Abstract
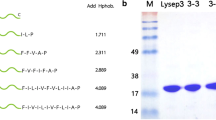
Phage lysins are considered promising antimicrobials against resistant bacterial infections. Some lysins have been reported for the prevention and treatment of Gram-positive bacterial infection. Gram-negative bacterial phage lysins, however, can only destroy the bacterial cell wall from inside because of the obstruction of the bacterial outer membrane that prevents direct hydrolysis of the bacterial wall peptidoglycan from the outside, severely restricting the development of lysins against Gram-negative bacteria. In this study, genetic engineering techniques were used to fuse a 5 cationic amino acid polypeptide (KRKRK), a 10 cationic amino acid polypeptide (KRKRKRKRKR), a 15 cationic amino acid polypeptide (KRKRKRKRKRKRKRK), and a polypeptide including both cationic and hydrophobic amino acids (KRKRKFFVAIIP) to the C-terminus of the Escherichia coli phage lysin Lysep3 to obtain four fusion lysins (5aa, 10aa, 15aa, Mix). The bactericidal effects of those four lysins on E. coli were then compared in vitro. Our results showed that the fusion of hydrophobic and positively charged amino acids, Mix, can kill E. coli effectively; the fusion of positively charged amino acids alone at the C-terminus (5aa, 10aa, 15aa) also showed bactericidal activity against E. coli from the outside, with the bactericidal activity gradually increasing with the positive charge at the C-terminus of the lysin. Collectively, improving the positive charge at the C-terminus of E. coli bacteriophage lysin Lysep3 increases its bactericidal ability from outside E. coli, providing a new practical method for the development of anti-Gram-negative bacterial lysins.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arima H, Ibrahim HR, Kinoshita T, Kato A (1997) Bactericidal action of lysozymes attached with various sizes of hydrophobic peptides to the C-terminal using genetic modification. FEBS Lett 415:114–118
Briers Y, Lavigne R (2015) Breaking barriers: expansion of the use of endolysins as novel antibacterials against Gram-negative bacteria. Future Microbiol 10:377–390
Briers Y, Volckaert G, Cornelissen A, Lagaert S, Michiels CW, Hertveldt K, Lavigne R (2007) Muralytic activity and modular structure of the endolysins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophages phiKZ and EL. Mol Microbiol 65:1334–1344
Briers Y, Schmelcher M, Loessner MJ, Hendrix J, Engelborghs Y, Volckaert G, Lavigne R (2009) The high-affinity peptidoglycan binding domain of Pseudomonas phage endolysin KZ144. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 383:187–191
Briers Y, Walmagh M, Lavigne R (2011) Use of bacteriophage endolysin EL188 and outer membrane permeabilizers against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Appl Microbiol 110:778–785
Briers Y, Walmagh M, Lavigne R (2014) Engineered endolysin-based “Artilysins” to combat multidrug-resistant Gram-negative pathogens. MBio 5:e1314–e1379
Gayoso CM, Mateos J, Mendez JA, Fernandez-Puente P, Rumbo C, Tomas M, Martinez DIO, Bou G (2014) Molecular mechanisms involved in the response to desiccation stress and persistence in Acinetobacter baumannii. J Proteome Res 13:460–476
Gerstmans H, Rodriguez-Rubio L, Lavigne R, Briers Y (2016) From endolysins to Artilysin(R)s: novel enzyme-based approaches to kill drug-resistant bacteria. Biochem Soc Trans 44:123–128
Hawkins C, Harper D, Burch D, Anggard E, Soothill J (2010) Topical treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa otitis of dogs with a bacteriophage mixture: a before/after clinical trial. Vet Microbiol 146:309–313
Ibrahim HR, Yamada M, Matsushita K, Kobayashi K, Kato A (1994) Enhanced bactericidal action of lysozyme to Escherichia coli by inserting a hydrophobic pentapeptide into its C terminus. J Biol Chem 269:5059–5063
Laxminarayan R, Duse A, Wattal C, Zaidi AK, Wertheim HF, Sumpradit N, Vlieghe E, Hara GL, Gould IM, Goossens H, Greko C, So AD, Bigdeli M, Tomson G, Woodhouse W, Ombaka E, Peralta AQ, Qamar FN, Mir F, Kariuki S, Bhutta ZA, Coates A, Bergstrom R, Wright GD, Brown ED, Cars O (2013) Antibiotic resistance-the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect Dis 13:1057–1098
