Abstract
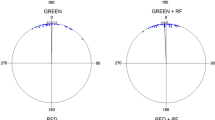
Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis is a spherical, multicellular, magnetotactic prokaryote (MMP) composed of 10–40 genetically-identical, Gram-negative cells. It is known that monochromatic light of low intensity influences its average swimming velocity, being higher for red light (628 nm) and lower for green light (517 nm). In this study, we determined the effect of light of different wavelengths and intensities on the swimming velocity of Ca. Magnetoglobus multicellularis under different magnetic field intensities. The swimming velocities of several organisms exposed to blue light (469 nm), green light (517 nm) and red light (628 nm) with intensities ranging from 0.36 to 3.68 Wm−2 were recorded under magnetic field intensities ranging from 0.26 to 1.47 Oe. Our results showed that MMPs exposed to green light display consistently lower average swimming velocities compared to other wavelengths of light. We also show for the first time that photokinesis in Ca. Magnetoglobus multicellularis is dependent on the magnetic field being applied. The relationship between light wavelength and intensity and magnetic field strength and swimming velocity in this MMP is therefore complex. Although the mechanism for the observed behaviour is not completely understood, a flavin-containing chromophore may be involved.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu F, Martins JL, Silveira TS, Keim CN, Lins de Barros HGP, Filho FJG, Lins U (2007) ‘Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis’, a multicellular, magnetotactic prokaryote from a hypersaline environment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1318–1322
Abreu F, Silva KT, Farina M, Keim CN, Lins U (2008) Greigite magnetosome membrane ultrastructure in ‘Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis’. Int Microbiol 11:75–80
Acosta-Avalos D, Azevedo LMS, Andrade TS, Lins de Barros H (2012) Magnetic configuration model for the multicelular magnetotactic prokaryote Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis. Eur Biophys J 41:405–413
Almedia FP, Viana NB, Lins U, Farina M, Keim CN (2013) Swimming behaviour of the multicellular magnetotactic prokaryote ‘Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis’ under applied magnetic fields and ultraviolet light. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103(4):845–857
Bazylinsky DA, Frankel RB, Heywood BR, Mann S, King JW, Donaghay PL, Hanson AK (1995) Controlled biomineralization of magnetite (Fe3O4) and greigite (Fe3S4) in a magnetotactic bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3232–3239
Bibikov SI, Barnes LA, Gitin Y, Parkinson JS (2000) Domain organization and Flavin adenine dinucleotide-binding determinants in the aerotaxis signal transducer Aer of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5830–5835
Blakemore RP (1982) Magnetotactic bacteria. Ann Rev Microbiol 36:217–238
De Azevedo LV, Lins de Barros HGP, Keim CN, Acosta-Avalos D (2013) Effect of light wavelength on motility and magnetic sensibility of the magnetotactic multicellular prokaryote ‘Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis’. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 104(3):405–412
Dederichs A, Schafer A, Hertel R, van den Ende H (1999) Characterization of flavin binding in flagella of Chlamydomonas. Plant Biol 1:315–320
Esquivel DMS, Lins de Barros H (1986) Motion of magnetotactic microorganisms. J Exp Biol 121:153–163
Frankel RB, Bazylinski DA, Schuler D (1998) Biomineralization of magnetic iron minerals in bacteria. J Supramol Sci 5:388–390
Fujita S, Iseki M, Yoshikawa S, Makino Y, Watanabe M, Motomura T, Kawai H, Murakami A (2005) Identification and characterization of a fluorescent flagellar protein from the brown alga Scytosiphon lomentaria (Scytosiphonales, Phaeophyceae): a flavoprotein homologous to old yellow enzyme. Eur J Phycol 40:159–167
Gorby YA, Beveridge TJ, Blakemore RP (1988) Characterization of the bacterial magnetosome membrane. J Bacteriol 170:834–841
Kalmijn AJ (1981) Biophysics of geomagnetic field detection. IEEE Trans Magn 17:1113–1124
Liedvogel M, Mouritsen H (2010) Cryptochromes-a potential magnetoreceptor: what do we know and what do we want to know? J R Soc Interface 7:S147–S162
Lins U, Farina M (2001) Amorphous mineral phases in magnetotactic multicellular aggregates. Arch Microbiol 176:323–328
Lins U, Freitas F, Keim CN, Lins de Barros H, Esquivel DMS, Farina M (2003) Simple homemade apparatus for harvesting uncultured magnetotactic microorganisms. Braz J Microbiol 34:111–116
Liu B, Liu H, Zhong D, Lin C (2010) Searching for a photocycle of the cryptochrome photoreceptors. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:578–586
Martins JL, Silveira TS, Silva KT, Lins U (2009) Salinity dependence of the distribution of multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes in a hypersaline lagoon. Int Microbiol 12:193–201
Pan Y, Lin W, Li J, Wu W, Tian L, Deng C, Liu Q, Zhu R, Winklhofer M, Petersen N (2009) Reduced efficiency of magnetotaxis in magnetotactic coccoid bacteria in higher than geomagnetic fields. Biophys J 97:986–991
Perantoni M, Esquivel DMS, Wajnberg E, Acosta-Avalos D, Cernicchiaro G, Lins de Barros HGP (2009) Magnetic properties of the microorganism ‘Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis’. Naturwissenschaften 96:685–690
Ritz T, Ahmad M, Mouritsen H, Wiltschko R, Wiltschko W (2010) Photoreceptor-based magnetoreception: optimal design of receptor molecules, cells, and neuronal processing. J R Soc Interface 7:S135–S146
Silva KT, Abreu F, Almeida FP, Keim CN, Farina M, Lins U (2007) Flagellar apparatus of south-seeking many-celled magnetotactic prokaryotes. Microsc Res Tech 70:10–17
Siponen MI, Adryanczyk G, Ginet N, Arnoux P, Pignol D (2012) Magnetochrome: a c-type cytochrome domain specific to magnetotactic bacteria. Biochem Soc Trans 40:1319–1323
Acknowledgments
D. Acosta-Avalos thanks CNPq and FAPERJ for financial support and L. V. de Azevedo thanks CBPF for PCI-DTI grant. We also thanks Dr. Donald Ellis of Northwestern University for reading and correcting the English grammar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Azevedo, L.V., Acosta-Avalos, D. Photokinesis is magnetic field dependent in the multicellular magnetotactic prokaryote Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 108, 579–585 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0513-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0513-4