Abstract
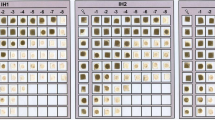
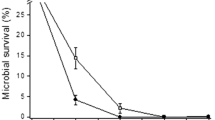
Planctomycetes are bacteria with particular characteristics such as internal membrane systems encompassing intracellular compartments, proteinaceous cell walls, cell division by yeast-like budding and large genomes. These bacteria inhabit a wide range of habitats, including marine ecosystems, in which ultra-violet radiation has a potential harmful impact in living organisms. To evaluate the effect of ultra-violet C on the genome of several marine strains of Planctomycetes, we developed an easy and fast DNA diffusion assay in which the cell wall was degraded with papain, the wall-free cells were embedded in an agarose microgel and lysed. The presence of double strand breaks and unwinding by single strand breaks allow DNA diffusion, which is visible as a halo upon DNA staining. The number of cells presenting DNA diffusion correlated with the dose of ultra-violet C or hydrogen peroxide. From DNA damage and viability experiments, we found evidence indicating that some strains of Planctomycetes are significantly resistant to ultra-violet C radiation, showing lower sensitivity than the known resistant Arthrobacter sp. The more resistant strains were those phylogenetically closer to Rhodopirellula baltica, suggesting that these species are adapted to habitats under the influence of ultra-violet radiation. Our results provide evidence indicating that the mechanism of resistance involves DNA damage repair and/or other DNA ultra-violet C-protective mechanism.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrage AA, Phelps TJ, Benoit RE, White DC (1993) Survival of subsurface microorganisms exposed to UV and hydrogen peroxide. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:3545–3550
Azevedo F, Marques F, Fokt H, Oliveira R, Johansson B (2011) Measuring oxidative DNA damage and DNA repair using the yeast comet assay. Yeast 28:55–61
Batista LF, Kaina B, Meneghini R, Menck CF (2009) How DNA lesions are turned into powerful killing structures: insights from UV-induced apoptosis. Mutat Res 681:197–208
Béjà O, Aravind L, Koonin EV et al (2000) Bacterial rhodopsin: evidence for a new type of phototrophy in the sea. Science 289:1902–1906
Brachmann CB, Davies A, Cost GJ, Caputo E, Li J, Hieter P, Boeke JD (1998) Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast 14:115–132
Cockell CS, Knowland J (1999) Ultraviolet radiation screening compounds. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 74:311–345
Cockell CS, Rettberg P, Rabbow E, Olsson-Francis K (2011) Exposure of phototrophs to 548 days in low earth orbit: microbial selection pressures in outer space and on early earth. ISME J 5:1671–1682
Coxx MM, Battista JR (2005) Deinococcus radiodurans—the consummate survivor. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:882–892
Daly MJ, Gaidamakova EK, Matrosova VY et al (2007) Protein oxidation implicated as the primary determinant of bacterial radioresistance. PLoS Biol 5:e92
de la Torre JR, Christianson L, Béjà O, Suzuki MT, Karl D, Heidelberg JF (2003) Proteorhodopsin genes are distributed among divergent bacterial taxa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:12830–12835
DeLong EF, Franks DG, Alldredge L (1993) Phylogenetic diversity of aggregate-attached vs. free-living marine bacterial assemblages. Limnol Oceanogr 38:924–934
Derakshani M, Lukow T, Liesack W (2001) Novel bacterial lineages at the (sub)division level as detected by signature nucleotide-targeted recovery of 16S rRNA genes from bulk soil and rice roots of flooded rice microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:623–631
Dhawan A, Bajpayee M, Parmar D (2009) Comet assay: a reliable tool for the assessment of DNA damage in different models. Cell Biol Toxicol 25:5–32
