Abstract
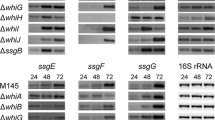
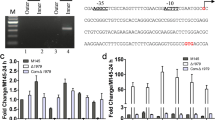
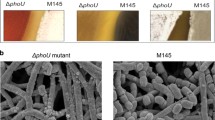
A segment of DNA was isolated that complemented several poorly characterised sporulation-defective white-colony mutants of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) from an early collection (Hopwood et al., J Gen Microbiol 61: 397–408, 1970). Complementation was attributable to a gene, SCO4543, named whiJ, encoding a likely DNA-binding protein. Surprisingly, although some mutations in whiJ had a white colony phenotype, complete deletion of the wild-type or mutant gene gave a wild-type morphology. The whiJ gene is a member of a large paralogous set of S. coelicolor genes including abaAorfA, which regulates antibiotic production; and genes flanking whiJ are paralogues of other gene classes that are often associated with whiJ-like genes (Gehring et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 9642–9647, 2000). Thus, the small gene SCO4542 encodes a paralogue of the abaAorfD gene product, and SCO4544 encodes a paralogue of a family of likely anti-sigma factors (including the product of abaAorfB). Deletion of SCO4542 resulted in a medium-dependent bald- or white-colony phenotype, which could be completely suppressed by the simultaneous deletion of whiJ. A model is proposed in which WhiJ binds to operator sequences to repress developmental genes, with repression being released by interaction with the WhiJ-associated SCO4542 protein. It is suggested that this activity of SCO4542 protein is prevented by an unknown signal.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aínsa JA, Ryding NJ, Hartley N, Findlay KC, Bruton CJ, Chater KF (2000) WhiA, a protein of unknown function conserved among gram-positive bacteria, is essential for sporulation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 182:5470–5478
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D, Bateman A, Brown S, Chandra G, Chen CW, Collins M, Cronin A, Fraser A, Goble A, Hidalgo J, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huang CH, Kieser T, Larke L, Murphy L, Oliver K, O’Neil S, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Seeger K, Saunders D, Sharp S, Squares R, Squares S, Taylor K, Warren T, Wietzorrek A, Woodward J, Barrell BG, Parkhill J, Hopwood DA (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147
Bentley SD, Brown S, Murphy LD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Parkhill J, Barrell BG, McCormick JR, Santamaría RI, Losick R, Yamasaki M, Kinashi H, Chen CW, Chandra G, Jakimowicz D, Kieser HM, Kieser T, Chater KF (2004) SCP1, a 356 023 bp linear plasmid adapted to the ecology and developmental biology of its host, Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 51:1615–1628
Bibb MJ, Molle V, Buttner MJ (2000) Sigma(BldN), an extracytoplasmic function RNA polymerase sigma factor required for aerial mycelium formation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 182:4606–4616
Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brien K, Seno ET, Rao N, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from E. coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49
Chater KF (1972) A morphological and genetic mapping study of white colony mutants of Streptomyces coelicolor. J Gen Microbiol 72:9–28
Chater KF (2001) Regulation of sporulation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): a checkpoint multiplex? Curr Opin Microbiol 4:667–673
Chater KF, Chandra G (2006) The evolution of development in Streptomyces analysed by genome comparisons. FEMS Microbiol Rev 30:651–672
Chater KF, Horinouchi S (2003) Signalling early developmental events in two highly diverged Streptomyces species. Mol Microbiol 48:9–15
Chater KF, Merrick MJ (1976) Approaches to the study of differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) In: Macdonald KD (ed) 2nd international symposium on the genetics of industrial micro-organisms. Academic Press, London, pp 583–593
Chen C-C, Lewis RJ, Harris R, Yudkin MD, Delumeau O (2003) A supramolecular complex in the environmental stress signalling pathway of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 49:1657–1669
Cho YH, Lee EJ, Ahn BE, Roe JH (2001) SigB, an RNA polymerase sigma factor required for osmoprotection and proper differentiation of Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 42:205–214
Dalton KA, Thibessard A, Hunter JI, Kelemen GH (2007) A novel compartment, the ‘subapical stem’ of the aerial hyphae, is the location of a sigN-dependent, developmentally distinct transcription in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 64:719–737
Eccleston M, Ali R, Seyler R, Westpheling J, Nodwell J (2002) Structural and genetic analysis of the BldB protein of Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol 184:4270–4276
Fernández-Moreno M, Martin-Triana AJ, Martinez E, Niemi J, Kieser H, Hopwood D, Malpartida F (2002) abaA, a new pleiotropic regulatory locus for antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol 174:2958–2967
Flärdh K, Buttner MJ (2009) Streptomyces morphogenetics: dissecting differentiation in a filamentous bacterium. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:36–49
Gehring A, Nodwell J, Beverley S, Losick R (2000) Genomewide insertional mutagenesis in Streptomyces coelicolor reveals additional genes involved in morphological differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9642–9647
Gust B, Challis GL, Fowler K, Kieser T, Chater KF (2003) PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene soil odor geosmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1541–1546
