Abstract
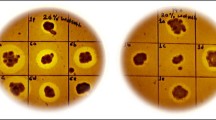
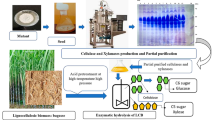
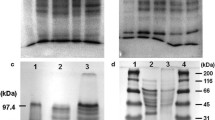
Spore suspensions of Aspergillus oryzae NRRL 3484 were subjected to mutagenesis using ultraviolet-irradiation followed by chemical treatments to improve the biosynthesis of cellulase. Ten mutant strains namely UEAC7, UEAR5, UNAC4, UNAC16, UNAR19, UNBC7, UNBR3, UNBR10, UNBR23 and UNBR25 were selected and their extracellular cellulase activities were assayed. Mutant UNAC4 gave the highest cellulase production [2,455 ± 28 U/g-dry substrate (ds) for filter paper-ase (FP-ase)] in a yield 4-fold exceeding that of the wild type strain (578 ± 5.0 U/g-ds for FP-ase). Rice straw (RS) was used as a sole carbon source for the enzyme production at a concentration of 10 % (w/v). Maximum cellulase production was achieved at initial medium pH 5.5, initial moisture content 77 % and an incubation temperature 28 °C on the fifth day of growth. NH4Cl proved to be the suitable added nitrogen source for maximum enzyme production followed by peptone. These results clearly indicate the cost-effectiveness of solid state fermentation technology in the economic production of extracellular cellulase. The hyper-production of cellulase by mutant strain UNAC4 has potential for industrial processes that convert lignocellulosic material (e.g. RS) into products of commercial value such as glucose and biofuels.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S, Sayed A, Sarker RI, Alam R (1991) Factors affecting cellulase production by Aspergillus terreus using water hyacinth. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 7:62–66
Allen AL, Andreotti RE (1982) Cellulase production in continuous and fed batch culture by Trichoderma reesei MCG80. Biotechnol Bioeng 12:451–459
Anita DD, Sridhar KR, Bhat R (2009) Diversity of fungi associated with mangrove legume Sesbania bispinosa (Jacq.) W. Wight (Fabaceae). Livest Res Rural Dev 21(5):1–15
Arpan D, Tanmay P, Suman KH, Arijit J, Chiranjit M, Pradeep KDM, Bikas RP, Keshab CM (2013) Production of cellulolytic enzymes by Aspergillus fumigatus ABK9 in wheat bran–rice straw mixed substrate and use of cocktail enzymes for deinking of waste office paper pulp. Bioresour Technol 128:290–296
Bahrin EK, Ibrahim MF, AbdRazak MN, Abd-Aziz S, Shah UK, Alitheen N, Salleh MM (2012) Improved cellulase production by Botryosphaeria rhodina from OPEFB at low level moisture condition through statistical optimization. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 42:155–170
Bai S, Kumar MR, Kumar DJM, Balashanmugam P, Kumaran MDB, Kalaichelvan PT (2012) Cellulase production by Bacillus subtilis isolated from cow dung. Arch Appl Sci Res 4:269–279
Bailey MJ, Nevalainen KM (1981) Induction, isolation and testing of stable Trichoderma ressei mutants with improved production of solubilizing cellulose. Enzym Microbiol Technol 3:153–157
Bailey MJ, Tahtiharju J (2003) Efficient cellulase production by Trichoderma reesei in continuous cultivation on lactose medium with a computer-controlled feeding strategy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62:156–162
Bara MTF, Lima AL, Ulhoa CJ (2003) Purification and characterization of an exo-β-1,3-glucanase produced by Trichoderma asperellum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 219:81–85
Bradner JR, Gillings M, Nevalainen KMH (1999) Qualitative assessment of hydrolytic activities in antarctic microfungi grown at different temperatures on solid media. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 15:131–132
Chand P, Aruna A, Maqsood AM, Rao LV (2004) Novel mutation method for increased cellulase production. J Appl Microbiol 98:318–323
