Paper 2013-24-0027 (2013). doi:10.4271/2013-24-0027
Piscaglia, F., Montorfano, A., Onorati, A.: Towards the LES Simulation of IC Engines with Parallel Topologically Changing Meshes. SAE Int. J. Engines 6(2), 926–940 (2013). doi:10.4271/2013-01-1096
Piscaglia, F., Montorfano, A., Onorati, A., Brusiani, F.: Boundary conditions and sgs models for les of wall-bounded separated flows: An application to engine-like geometries. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. - Rev. IFP Energies nouvelles 69(1), 11–27 (2014). doi:10.2516/ogst/2013143
Pope, S.: Turbulent flows. Cambridge University Press (2000)
Pope, S.: Ten questions concerning the large eddy simulation. New J. Phys. 6, 35 (2004)
Sagaut, P.: Large eddy simulation for incompressible flows: An introduction. Scientific computation. Springer (2006)
Schmitt, M., Frouzakis, C., Tomboulides, A., Wright, Y., Boulouchos, K.: Direct numerical simulation of multiple cycles in a valve/piston assembly. Phys. Fluids 26(3) (2014)
Schmitt, M., Frouzakis, C., Tomboulides, A., Wright, Y., Boulouchos, K.: Direct numerical simulation of the effect of compression on the flow, temperature and composition under engine-like conditions. Proc. Combust. Inst. 35(3), 3069–3077 (2015)
Schmitt, M., Frouzakis, C., Wright, Y., Tomboulides, A., Boulouchos, K.: Investigation of cycle-to-cycle variations in an engine-like geometry. Physics of Fluids 26(12), 125104 (2014)
Sirovich, L.: Turbulence and the dynamic of coherent structures. Q. Appl. Math. 45, 561–590 (1987)
The OpenFOAM Foundation: OpenFOAM web page (2006). http://www.openfoam.org
Thobois, L., Rymer, G., Soulères, T., Poinsot, T.: Large-eddy simulation in IC engine geometries. Sae Pdes of the arbitrarily structured C grid. Mon. Weatheraper n. 2004-01-1854. SAE world Congress & exhibition (2004)
Thobois, L., Rymer, G., Soulères, T., Poinsot, T., den Heuvel, B.V.: Large-eddy simulation for the prediction of aerodynamics in ic engines. In: Int. J. Vehicle Design “New strategies in Automotive Diesel Engines for Meeting Upcoming Pollutant Emission Restrictions” (2005)
Versteeg, H.K., Malalasekera, W.: An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall College Div (2007)
Weller, H.: Controlling the computational modes of the arbitrarily structured C grid. Mon. Weather Rev. 140, 3220–3234 (2012). doi:10.1175/MWR-D-11-00221.1. http://journals.ametsoc.org/doi/pdf/10.1175/MWR-D-11-00221.1
Wollblad, C., Davidson, L., Eriksson, L.E.: Large eddy simulation of transonic flow with shock wave/turbulent boundary layer interaction. AIAA J. 44, 2340–2353 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montorfano, A., Piscaglia, F., Schmitt, M. et al. Comparison of Direct and Large Eddy Simulations of the Turbulent Flow in a Valve/Piston Assembly. Flow Turbulence Combust 95, 461–480 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-015-9620-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-015-9620-6