Gust B, Chandra G, Jakimowicz D, Yuqing T, Bruton CJ, Chater KF (2004) Lambda red-mediated genetic manipulation of antibiotic-producing Streptomyces. Adv Appl Microbiol 54:107–128
Helmann JD (1998) Anti-sigma factors. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:135–141
Hillemann D, Pühler A, Wohlleben W (1991) Gene disruption and gene replacement in Streptomyces via single-stranded DNA transformation of integration vectors. Nucleic Acids Res 19:727–731
Hopwood DA, Wildermuth H, Palmer HM (1970) Mutants of Streptomyces coelicolor defective in sporulation. J Gen Microbiol 61:397–408
Kelemen GH, Viollier PH, Tenor JL, Marri L, Buttner MJ, Thompson CJ (2001) A connection between stress and development in the multicellular prokaryote Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 40:804–814
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kim ES, Song JY, Kim DW, Chater KF, Lee KJ (2008) A possible extended family of regulators of sigma factor activity in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol 190:7559–7566
Lee E, Karoonuthaisiri N, Kim H, Park J, Cha C, Kao C, Roe J (2005) A master regulator sigma governs osmotic and oxidative response as well as differentiation via a network of sigma factors in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 57:1252–1264
McNeil DJ (1988) Characterisation of a unique methyl-specific restriction system in Streptomyces avermitilis. J Bacteriol 170:5607–5612
Merrick M (1976) A morphological and genetic mapping study of bald colony mutants of Streptomyces coelicolor. J Gen Microbiol 96:299–315
Mittenhuber G (2002) A phylogenomic study of the general stress response sigma factor σB of Bacillus subtilis and its regulatory proteins. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 4:427–452
Noens EEE, Mersinias V, Traag BA, Smith CP, Koerten HK, Van Wezel GP (2005) SsgA-like proteins determine the fate of peptidoglycan during sporulation of Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 58:929–944
Pope MK, Green B, Westpheling J (1998) The bldB gene encodes a small protein required for morphogenesis, antibiotic production, and catabolite control in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Bacteriol 180:1556–1562
Potuckova L, Kelemen GH, Findlay KC, Lonetto MA, Buttner MJ, Kormanec J (1995) A new RNA polymerase sigma factor, sigma(F), is required for the late stages of morphological differentiation in Streptomyces spp. Mol Microbiol 17:37–48
Redenbach M, Kieser HM, Denapaite D, Eichner A, Cullum J, Kinashi H, Hopwood DA (1996) A set of ordered cosmids and a detailed genetic and physical map for the 8 Mb Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) chromosome. Mol Microbiol 21:77–96
Ryding NJ, Kelemen GH, Whatling CA, Flärdh K, Buttner MJ, Chater KF (1998) A developmentally regulated gene encoding a repressor-like protein is essential for sporulation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 29:343–357
Ryding NJ, Bibb MJ, Molle V, Findlay KC, Chater KF, Buttner MJ (1999) New sporulation loci in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 181:5419–5425
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Sevcikova B, Benada O, Kofronova O, Kormanec J (2001) Stress response sigma factor sigma(H) is essential for morphological differentiation of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Arch Microbiol 177:98–106
Traag BA, Van Wezel GP (2008) The SsgA-like proteins in actinomycetes: small proteins up to a big task. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 94:85–97
Viollier PH, Kelemen GH, Dale GE, Nguyen KT, Buttner MJ, Thompson CJ (2003) Specialized osmotic stress response systems involve multiple SigB-like sigma factors in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 47:699–714
Xu Q, Traag BA, Willemse J, McMullan D, Miller MD, Elsliger MA, Abdubek P, Astakhova T, Axelrod HL, Bakolitsa C, Carlton D, Chen C, Chiu HJ, Chruszcz M, Clayton T, Das D, Deller MC, Duan L, Ellrott K, Ernst D, Farr CL, Feuerhelm J, Grant JC, Grzechnik A, Grzechnik SK, Han GW, Jaroszewski L, Jin KK, Klock HE, Knuth MW, Kozbial P, Krishna SS, Kumar A, Marciano D, Minor W, Mommaas AM, Morse AT, Nigoghossian E, Nopakun A, Okach L, Oommachen S, Paulsen J, Puckett C, Reyes R, Rife CL, Sefcovic N, Tien HJ, Trame CB, van den Bedem H, Wang S, Weekes D, Hodgson KO, Wooley J, Deacon AM, Godzik A, Lesley SA, Wilson IA, van Wezel GP (2009) Structural and functional characterizations of SsgB, a conserved activator of developmental cell division in morphologically complex actinomycetes. J Biol Chem 284:25268–25279
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank Helen Kieser and David Hopwood for strains recovered from archives, Govind Chandra for carrying out bioinformatic analysis and Kay Fowler for technical advice. This work was supported by grants from the John Innes Foundation (NJR) and the BBSRC grant CAD 04380 (JAA). KFC is a John Innes Foundation Emeritus Fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
José A. Aínsa, Nick Bird, and N. Jamie Ryding have made equal contributions to the work reported.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aínsa, J.A., Bird, N., Ryding, N.J. et al. The complex whiJ locus mediates environmentally sensitive repression of development of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 98, 225–236 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9443-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9443-3