Fernández JL, Cartelle M, Muriel L, Santiso R, Tamayo M, Goyanes V, Gosálvez J, Bou G (2008) DNA fragmentation in microorganisms assessed in situ. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:5925–5933
Friedrich AB, Merkert H, Fendert T, Hacker J, Proksch P, Hentschel U (1999) Microbial diversity in the marine sponge Aplysina cavernicola (formerly Verongia cavernicola) analyzed by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Mar Biol 134:461–470
Friedrich AB, Fischer I, Proksch P, Hacker J, Hentschel U (2001) Temporal variation of the microbial community associated with the Mediterranean sponge Aplysina aerophoba. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 38:105–113
Fuerst JA (1995) The Planctomycetes: emerging models for microbial ecology, evolution and cell biology. Microbiology 141:1493–1506
Fuerst JA (2005) Intracellular compartmentation in Planctomycetes. Annu Rev Microbiol 59:99–328
Fuerst JA, Sambhi SK, Paynter JL, Hawkins JA, Atherton JG (1991) Isolation of a bacterium resembling Pirellula species from primary tissue culture of the giant tiger prawn (Penaeus monodon). Appl Environ Microbiol 57:3127–3134
Fuerst JA, Gwilliam HG, Lindsay M, Lichanska A, Belcher C, Vickers JE, Hugenholtz P (1997) Isolation and molecular identification of planctomycete bacteria from postlarvae of the giant tiger prawn, Penaeus monodon. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:254–262
Gade D, Gobom J, Rabus R (2005) Proteomic analysis of carbohydrate catabolism and regulation in the marine bacterium Rhodopirellula baltica. Proteomics 5:3672–3683
Garcia-Pichel F (1998) Solar ultraviolet and the evolutionary history of cyanobacteria. Orig Life Evol Biosph 28:321–347
Glöckner FO, Kube M, Bauer M, Bauer M, Teeling H, Lombardot T, Ludwig W, Gade D, Beck A, Borzym K, Heitmann K, Rabus R, Schlesner H, Amann R, Reinhardt R (2003) Complete genome sequence of the marine planctomycete Pirellula sp. strain 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8298–8303
Hanway D, Chin JK, Xia G, Oshiro G, Winzeler EA, Romesberg FE (2002) Previously uncharacterized genes in the UV- and MMS-induced DNA damage response in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:10605–10610
Hermansson M, Jones GW, Kjelleberg S (1987) Frequency of antibiotic and heavy metal resistance, pigmentation, and plasmids in bacteria of the marine air-water interface. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:2338–2342
Hieu CX, Voigt B, Albrecht D, Becher D, Lombardot T, Glöckner FO, Amann R, Hecker M, Schweder T (2008) Detailed proteome analysis of growing cells of the planctomycete Rhodopirellula baltica SH1. Proteomics 8:1608–1623
Joux F, Jeffrey WH, Lebaron P, Mitchell DL (1999) Marine bacterial isolates display diverse responses to UV-B radiation. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3820–3827
Kolber ZS, Van Dover CL, Niederman RA, Falkowski PG (2000) Bacterial photosynthesis in surface waters of the open ocean. Nature 407:177–179
Krisko A, Radman M (2010) Protein damage and death by radiation in Escherichia coli and Deinococcus radiodurans. PNAS 107:14373–14377
Kuhlman KR, Allenbach LB, Ball CL, Fusco WG, La Duc MT, Kuhlman GM, Anderson RC, Stuecker T, Erickson IK, Benardini J, Crawford RL (2005) Enumeration, isolation, and characterization of ultraviolet (UV-C) resistant bacteria from rock varnish in the Whipple Mountains, California. Icarus 174:585–595
Kulichevskaia IS, Pankratov TA, Dedysh SN (2006) Detection of representatives of the Planctomycetes in Sphagnum peat bogs by molecular and cultivation methods. Microbiology 75:329–335
Lage OM, Bondoso J (2011) Planctomycetes diversity associated with macroalgae. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 78:366–375
Lieber A, Leis A, Kushmaro A, Minsky A, Medalia O (2009) Chromatin organization and radio resistance in the bacterium Gemmata obscuriglobus. J Bacteriol 191:1439–1445
