Abstract
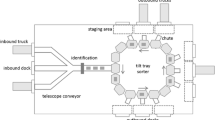
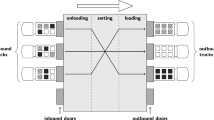
This paper presents a model for a dock assignment problem, where trailers need to be assigned to gates for a given period of time for loading or unloading activities. The parking lot is used as a buffer zone. Transportation between the parking lot and the gates is performed by additional resources called terminal tractors. The problem is modeled as a three-stage flexible flow shop, where the first and the third stage share the same identical parallel machines and the second stage consists of a different set of identical parallel machines. We examine multiple integer-programming formulations for the parallel-machine model in stage two and for the three-stage flow shop and we provide extensive computational results. Our goal is to explore the limits of the instance sizes that can be solved to guaranteed optimality within acceptable running times using integer programming.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artigues, C., Demassey, S., & Néron, E. (2008). Control systems, robotics and manufacturing series. Resource-constrained project scheduling. London: ISTE Ltd.
Bard, J. F., & Rojanasoonthon, S. (2006). A branch-and-price algorithm for parallel machine scheduling with time windows and job priorities. Naval Research Logistics, 53, 24–44.
Berghman, L., Leus, R., & Spieksma, F. C. R. (2010). Optimal solutions for a dock assignment problem with trailer transportation (Working Paper KBI-1010). Department of Decision Sciences and Information Management (KBI), Faculty of Business and Economics, KULeuven, Leuven (Belgium).
Bierwirth, C., & Meisel, F. (2010). A survey of berth allocation and quay crane scheduling problems in container terminals. European Journal of Operational Research, 202, 615–627.
Bigras, L., Gamache, M., & Savard, G. (2008). Time-indexed formulations and the total weighted tardiness problem. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 20(1), 133–142.
Bish, E. K., Leong, T., Li, C., Ng, J. W. C., & Simchi-Levi, D. (2001). Analysis of a new vehicle scheduling and location problem. Naval Research Logistics, 48, 363–385.
Bish, E. K., Chen, F. Y., Leong, Y. T., Nelson, B. L., Ng, J. W. C., & Simchi-Levi, D. (2005). Dispatching vehicles in a mega container terminal. OR-Spektrum, 27, 491–506.
Blazewicz, J., Dror, M., & Weglarz, J. (1991). Mathematical programming formulations for machinery scheduling: a survey. European Journal of Operational Research, 51, 283–300.
Böse, J., Reiners, T., Steenken, D., & Voss, S. (2000). Vehicle dispatching at seaport container terminals using evolutionary algorithms. In Proceedings of the 33rd Hawaii international conference on system sciences (pp. 1–10).
Boysen, N., Fliedner, M., & Scholl, A. (2010). Scheduling inbound and outbound trucks at cross docking terminals. OR-Spektrum, 32, 135–161.
Chen, J. S., Pan, J. C. H., & Wu, C. K. (2007). Minimizing makespan in reentrant flow-shops using hybrid tabu search. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 34, 353–361.
Cheng, T. C. E., & Sin, C. C. S. (1990). A state-of-the-art review of parallel-machine scheduling research. European Journal of Operational Research, 47, 271–292.
Cheong, C. Y., Tan, K. C., Liu, D. K., & Lin, C. J. (2010). Multi-objective and prioritized berth allocation in container ports. Annals of Operations Research, 180, 63–103.
Choi, S. W., & Kim, Y. D. (2008). Minimizing makespan on an m-machine re-entrant flowshop. Computers & Operations Research, 35, 1684–1696.
Christofides, N., Alvarez-Valdés, R., & Tamarit, J. M. (1987). Project scheduling with resource constraints: a branch-and-bound approach. European Journal of Operational Research, 29(3), 262–273.
Crama, Y., & Spieksma, F. C. R. (1996). Scheduling jobs of equal length: complexity, facets and computational results. Mathematical Programming, 72, 207–227.
Dallery, Y., & Gershwin, S. B. (1992). Manufacturing flow line systems: a review of models and analytical results. Queueing Systems, 12, 3–94.
Dessouky, M. M. (1998). Scheduling identical jobs with unequal ready times on uniform parallel machines to minimize the maximum lateness. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 34(4), 793–806.
Dyer, M. E., & Wolsey, L. A. (1990). Formulating the single machine sequencing problem with release dates as a mixed integer problem. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 26, 255–270.
Graves, S. C., Meal, H. C., Stefeka, D., & Zeghmi, A. H. (1983). Scheduling of re-entrant flow shops. Journal of Operations Management, 3(4), 197–207.
Guan, Y., Yang, K. H., & Zhou, Z. (2010). The crane scheduling problem: models and solution approaches. Annals of Operations Research. doi:10.1007/s10479-010-0765-3.