Das M, Banerjee R, Bal S (2008) Multivariable parameter optimization for the endoglucanase production by Trichoderma reesei Rut C30 from Ocimum gratissimum seed. Braz Arch Biol Technol 51:35–41
Dashtban M, Schraft H, Qin W (2009) Fungal bioconversion of lignocellulosic residues: opportunities and perspectives. Int J Biol Sci 5:578–595
Dedavid ESLA, Lopes FC, Silveira ST, Brandelli A (2008) Production of cellulolytic enzymes by Aspergillus phoenicis in grape waste using response surface methodology. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s12010-008-8190-7
Dekker M (2003) In: Arora DK (ed) Handbook of fungal biotechnology. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York
Deswal D, Khasa YP, Kuhad RC (2011) Optimization of cellulase production by a brown rot fungus Fomitopsis sp. RCK2010 under solid state fermentation. Bioresour Technol 102:6065–6072
Devendra PM, Dhananjay S, Durgesh P, Jitendra PM (2012) Optimization of solid state fermentation conditions for the production by Trichoderma reesei. J Environ Biol 33:5–8
Dhawan S, Lal R, Kuhad RC (2003) Ethidium bromide stimulated hyper laccase production from bird’s nest fungus Cyathusbulleri. Lett Appl Microbiol 36:64–67
Dillon AJP, Bettio M, Pozzan FG, Andrighetti T, Camassola M (2011) A new Penicillium echinulatum strain with faster cellulase secretion obtained using hydrogen peroxide mutagenesis and screening with 2 deoxyglucose. J Appl Microbiol 111:48–53
Durand H, Baron M, Calmels T, Tiraby G (1988) Classical and molecular genetics applied to Trichoderma reesei for the selection of improved cellulolytic industrial strains. In: Aubert JP, Beguin P, Millet J (eds) Biochemistry and genetics of cellulose degradation. Academic Press, New York, pp 135–151
El-Bondkly AM (2012) Molecular identification using ITS sequences and genome Shuffling to improve 2-Deoxyglucose tolerance and xylanase activity of marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus sp. NRC-F5. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167:2160–2173
El-Bondkly AM, Aboshosha AAM, Radwan NH, Dora SA (2010) Successive construction of β-glucosidase hyperproducers of Trichoderma harzianum using microbial biotechnology techniques. J Microb Biochem Technol 2:70–73
El-Ghonemy DHI, Ali TH, Moharam ME (2014) Optimization of culture conditions for the production of extracellular cellulases via solid state fermentation. Br Microbiol Res J 4:698–714
Elshafei AM, Hassan MM, Morsi NM, El-Ghonemy DH (2009a) Screening studies on the Formation of β-glucosidase from some Filamentous Fungi. Adv Food Sci 31:158–163
Elshafei AM, Hassan MM, Morsi NM, El-Ghonemy DH (2009b) Optimization of culture condition for β-glucosidase production by Aspergillus terreus NRRL 265. Bull Fac Sci Cairo Univ 77:63–106
Elshafei AM, Hassan MM, Morsi NM, El-Ghonemy DH (2011) Purification and some kinetic properties of β-glucosidase from Aspergillus terreus NRRL 265. Afr J Biotechnol 10:19556–19569
Fawzi EM, Hamdy HS (2011) Improvement of carboxymethyl cellulase production from Chaetomium cellulolyticum NRRL 18756 by mutation and optimization of solid state fermentation. Bangladesh J Bot 40(2):139–147
Gao J, Weng H, Zhu D, Yuan M, Guan F, Xi Y (2008) Production and characterization of cellulolytic enzymes from the thermoacidophilic fungal Aspergillus terreus M11 under solid-state cultivation of corn stover. Bioresour Technol 99:7623–7629
Garg SK, Neelakantan S (1981) Effect of cultural factors on cellulase activity and protein production by Aspergillus terreus. Biotechnol Bioeng 23:1653–1659