Mitchell DL, Karentz D (1993) The induction and repair of DNA photodamage in the environment. In: Young AR, Bjorn LO, Moan J, Nultsch W (eds) Environmental UV photobiology. Plenum Press, New York, pp 345–377
Osman S, Peeters Z, La Duc MT, Mancinelli R, Ehrenfreund P, Venkateswaran K (2008) Effect of shadowing on survival of bacteria under conditions simulating the Martian atmosphere and UV radiation. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:959–970
Östling O, Johanson KJ (1984) Microelectrophoretic study of radiation-induced DNA damages in individual mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 123:291–298
Rabus R, Gade D, Helbig R, Bauer M, Glöckner FO, Kube M, Schlesner H, Reinhardt R, Amann R (2002) Analysis of N-acetylglucosamine metabolism in the marine bacterium Pirellula sp. strain 1 by a proteomic approach. Proteomics 2:649–655
Sancar A (1994) Structure and function of DNA photolyase. Biochemistry 33:2–9
Schlesner H, Rensmann C, Tindall BJ, Gade D, Rabus R, Pfeiffer S, Hirsch P (2004) Taxonomic heterogeneity within the Planctomycetales as derived by DNA–DNA hybridization, description of Rhodopirellula baltica gen. nov., sp. nov., transfer of Pirellula marina to the genus Blastopirellula gen. nov. as Blastopirellula marina comb. nov. and emended description of the genus Pirellula. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1567–1580
Schuch AP, Menck CFM (2010) The genotoxic effects of DNA lesions induced by artificial UV-radiation and sunlight. J Photochem Photobiol B 99:111–116
Singh NP (2000) A simple method for accurate estimation of apoptotic cells. Exp Cell Res 256:328–337
Singh NP, Stephens RE, Singh H, Lai H (1999) Visual quantification of DNA double-strand breaks in bacteria. Mutat Res 429:159–168
Sinha RP, Häder DP (2002) UV-induced DNA damage and repair: a review. Photochem Photobiol Sci 1:225–236
Strous M, Fuerst JA, Kramer EH, Logemann S, Muyzer G, van de Pas-Schoonen KT, Webb R, Kuenen JG, Jetten MS (1999) Missing lithotroph identified as new planctomycete. Nature 400:446–449
Suter B, Livingstone-Zatchej M, Thoma F (1997) Chromatin structure modulates DNA repair by photolyase in vivo. EMBO J 16:2150–2160
Ward N, Staley JT, Fuerst JA, Giovannoni S, Schlesner H, Stackebrandt E (2006) The order Planctomycetales, including the genera Planctomyces, Pirellula, Gemmata and Isosphaera and the Candidatus genera Brocadia, Kuenenia and Scalindua. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer, New York, pp 757–793
Webster NS, Wilson KJ, Blackall LL, Hill RT (2001) Phylogenetic diversity of bacteria associated with the marine sponge Rhopaloeides odorabile. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:434–444
Wecker P, Klockow C, Ellrott A, Quast C, Langhammer P, Harder J, Glöckner FO (2009) Transcriptional response of the model planctomycete Rhodopirellula baltica SH1T to changing environmental conditions. BMC Genomics 10:410
Wegner CE, Richter-Heitmann T, Klindworth A, Klockow C, Richter M, Achstetter T et al (2013) Expression of sulfatases in Rhodopirellula baltica and the diversity of sulfatases in the genus Rhodopirellula. Mar Genomics 9:51–61
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) through the COMPETE—Operational Competitiveness Programme and national funds through FCT—Foundation for Science and Technology, under the projects Pest-C/BIA/UI4050/2011 and PEst-C/MAR/LA0015/2013. We are grateful to Cátia Moreira for helping with the extraction of the pigments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viana, F., Lage, O.M. & Oliveira, R. High ultraviolet C resistance of marine Planctomycetes. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 104, 585–595 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-0027-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-0027-x