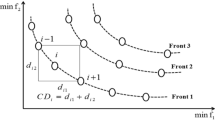
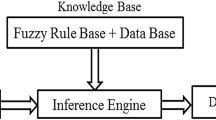
Abstract
Fuzziness is the primary and foremost perception of science and technology. This paper, for the first time, introduces a new concept on solution technique for fuzzy variable based non-linear programming problem with both decision variables and restriction being fuzzy in nature. First the problem is transformed in to a multi-objective non-linear programming problem, and then solving it by multiobjective genetic algorithm (MOGA) approach. The proposed procedure is applied on complex system reliability model to evaluate the system reliability in fuzzy environment, using MOGA by implementing new feature as refining operation. Numerical example is presented to illustrate proposed fuzzy system reliability model.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baoliang, L., Lirong, C., & Yanqing, W. (2014). Interval reliability for aggregated Markov repairable system with repair time omission. Annals of Operations Research, 212(1), 169–183.
Baykasoglu, A., & Gocken, T. (2012). A direct solution approach to fuzzy mathematical programs with fuzzy decision variables. Expert System with Applications, 39, 1972–1978.
Bector, C. R., & Chandra, S. (2002). On duality in linear programming under fuzzy environment. Fuzzy Sets and System, 125(3), 317–325.
Bellmann, R. E., & Zadeh, L. A. (1970). Decision making in a fuzzy environment. Management Science, 17(4), 141–164.
Bosma, R., van den Berg, J., Kaymak, U., Udo, H., & Verreth, J. (2012). A generic methodology for developing fuzzy decision models. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(1), 1200–1210.
Cao, B.Y. (2004). Multi-objective linear programming model with T-fuzzy variables, Journal of Fuzzy Mathematics, 12(2), 425–432.
Chanas, D. (1989). Fuzzy programming in multiobjective linear programming-a parametric approach. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 29, 303–313.
Chang, J. R., Chang, K. H., Liao, S. H., & Cheng, C. H. (2006). The reliability of general vague fault-tree analysis on weapon systems fault diagnosis. Soft Computing, 10(7), 531–542.
Chang, K. H., Cheng, C. H., & Chang, Y. C. (2010). Reprioritization of failures in a silane supply system using an intuitionistic fuzzy set ranking technique. Soft Computing, 14(3), 285–298.
Chatterjee, S., & Bandopadhyay, S. (2012). Reliability estimation using a genetic algorithm-based artificial neural network: An application to a load–haul–dump machine. Expert System Applications, 39(12), 10943–10951.
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., & Meyarivan, T. (2002). A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 6(2), 182–197.
Durillo, J. J., Nebro, A. J., Luna, F., Coello Coello, C. A., & Alba, E. (2010). Convergence speed in multi-objective metaheuristics: Efficiency criteria and empirical study. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 84(11), 1344–1375.
Garg, H., & Sharma, S. P. (2013). Multi-objective reliability-redundancy allocation problem using particle swarm optimizzation. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 64, 247–255.
Holland, H. J. (1975). Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. Michigan: University of Michigan.
Hong, D. H. (2010). Blackwell’s theorem for T-related fuzzy variables. Informations sciences, 180, 1769–1777.
Hsu, F., & Fu, L. (2001). A novel adaptive fuzzy variable structure control for a class of nonlinear uncertain systems via backstepping. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 122, 83–106.
Jeffrey, P. K., Steven, M. C., & Mark, E. O. (2013). Reliability of manufacturing equipment in complex environments. Annals of Operations Research, 209(1), 231–254.
Kaymak, U., & Sousa, J. M. C. (2001). Model predictive control using fuzzy decision functions. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics. Part B, Cybernetics, 31(1), 54–65.
Kaymak, U., & Sousa, J. M. C. (2003). Weighted constraint aggregation in fuzzy optimization. Constraints, 8(1), 29–46.
Koc, M. L., & Balas, C. E. (2013). Reliability analysis of a rubble mound breakwater using the theory of fuzzy random variables. Applied Ocean Research, 39, 83–88.
Lai, Y. J., & Hwang, C. L. (1992). Fuzzy mathematical programming methods and application. Berlin: Springer.
Li, X., Yan, R., & Zuo, M. J. (2009). Evaluating a warm standby system with components having proportional hazard rates. Operation Research Letters, 37, 56–60.
Lirong, C., Haijun, L., & Susan, H. X. (2014). Stochastic methods in reliability and risk management. Annals of Operations Research, 212(1), 1–2.
