Abstract
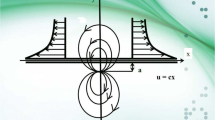
The present research explores the three-dimensional boundary layer flow of the Maxwell nanofluid. The flow is generated by a bidirectional stretching surface. The mathematical formulation is carried out through a boundary layer approach with the heat source/sink, the Brownian motion, and the thermophoresis effects. The newly developed boundary conditions requiring zero nanoparticle mass flux at the boundary are employed in the flow analysis for the Maxwell fluid. The governing nonlinear boundary layer equations through appropriate transformations are reduced to the coupled nonlinear ordinary differential system. The resulting nonlinear system is solved. Graphs are plotted to examine the effects of various interesting parameters on the non-dimensional velocities, temperature, and concentration fields. The values of the local Nusselt number are computed and examined numerically.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Masuda, H., Ebata, A., Teramae, K., and Hishiunma, N. Alteration of thermal conductivity and viscosity of liquid by dispersed ultra-fine particles (dispersion of Al2O3, SiO2 and TiO2 ultra-fine particles). Netsu Bussei, 4, 227–233 (1993)
Choi, S. U. S. and Eastman, J. A. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposisition, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, San Francisco (1995)
Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. Journal of Heat Transfer, 128, 240–250 (2006)
Khan, W. A. and Pop, I. Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 53, 2477–2483 (2010)
Turkyilmazoglu, M. Exact analytical solutions for heat and mass transfer of MHD slip flow in nanofluids. Chemical Engineering Science, 84, 182–187 (2012)
Makinde, O. D., Khan, W. A., and Khan, Z. H. Buoyancy effects on MHD stagnation point flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid past a convectively heated stretching/shrinking sheet. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 62, 526–533 (2013)
Rashidi, M. M., Abelman, S., and Mehr, N. F. Entropy generation in steady MHD flow due to a rotating porous disk in a nanofluid. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 62, 515–525 (2013)
Sheikholeslami, M. and Ganji, D. D. Heat transfer of Cu-water nanofluid flow between parallel plates. Powder Technology, 235, 873–879 (2013)
Mustafa, M., Farooq, M. A., Hayat, T., and Alsaedi, A. Numerical and series solutions for stagnation point flow of nanofluid over an exponentially stretching sheet. PloS One, 8, e61859 (2013)
Kuznetsov, A. V. and Nield, D. A. Natural convective boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate: a revised model. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 77, 126–129 (2014)
Wang, S. and Tan, W. Stability analysis of Soret-driven double-diffusive convection of Maxwell fluid in a porous medium. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 32, 88–94 (2011)
Fetecau, C., Fetecau, C., Jamil, M., and Mahmood, A. Flow of fractional Maxwell fluid between coaxial cylinders. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 81, 1153–1163 (2011)
Hayat, T., Shehzad, S. A., Qasim, M., and Obaidat, S. Steady flow of Maxwell fluid with convective boundary conditions. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A, 66a, 417–422 (2011)
Mukhopadhyay, S. Heat transfer analysis of the unsteady flow of a Maxwell fluid over a stretching surface in the presence of a heat source/sink. Chinese Physics Letters, 29, 054703 (2012)
Abel, M. S., Tawade, V., and Shinde, N. The effects of MHD flow and heat transfer for the UCM fluid over a stretching surface in presence of thermal radiation. Advances in Mathematical Physics, 21, 702681 (2012)
Hayat, T., Shehzad, S. A., Al-Sulami, H. H., and Asghar, S. Influence of thermal stratification on the radiative flow of Maxwell fluid. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 35, 381–389 (2013)
Abbasbandy, S., Hayat, T., Ghehsareh, H. R., and Alsaedi, A. MHD Falkner-Skan flow of Maxwell fluid by rational Chebyshev collocation method. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 34, 921–930 (2013) DOI 10.1007/s10483-013-1717-7
Shehzad, S. A., Alsaedi, A., and Hayat, T. Hydromagnetic steady flow of Maxwell fluid over a bidirectional stretching surface with prescribed surface temperature and prescribed surface heat flux. PloS One, 8, e68139 (2013)
Liao, S. J. Homotopy Analysis Method in Nonlinear Differential Equations, Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Turkyilmazoglu, M. Solution of the Thomas-Fermi equation with a convergent approach. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 17, 4097–4103 (2012)
Rashidi, M. M., Keimanesh, M., and Rajvanshi, S. C. Study of pulsatile flow in a porous annulus with the homotopy analysis method. International Journal of Numerical Methods for Heat & Fluid Flow, 22, 971–989 (2012)
Shehzad, S. A., Alsaedi, A., Hayat, T., and Alhuthali, M. S. Three-dimensional flow of an Oldroyd-B fluid with variable thermal conductivity and heat generation/absorption. PloS One, 8, e78240 (2013)
Abbasbandy, S., Hashemi, M. S., and Hashim, I. On convergence of homotopy analysis method and its application to fractional integro-differential equations. Quaestiones Mathematicae, 36, 93–105 (2013)
Hayat, T., Shehzad, S. A., Alsaedi, A., and Alhothuali, M. S. Three-dimensional flow of Oldroyd-B fluid over surface with convective boundary conditions. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 34, 489–500 (2013) DOI 10.1007/s10483-013-1685-9
Hayat, T., Shehzad, S. A., and Alsaedi, A. Three-dimensional stretched flow of Jeffrey fluid with variable thermal conductivity and thermal radiation. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 34, 823–832 (2013) DOI 10.1007/s10483-013-1710-7
Imtiaz, M., Hayat, T., Hussain, M., Shehzad, S. A., Chen, G. Q., and Ahmad, B. Mixed convection flow of nanofluid with Newtonian heating. The European Physical Journal Plus, 129, 97 (2014)
Hayat, T. and Awais, M. Three-dimensional flow of upper-convected Maxwell (UCM) fluid. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 66, 875–884 (2011)
Harris, J. Rheology and Non-Newtonian Flow, Longman, London (1977)
Schilchting, H. Boundary Layer Theory, McGraw-Hill, New York (1964)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayat, T., Muhammad, T., Shehzad, S.A. et al. Three-dimensional boundary layer flow of Maxwell nanofluid: mathematical model. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 36, 747–762 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-015-1948-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-015-1948-6