Li XZ, Plesiat P, Nikaido H (2015) The challenge of efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Clin Microbiol Rev 28:337–418
Li M, Li M, Lin H, Wang J, Jin Y, Han F (2016) Characterization of the novel T4-like Salmonella enterica bacteriophage STP4-a and its endolysin. Arch Virol 161:377–384
Loeffler JM, Nelson D, Fischetti VA (2001) Rapid killing of Streptococcus pneumoniae with a bacteriophage cell wall hydrolase. Science 294:2170–2172
Lood R, Winer BY, Pelzek AJ, Diez-Martinez R, Thandar M, Euler CW, Schuch R, Fischetti VA (2015) Novel phage lysin capable of killing the multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterium Acinetobacter baumannii in a mouse bacteremia model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59:1983–1991
Lukacik P, Barnard TJ, Keller PW, Chaturvedi KS, Seddiki N, Fairman JW, Noinaj N, Kirby TL, Henderson JP, Steven AC, Hinnebusch BJ, Buchanan SK (2012) Structural engineering of a phage lysin that targets Gram-negative pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:9857–9862
Lv M, Wang S, Yan G, Sun C, Feng X, Gu J, Han W, Lei L (2015) Genome sequencing and analysis of an Escherichia coli phage vB_EcoM-ep3 with a novel lysin, Lysep3. Virus Genes 50:487–497
Maal-Bared R, Bartlett KH, Bowie WR, Hall ER (2013) Phenotypic antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli and E. coli O157 isolated from water, sediment and biofilms in an agricultural watershed in British Columbia. Sci Total Environ 443:315–323
Morita M, Tanji Y, Orito Y, Mizoguchi K, Soejima A, Unno H (2001) Functional analysis of antibacterial activity of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens phage endolysin against Gram-negative bacteria. FEBS Lett 500:56–59
Obeso JM, Martinez B, Rodriguez A, Garcia P (2008) Lytic activity of the recombinant staphylococcal bacteriophage PhiH5 endolysin active against Staphylococcus aureus in milk. Int J Food Microbiol 128:212–218
Orito Y, Morita M, Hori K, Unno H, Tanji Y (2004) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens phage endolysin can enhance permeability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane and induce cell lysis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:105–109
Pastagia M, Schuch R, Fischetti VA, Huang DB (2013) Lysins: the arrival of pathogen-directed anti-infectives. J Med Microbiol 62:1506–1516
Potron A, Poirel L, Nordmann P (2015) Emerging broad-spectrum resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii: mechanisms and epidemiology. Int J Antimicrob Agents 45:568–585
Sass P, Bierbaum G (2007) Lytic activity of recombinant bacteriophage phi11 and phi12 endolysins on whole cells and biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:347–352
Schmelcher M, Loessner MJ (2016) Bacteriophage endolysins: applications for food safety. Curr Opin Biotechnol 37:76–87
Schmelcher M, Donovan DM, Loessner MJ (2012) Bacteriophage endolysins as novel antimicrobials. Future Microbiol 7:1147–1171
Thandar M, Lood R, Winer BY, Deutsch DR, Euler CW, Fischetti VA (2016) Novel engineered peptides of a phage lysin as effective antimicrobials against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:2671–2679
Walmagh M, Boczkowska B, Grymonprez B, Briers Y, Drulis-Kawa Z, Lavigne R (2013) Characterization of five novel endolysins from Gram-negative infecting bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:4369–4375
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by funds from the National Key Basic Research Program of China (No. 2013CB127205).
Author contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: L.L., G.Y., Q.M. Performed the experiments: Q.M., G.Y. Contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation: Q.M., G.Y., W.Q., X.X. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: L.L., G.Y., Q.M., R.Z., Z.G., C.G., S.W., L.Y., J.G. All authors contributed to the writing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Q., Guo, Z., Gao, C. et al. Enhancement of the direct antimicrobial activity of Lysep3 against Escherichia coli by inserting cationic peptides into its C terminus. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 110, 347–355 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0806-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0806-2