Liu, X. (2001). Measuring the satisfaction of constraints in fuzzy linear programming. Fuzzy Sets and System, 122, 263–275.
Mahapatra, G. S., & Roy, T. K. (2006). Fuzzy multi-objective mathematical programming on reliability optimization model. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 174(1), 643–659.
Mahapatra, G. S., & Roy, T. K. (2012). Reliability evaluation of bridge system with fuzzy reliability of components using interval nonlinear programming. Electronic Journal of Applied Statistical Analysis, 5(2), 151–163.
Mahapatra, G. S., Mahapatra, B. S., & Roy, P. K. (2014). Network reliability evaluation for fuzzy components: An interval programming approach. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems, 27, 743–751.
Mahdavi-Amiri, N., & Nasseri, S. H. (2007). Duality results and a dual simplex method for linear programming problems with trapezoidal fuzzy variables. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 158, 1961–1978.
Maleki, H. R., Tata, M., & Mashinchi, M. (1994). Linear programming with fuzzy variables. Fuzzy Sets and System, 66(3), 301–306.
Padmanabhan, D., Agarwal, H., Renaud, J. E., & Batill, S. M. (2006). A study using Monte Carlo simulation for failure probability calculation in reliability-based optimization. Optimization and Engineering, 7(3), 297–316.
Qin, R., Liu, Y., & Liu, Z. (2011). Methods of critical value reduction for type-2 fuzzy variables and their applications. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 235(5), 1454–1481.
Sakawa, M. (1993). Fuzzy Sets and Interactive multi-objective Optimization. New York: Plenum Press.
Satnciulescu, C., Fortemps, Ph, Installe, M., & Wertz, V. (2003). Multiobjective fuzzy linear programming problem with fuzzy decision variables. European Journal of Operational Research, 149, 654–675.
Schutze, O., Lara, A., & Coello Coello, C. A. (2011). On the influence of the number of objectives on the hardness of a multiobjective optimization problem. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 15(4), 444–455.
Shaocheng, T., Jiantao, T., & Tao, W. (2000). Fuzzy adaptive control of non-linear systems. Fuzzy Sets and System, 111(2), 153–167.
Srinivas, N., & Deb, K. (1994). Multi-objective function optimization using nondominated sorting genetic algorithms. Evolutionary computation, 2(3), 221–248.
Wang, S., & Watada, J. (2011). Some properties of T-independent fuzzy variables. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 53(5), 970–984.
Wu, F., Lu, J., & Zhang, G. (2006). A new approximate algorithm for solving multiple objective linear programming problems with fuzzy parameters. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 174(1), 524–544.
Xiaoyan, Z., & Way, K. (2014). Importance measures in reliability and mathematical programming. Annals of Operations Research, 212(1), 241–267.
Xue, F., Tang, W., & Zhao, R. (2008). The expected value of a function of a fuzzy variable with a continuous membership function. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 55(6), 1215–1224.
Zadeh, L. A. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Information and Control, 8, 338–353.
Zhong, X., Ichchou, M., & Saidi, A. (2010). Reliability assessment of complex mechatronic systems using a modified nonparamertic belief propagation algorithm. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 95, 1174–1185.
Acknowledgments
The first author acknowledges the research grant supported by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research of India under the research project 25(0191)/10/EMR-II.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Definition: symmetrical triangular fuzzy number
Appendix: Definition: symmetrical triangular fuzzy number
Parametric form: A fuzzy number is a pair \((\underline{\nu },~ \overline{\nu })\) of function \(\underline{\nu }(t)\), \(\overline{\nu }(t) :~ 0\le t\le ~1\) which must satisfy the following properties:
-
(1)
\(\underline{\nu }(t)\) is bounded monotonic increasing left continuous function.
-
(2)
\(\overline{\nu }(t)\) is bounded monotonic decreasing right continuous function.
-
(3)
\(\underline{\nu }(t)~\le ~\overline{\nu }(t)\), \(0~\le ~t~\le ~1\).
A symmetric triangular fuzzy number \(\tilde{A}=[x_{0},~\omega ]\) center at \( x_{0}\) with basis \(2\omega \), is defined with following membership functions (Fig. 4)
The parametric form of the above TFN is \(\underline{\nu }(t)=x_{0}-\omega +\omega t,~\overline{\nu }(t)=x_{0}+\omega -\omega t\).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahapatra, G.S., Mahapatra, B.S. & Roy, P.K. A new concept for fuzzy variable based non-linear programming problem with application on system reliability via genetic algorithm approach. Ann Oper Res 247, 853–866 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-015-1863-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-015-1863-z