Gomori G (1955) Preparations of buffers for the use in enzyme studies. Methods Enzymol 1:138–146
Gonzalez VG, Favela-Torres E, Aguilar CN, Romero-Gomez S, Diaz-Godinez G, Augar C (2003) Advantages of fungal enzyme production in solid state over liquid fermentation systems. Biochem Eng J 13:157–167
Graminha EBN, Gonçalves AZL, Pirota RDPB, Balsalobre MAA, Da Silva R, Gomes E (2008) Enzyme production by solid-state fermentation: application to animal nutrition. Anim Feed Sci Technol 144:1–22
Hao XC, Yu XB, Yan ZL (2006) Optimization of the medium for the production of cellulase by the mutant Trichoderma reesei WX-112 using response surface methodology. Food Technol Biotechnol 44:89–94
Ikram-ul-Haq S, Khurshid S, Ali H, Ashraf MA, Rajoka MI (2001) Mutation of Aspergillus niger for hyper production of citric acid from black strap molasses. World J Microbiol Biol 17:35–37
Immanuel G, Dhanusa R, Prema P, Palavesam A (2006) Effect of different growth parameters on endo-glucanase enzyme activity by bacteria isolated from coir retting effluents of estuarine environment. Int J Environ Sci Technol 3:25–34
Jatinder K, Bhupinder SC, Badhan AK, Ghatora SK, Harvinder SS (2007) Purification and characterization of β-glucosidase from Melanocarpus sp. MTCC 3922. Electron J Biotechnol 10:261–270
Jeya M, Joo A, Lee KM, Sim WI, Oh DK, Kim YS, Kim IW, Lee JK (2010) Characterization of endo-β-1,4-glucanase from 1 novel strain of Penicillium pinophilum KMJ601. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1005–1014
Kalogeris E, Iniotaki F, Topakas E, Christakopoulos P, Kekos D, Macris BJ (2003) Performance of an intermittent agitation rotating drum type bioreactor for solid-state fermentation of wheat straw. Bioresour Technol 86:207–312
Kang SW, Park YS, Lee JS, Hong SI, Kim SW (2004) Production of cellulases and hemicellulases by Aspergillus niger KK2 from lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 91:153–156
Karlsson J, Momcilovic D, Wittgren B, Schulein M, Tjerneld F, Brinkmalm G (2002) Enzymatic degradation of carboxymethyl cellulose hydrolyzed by the endoglucanases Cel5A, Cel7B, and Cel45A from Humicola insolens and Cel7B, Cel12A and Cel45Acore from Trichoderma reesei. Biopolymers 63:32–40
Kawamori M, Morikawa Y, Takasawa S (1985) Inductive formation of cellulases by l-sorbose in Trichoderma reesei. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 22:235–236
Kenney JF, Keeping ES (1962) “The Standard Deviation” and “Calculation of the Standard Deviation” §6.5–6.6. In: Mathematics of statistics, Pt. 1, 3rd edn. Van Nostrand, Princeton, pp 77–80
Kim DM, Cho EJ, Kim JW, Lee YW, Chung HJ (2014) Production of cellulases by Penicillium sp. in a solid-state fermentation of oil palm empty fruit bunch. Afr J Biotechnol 13:145–155
Kirchner OG, Granados MS, Pascual PR (2005) Effect of media composition and growth conditions on production of β-glucosidase by Aspergillus niger C-6. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 121:347–359
Kotaka A, Bando H, Kaya M, KatoMurai M, Kuroda K, Sahara H, Hata Y, Kondo A, Ueda M (2008) Direct ethanol production from barley β-glucan by sake yeast displaying Aspergillus oryzae β-glucosidase and endoglucanase. J Biosci Bioeng 105:622–627
Krishna C (1999) Production of bacterial cellulases by solid state bioprocessing of banana wastes. Bioresour Technol 69:231–239
Kubicek CP, Mikus M, Schuster A, Schmoll M, Seiboth B (2009) Metabolic engineering strategies to improve cellulase production by Hypocrea jecorina. Biotechnol Biofuels 2:19–23
Liu YT, Luo ZY, Long CN, Wang HD, Long MN, Hu Z (2011) Cellulase production in a new mutant strain of Penicillium decumbens ML-017 by solid state fermentation with rice bran. N Biotechnol 28:733–737