Gupta, J. N. C., Krüger, K., Lauff, V., Werner, F., & Sotskov, Y. N. (2002). Heuristics for hybrid flow shops with controllable processing times and assignable due dates. Computers & Operations Research, 29, 1417–1439.
Gupta, J. N. D., Hairiri, A. M. A., & Potts, C. N. (1997). Scheduling a two-stage hybrid flow shop with parallel machines at the first stage. Annals of Operations Research, 69, 171–191.
Haouari, M., Hidri, L., & Gharbi, A. (2006). Optimal scheduling of a two-stage hybrid flow shop. Mathematical Methods of Operations Research, 64, 107–124.
ILOG (2008). ILOG. CPLEX, 11, 0 user’s manual. ILOG, Inc., available online at http://www.decf.berkeley.edu/help/apps/ampl/cplex-doc/.
Jain, V., & Grossmann, I. E. (2001). Algorithms for hybrid MILP/CP models for a class of optimization problems. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 13(4), 258–276.
Kedad-Sidhoum, S., Solis, Y. R., & Sourd, F. (2008). Lower bounds for the earliness-tardiness scheduling problem on parallel machines with distinct due dates. European Journal of Operational Research, 189, 1305–1316.
Kis, T., & Pesch, E. (2005). A review of exact solution methods for the non-preemptive multiprocessor flowshop problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 164, 592–608.
Kise, H., Shioyama, T., & Ibaraki, T. (1991). Automated two-machine flow-shop scheduling: a solvable case. IIE Transactions, 23(1), 10–16.
Lenstra, J. K., Rinnooy Kan, A. H. G., & Brucker, P. (1977). Complexity of machine scheduling problems. Annals of Discrete Mathematics, 1, 343–362.
Linn, R., & Zhang, W. (1999). Hybrid flow shop scheduling: a survey. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 37, 57–61.
Mellouli, R., Sadfi, C., Chu, C., & Kacem, I. (2009). Identical parallel-machine scheduling under availability constraints to minimize the sum of completion times. European Journal of Operational Research, 179, 1150–1165.
Miao, Z., Lim, A., & Ma, H. (2009). Truck dock assignment problem with operational time constraint within crossdocks. European Journal of Operational Research, 192, 105–115.
Moursli, O., & Pochet, Y. (2000). A branch-and-bound algorithm for the hybrid flowshop. International Journal of Production Economics, 64, 113–125.
Nichi, T., Hiranaka, Y., & Inuiguchi, M. (2010). Lagrangian relaxation with cut generation for hybrid flowshop scheduling problems to minimize the total weighted tardiness. Computers & Operations Research, 37, 189–198.
Paternina-Arboleda, C. D., Montoya-Torres, J. R., Acero-Domingues, M. J., & Herrera-Hernandez, M. C. (2008). Scheduling jobs on a k-stage flexible flow-shop. Annals of Operations Research, 164, 29–40.
Ribas, I., Leisten, R., & Framiñan, J. M. (2010). Review and classification of hybrid flow shop scheduling problems from a production system and a solutions procedure perspective. Computers & Operations Research, 37, 1439–1454.
Sadykov, R., & Wolsey, L. A. (2006). Integer programming and constraint programming in solving a multimachine assignment scheduling problem with deadlines and release dates. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 18(2), 209–217.
Sousa, J. P., & Wolsey, L. A. (1992). A time indexed formulation of non-preemptive single machine scheduling problems. Mathematical Programming, 54, 353–367.
Stahlbock, R., & Voß, S. (2008). Operations research at container terminals: a literature update. OR-Spektrum, 30, 1–52.
Tang, L., & Xuan, H. (2006). Lagrangian relaxation algorithms for real-time hybrid flowshop scheduling with finite intermediate buffers. The Journal of the Operational Research Society, 57, 316–324.
Uetz, M. (2001). Algorithms for deterministic and stochastic scheduling. PhD thesis, Technische Universität Berlin, Germany.
van den Akker, J. M. (1994). LP-based solution methods for single-machine scheduling problems. PhD thesis, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, the Netherlands.
van den Akker, J. M., Hurkens, C. A. J., & Savelsbergh, M. W. P. (2000). Time-indexed formulations for machine scheduling problems: column generation. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 12(2), 111–124.
Vignier, A., Billaut, J. C., & Proust, C. (1999). Hybrid flowshop scheduling problems: state of the art. RAIRO Operations Research, 33(2), 117–183.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berghman, L., Leus, R. & Spieksma, F.C.R. Optimal solutions for a dock assignment problem with trailer transportation. Ann Oper Res 213, 3–25 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-011-0971-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-011-0971-7