Abstract
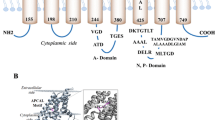
Cupriavidus metallidurans CH34 genome contains an ortholog of Atm1p named AtmA (Rmet_0391, YP_582546). In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the ABC-type transport system Atm1p is involved in export of iron–sulfur clusters from mitochondria into the cytoplasm for assembly of cytoplasmic iron–sulfur containing proteins. An ∆atmA mutant of C. metallidurans was sensitive to nickel and cobalt but not iron cations. AtmA increased also resistance to these cations in Escherichia coli strains that carry deletions of the genes for other nickel and cobalt transport systems. In C. metallidurans, atmA expression was not significantly induced by nickel and cobalt, but repressed by zinc. AtmA was purified as a 70 kDa protein after expression in E. coli. ATPase activity of AtmA was stimulated by nickel and cobalt.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akama H, Matsuura T, Kashiwagi S, Yoneyama H, Narita SI, Tsukihara T, Nakagawa A, Nakae T (2004) Crystal structure of the membrane fusion protein, MexA, of the multidrug transporter in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem 279:25939–25942. doi:10.1074/jbc.C400164200
Anton A, Weltrowski A, Haney JH, Franke S, Grass G, Rensing C, Nies DH (2004) Characteristics of zinc transport by two bacterial cation diffusion facilitators from Ralstonia metallidurans and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 186:7499–7507. doi:10.1128/JB.186.22.7499-7507.2004
Chen CA, Cowan JA (2003) Characterization of the soluble domain of the ABC7 type transporter Atm1. J Biol Chem 278:52681–52688. doi:10.1074/jbc.M306472200
Fagan MJ, Saier MH Jr (1994) P-type ATPases of eukaryotes and bacteria: sequence comparisons and construction of phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol 38:57–99. doi:10.1007/BF00175496
Fath MJ, Kolter R (1993) ABC-transporters: the bacterial exporters. Microbiol Rev 57:995–1017
Froschauer EM, Kolisek M, Dieterich F, Schweigel M, Schweyen RJ (2004) Fluorescence measurements of free [Mg2+] by use of mag-fura 2 in Salmonella enterica. FEMS Microbiol Lett 237:49–55
Grass G, Große C, Nies DH (2000) Regulation of the cnr cobalt/nickel resistance determinant from Ralstonia sp. CH34. J Bacteriol 182:1390–1398. doi:10.1128/JB.182.5.1390-1398.2000
Grass G, Franke S, Taudte N, Nies DH, Kucharski LM, Maguire ME, Rensing C (2005a) The metal permease ZupT from Escherichia coli is a transporter with a broad substrate spectrum. J Bacteriol 187:1604–1611. doi:10.1128/JB.187.5.1604-1611.2005
Grass G, Fricke B, Nies DH (2005b) Control of expression of a periplasmic nickel efflux pump by periplasmic nickel concentrations. Biometals 18:437–448. doi:10.1007/s10534-005-3718-6
Große C, Grass G, Anton A, Franke S, Navarrete Santos A, Lawley B, Brown NL, Nies DH (1999) Transcriptional organization of the czc heavy metal homoeostasis determinant from Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 181:2385–2393
Higgins CF (1992) ABC-transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol 8:67–113. doi:10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000435
Kispal G, Csere P, Guiard B, Lill R (1997) The ABC transporter Atm1p is required for mitochondrial iron homeostasis. FEBS Lett 418:346–350. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(97)01414-2
Kispal G, Csere P, Prohl C, Lill R (1999) The mitochondrial proteins Atm1p and Nfs1p are essential for biogenesis of cytosolic Fe/S proteins. EMBO J 18:3981–3989. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.14.3981
Koch D, Nies DH, Grass G (2007) The RcnRA (YohLM) system of Escherichia coli: a connection between nickel, cobalt and iron homeostasis. Biometals 20:759–771. doi:10.1007/s10534-006-9039-6
Koronakis V, Sharff A, Koronakis E, Luisi B, Hughes C (2000) Crystal structure of the bacterial membrane protein TolC central to multidrug efflux and protein export. Nature 405:914–919. doi:10.1038/35016007
Kuhnke G, Neumann K, Muehlenhoff U, Lill R (2006) Stimulation of the ATPase activity of the yeast mitochondrial ABC transporter Atm1p by thiol compounds. Mol Membr Biol 23:173–184. doi:10.1080/09687860500473630
Lanzetta PA, Alvarez LJ, Reinach PS, Candia A (1979) An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem 700:95–97. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(79)90115-5
Lenz O, Schwartz E, Dernedde J, Eitinger T, Friedrich B (1994) The Alcaligenes eutrophus H16 hoxX gene participates in hydrogenase regulation. J Bacteriol 176:4385–4393
Liesegang H, Lemke K, Siddiqui RA, Schlegel H-G (1993) Characterization of the inducible nickel and cobalt resistance determinant cnr from pMOL28 of Alcaligenes eutrophus CH34. J Bacteriol 175:767–778
Lill R, Muhlenhoff U (2006) Iron–sulfur protein biogenesis in eukaryotes: components and mechanisms. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22:457–486. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.22.010305.104538
Liu Y-C, Liao L-C, Wu W-T (2000) Cultivation of recombinant Escherichia coli to achieve high cell density with level of penicillin G acylase activity. Proc Natl Sci Counc 24:156–160
Marx CJ, Lidstrom ME (2002) Broad-host-range cre-lox system for antibiotic marker recycling in gram-negative bacteria. Biotechniques 33:1062–1067
Mergeay M, Nies D, Schlegel HG, Gerits J, Charles P, van Gijsegem F (1985) Alcaligenes eutrophus CH34 is a facultative chemolithotroph with plasmid-bound resistance to heavy metals. J Bacteriol 162:328–334