Lonsane BK, Krishnaiah MM (1991) Leaching of the product and further downstream processing. In: Doelle HW, Mitchell DA, Rolz CE (eds) Solid substrate cultivation. Elsevier Science Publishers, Essex, pp 147–171
Lonsane BK, Ghidyal NP, Budiatman S, Ramakrishna SV (1985) Engineering aspects of solid state fermentation. Enzym Microbiol Technol 7:258–265
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:506–577
Lynd LR, Zyl WH, McBride JE, Laser M (2005) Consolidated bioprocessing of cellulosic biomass: an update. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:577–583
Mandel M, Weber J (1969) Exoglucanase activity by microorganisms. Adv Chem 95:391–414
Mishra S, Gopalkrishnan KS (1984) New method for isolation of cellulase constitutive mutants in Trichoderma reesei and partial characterization. J Ferment Technol 62:495–500
Nevalainen KMH, Palva ET, Bailey MJ (1980) A high cellulase producing mutant strain of Trichoderma reesei. Enzym Microb Technol 2:59–60
Nicoletta C, Mario A, Brunella P, Antonio R, Enrico S, Augusto R (2002) Complete and efficient enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated wheat straw. Process Biochem 37:937–941
Niranjane AP, Madhou P, Stevenson TW (2007) The effect of carbohydrate carbon sources on the production of cellulase by Phlebia gigantea. Enzym Microbiol Technol 40:1464–1468
Ögel ZB, Yarangümeli K, Dündar H, Ifrij I (2001) Submerged cultivation of Scytalidium thermophilum on complex lingo-cellulosic biomass for endo-glucanase production. Enzym Microbiol Technol 28(7–8):689–695
Ong LG, Abd-Aziz S, Noraini S, Karim MI, Hassan MA (2004) Enzyme production and profile by Aspergillus niger during solid state fermentation using palm kernel cake as substrate. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 118:73–79
Pathak H, Singh R, Bhatia A, Jain N (2006) Recycling of rice straw to improve wheat yield and soil fertility and reduce atmospheric pollution. Paddy Water Environ 4:111–117
Peciulyte D (2007) Isolation of cellulolytic fungi from waste paper gradual recycling materials. EKOLOGIJA 53:11–18
Pradeep MR, Narasimha G (2011) Utilization of pea seed husk as a substrate for cellulase production by mutant Aspergillus niger. Insight Biotechnol 1(2):17–22
Pradeep MR, Janardhan A, Kumar AP, Narasimha G (2012) Induction of chemical mutations in Aspergillus niger to enhance cellulase production. J Environ Biol 2:129–132
Pushalkar S, Rao KK, Menon K (1995) Production of β-glucosidase by Aspergillus terreus. Curr Microbiol 30:255–258
Rodriguez IA, Escobedo CP, Paramo MGZ, Romero EL, Camacho HC (2005) Degradation of cellulose by the bean-pathogenic fungus Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Agric técn Méx 32:101–114
Sadhu S, Maiti TK (2013) Cellulase production by bacteria: a review. Br Microbiol Res J 3:235–258
Saha S, Roy R, Sen SK, Ray AK (2006) Characterization of cellulase producing bacteria from the digestive tract of tilapia, Oreochromis mossambica (Peters) and grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella (Valenciennes). Aquac Res 37:380–388
Sakthivel M, Karthikeyan N, Jayaveny R, Palani P (2010) Optimization of culture conditions for the production of extracellular cellulase from Corynebacterium lipophiloflavum. J Ecobiotechnol 2:06–13
Shafique S, Rukhsana B, Sobiya S (2011) Strain improvement in Trichoderma viride through mutation for over expression of cellulase and characterization of mutants using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). Afr J Biotechnol 10:19590–19597
Shaikh NM, Patel AA, Mehta SA, Patel ND (2013) Isolation and screening of cellulolytic bacteria inhabiting different environment and optimization of cellulase production. Univ J Environ Res Technol 3:39–49
Shamala TR, Sreekantiah KR (1985) Production of cellulases and d-xylanase by some selected fungal isolates. Enzym Microbiol Technol 8:178–182
Shankar T, Isaiarasu L (2011) Cellulase production by Bacillus pumilus EWBCM1 under varying cultural conditions. Middle East J Sci Res 8:40–45
Shanmugapriya K, Saravana P, Krishnapriya S, Manoharan M, Mythili A, Joseph S (2012) Isolation, screening and partial purification of cellulase from cellulase producing bacteria. Int J Adv Biotechnol Res 3:509–514
Sing S, Brar JK, Sandhu DK, Kaur A (1996) Isozyme polymorphism of cellulases in Aspergillus terreus. J Basic Microbiol 36:289–296
Singhania RR, Sukumaran RK, Pillai A, Szakacs G, Pandey A (2006) Solid-state fermentation of lignocellulosic substrates for cellulase production by Trichoderma reesei NRRL 11460. Indian J Biotechnol 5:332–336
Singhania RR, Patel AK, Soccol CR, Pandey A (2009) Recent advances in solid-state fermentation. Biochem Eng J 44:13–18
Singhvi MS, Adsul MG, Gokhale DV (2011) Comparative production of cellulase by mutant of Penicillium janthinellum NCIM 1171 and its application in hydrolysis of Avicel and cellulose. Bioresour Technol 102:6569–6572
Sukumaran RK, Singhania RR, Pandey A (2005) Microbial cellulases-production, applications and challenges. J Sci Ind Res 64:832–844
Sun Y, Cheng J (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour Technol 83:1–11
Takashima S, Nakamura A, Hidaka M, Masaki H, Uozumi T (1996) Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the cellulase genes of Humicola grisea var. thermoidea. J Biotechnol 50:137–147
Villena GK, Gutierrez-Correa M (2006) Production of cellulase by Aspergillus niger biofilms developed on polyester cloth. Lett Appl Microbiol 43:226–262
Vu VH, Pham TA, Kim K (2009) Fungal strain improvement for cellulase production using repeated and sequential mutagenesis. Mycobiology 37:267–271
Vu VH, Pham TA, Kim K (2010) Improvement of a fungal strain by repeated and sequential mutagenesis and optimization of solid-state fermentation for the hyper-production of raw starch-digesting enzyme. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:718–726
Vu VH, Pham TA, Kim K (2011) Improvement of fungal cellulase production by mutation and optimization of solid state fermentation. Mycobiology 39:20–25
Xiong H, von Weymarn N, Leisola M, Turunen O (2004) Influence of pH on the production of xylanases by Trichoderma reesei Rut C-30. Process Biochem 39(6):731–736
Yun SI, Jeono CS, Chung DK, Choi HS (2001) Purification and some properties of a β-glucosidase from Trichoderma harzianum Type C-4. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:2028–2032
Zhang YH, Himmel ME, Mielenz JR (2006) Outlook for cellulase improvement: screening and selection strategies. Biotechnol Adv 24:452–481
Zhou J, Wang YH, Chu J, Zhuang YP, Zhang SL, Yin P (2008) Identification and purification of the main components of cellulases from a mutant strain of Trichoderma viride T 100-14. Bioresour Technol 99:6826–6833
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Ghonemy, D.H., Ali, T.H., El-Bondkly, A.M. et al. Improvement of Aspergillus oryzae NRRL 3484 by mutagenesis and optimization of culture conditions in solid-state fermentation for the hyper-production of extracellular cellulase. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 106, 853–864 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0255-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0255-8