Moncrief MB, Maguire ME (1999) Magnesium transport in prokaryotes. J Biol Inorg Chem 4:523–527. doi:10.1007/s007750050374
Mühlenhoff U, Lill R (2000) Biogenesis of iron–sulfur proteins in eukaryotes: a novel task of mitochondria that is inherited from bacteria. BBA-Bioenergetics 1459:370–382. doi:10.1016/S0005-2728(00)00174-2
Munkelt D, Grass G, Nies DH (2004) The chromosomally encoded cation diffusion facilitator proteins DmeF and FieF from Wautersia metallidurans CH34 are transporters of broad metal specificity. J Bacteriol 186:8036–8043. doi:10.1128/JB.186.23.8036-8043.2004
Murakami S, Nakashima R, Yamashita R, Yamaguchi A (2002) Crystal structure of bacterial multidrug efflux transporter AcrB. Nature 419:587–593. doi:10.1038/nature01050
Navarro C, Wu LF, Mandrand-Berthelot MA (1993) The nik operon of Escherichia coli encodes a periplasmic binding-protein-dependent transport-system for nickel. Mol Microbiol 9:1181–1191. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01247.x
Netz DJA, Pierik AJ, Stümpfig M, Mühlenhoff U, Lill R (2007) The Cfd1-Nbp35 complex acts as a scaffold for iron–sulfur protein assembly in the yeast cytosol. Nat Chem Biol 3:278–286. doi:10.1038/nchembio872
Nies DH (1992) CzcR and CzcD, gene products affecting regulation of resistance to cobalt, zinc and cadmium (czc system) in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 174:8102–8110
Nies DH (2003) Efflux-mediated heavy metal resistance in prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:313–339. doi:10.1016/S0168-6445(03)00048-2
Nies DH (2007) Bacterial transition metal homeostasis. In: Nies DH, Silver S (eds) Molecular microbiology of heavy metals. Springer, Berlin, pp 118–142
Nies DH, Silver S (1989) Plasmid-determined inducible efflux is responsible for resistance to cadmium, zinc, and cobalt in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 171:896–900
Nies D, Mergeay M, Friedrich B, Schlegel HG (1987) Cloning of plasmid genes encoding resistance to cadmium, zinc, and cobalt in Alcaligenes eutrophus CH34. J Bacteriol 169:4865–4868
Nies A, Nies DH, Silver S (1989) Cloning and expression of plasmid genes encoding resistances to chromate and cobalt in Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 171:5065–5070
Pardee AB, Jacob F, Monod J (1959) The genetic control and cytoplasmic expression of inducibility in the synthesis of β-galactosidase of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 1:165–168
Paulsen IT, Saier MH Jr (1997) A novel family of ubiquitous heavy metal ion transport proteins. J Membr Biol 156:99–103. doi:10.1007/s002329900192
Paulsen IT, Park JH, Choi PS, Saier MHJ (1997) A family of Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane factors that function in the export of proteins, carbohydrates, drugs and heavy metals from Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 156:1–8
Pfeiffer J, Guhl J, Waidner B, Kist M, Bereswill S (2002) Magnesium uptake by CorA is essential for viability of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun 70:3930–3934. doi:10.1128/IAI.70.7.3930-3934.2002
Pohlmann A, Fricke WF, Reinecke F, Kusian B, Liesegang H, Cramm R, Eitinger T, Ewering C, Potter M, Schwartz E, Strittmatter A, Voss I, Gottschalk G, Steinbuchel A, Friedrich B, Bowien B (2006) Genome sequence of the bioplastic-producing “Knallgas” bacterium Ralstonia eutropha H16. Nat Biotechnol 24:1257–1262. doi:10.1038/nbt1244
Ranquet C, Ollagnier-de-Choudens S, Loiseau L, Barras F, Fontecave M (2007) Cobalt stress in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 282:30442–30451. doi:10.1074/jbc.M702519200
Rodrigue A, Effantin G, Mandrand-Berthelot MA (2005) Identification of rcnA (yohM), a nickel and cobalt resistance gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 187:2912–2916. doi:10.1128/JB.187.8.2912-2916.2005
Saier MH Jr, Tam R, Reizer A, Reizer J (1994) Two novel families of bacterial membrane proteins concerned with nodulation, cell division and transport. Mol Microbiol 11:841–847. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00362.x
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in Gram-negative bacteria. Bio/Technology 1:784–791. doi:10.1038/nbt1183-784
Smith RL, Banks JL, Snavely MD, Maguire ME (1993) Sequence and topology of the CorA magnesium transport system of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Identification of a new class of transport protein. J Biol Chem 268:14071–14080
Thorgersen MP, Downs DM (2007) Cobalt targets multiple metabolic processes in Salmonella enterica. J Bacteriol 189:7774–7781. doi:10.1128/JB.00962-07
Tindall BJ (2008) Rule 15 of the international code of nomenclature of bacteria: a current source of confusion. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1775–1778. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.2008/005314-0
Ullmann A (1984) One-step purification of hybrid proteins which have β-galactosidase activity. Gene 29:27–31. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(84)90162-8
von Rozycki T, Nies DH (2008) Cupriavidus metallidurans: evolution of a metal-resistant bacterium. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. doi:10.1007/s10482-008-9284-5
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mikolay, A., Nies, D.H. The ABC-transporter AtmA is involved in nickel and cobalt resistance of Cupriavidus metallidurans strain CH34. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 96, 183–191 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-008-9303-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-008-9303-6