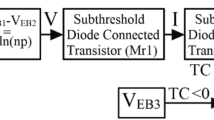
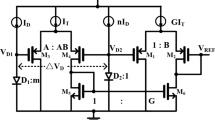
Abstract
This work presents a resistorless self-biased and small area sub-bandgap voltage reference that works in the nano-ampere consumption range with 0.75 V of power supply. The circuit applies a curvature compensation technique that allows an extended temperature range without compromising the temperature stability. The behavior of the circuit is analytically described, and a design methodology is proposed which allows the separate adjustment of the bipolar junction transistor bias current and its curvature compensation. Simulation results are presented for a 180 nm CMOS process, where a reference voltage of 469 mV is designed, with a temperature coefficient of 5 ppm/°C for the −40 to 125 °C extended temperature range. The power consumption of the whole circuit is 16.3 nW under a 0.75 V power supply at 27 °C. The estimated silicon area is 0.0053 mm2.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duan, Q., & Roh, J. (2015). A 1.2-V 4.2 ppm/°C high-order curvature-compensated CMOS bandgap reference. Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, IEEE Transactions on, 62(3), 662–670. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2014.2374832.
Galup-Montoro, C., & Schneider, M. R. C. (2007). MOSFET modeling for circuit analysis and design. Hackensack: World Scientific.
Magnelli, L., Crupi, F., Corsonello, P., Pace, C., & Iannaccone, G. (2011). A 2.6 nW, 0.45 V temperature-compensated subthreshold CMOS voltage reference. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 46(2), 465–474. doi:10.1109/JSSC.2010.2092997.
Mattia, O.E., Klimach, H., Bampi, S. (2014). 0.7 V supply, 8 nW, 8 ppm/°C resistorless sub-bandgap voltage reference. In: 2014 IEEE 57th international midwest symposium on circuits and systems (MWSCAS), pp. 479–482. IEEE, doi: 10.1109/MWSCAS.2014.6908456.
Mattia, O. E., Klimach, H., & Bampi, S. (2014). Resistorless BJT bias and curvature compensation circuit at 3.4 nW for CMOS bandgap voltage references. Electronics Letters, 50(12), 863–864. doi:10.1049/el.2013.3417.
Mattia, O. E., Klimach, H., & Bampi, S. (2015). Sub-1 V supply 5 nW 11 ppm/°C resistorless sub-bandgap voltage reference. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 85(1), 17–25. doi:10.1007/s10470-015-0582-3. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10470-015-0582-3.
Meijer, G.C., Schmale, P.C., Zalinge, K.V. (1981). A new curvature-corrected bandgap reference. Solid State Circuits Conference, 1981. ESSCIRC ’81. 7th European (6), doi:10.1109/JSSC.1982.1051872.
Ming, X., Ma, Y. Q., Zhou, Z. K., & Zhang, B. (2010). A high-precision compensated CMOS bandgap voltage reference without resistors. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 57(10), 767–771. doi:10.1109/TCSII.2010.2067770.
Osaki, Y., Hirose, T., Kuroki, N., & Numa, M. (2013). 1.2-V supply, 100-nW, 1.09-V bandgap and 0.7-V supply, 52.5-nW, 0.55-V subbandgap reference circuits for nanowatt CMOS LSIs. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 48(6), 1530–1538. doi:10.1109/JSSC.2013.2252523.
Seok, M., Kim, G., Blaauw, D., & Sylvester, D. (2012). A portable 2-transistor picowatt temperature-compensated voltage reference operating at 0.5 V. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 47(10), 2534–2545. doi:10.1109/JSSC.2012.2206683.
Song, B.S.S.B.S., Gray, P. A (1983). precision curvature-compensated CMOS bandgap reference. 1983 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference. Digest of Technical Papers XXVI (6). doi:10.1109/ISSCC.1983.1156435.
Tsividis, Y. P. (1980). Accurate analysis of temperature effects in IC-VBE characteristics with application to bandgap reference sources. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 15(6), 1076–1084.
Vittoz, E., & Neyroud, O. (1979). A low-voltage CMOS bandgap reference. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuit, 14(3), 573–579. doi:10.1109/JSSC.1979.1051218.
Wang, Y., Zhu, Z., Yao, J., & Yang, Y. (2015). A 0.45-V, 14.6-nW CMOS subthreshold voltage reference with no resistors and no BJTs. Circuits Systtems II Express Briefs, IEEE Transaction, 62(7), 621–625.
Widlar, R. (1971). New developments in IC voltage regulators. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 6(1), 2–7. doi:10.1109/JSSC.1971.1050151.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to MOSIS Education Program, CNPq and CAPES brazilian agencies, CI-BRASIL Program and NSCAD Microelectronics for support
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gomez Caicedo, J.A., Mattia, O.E., Klimach, H. et al. 0.75 V supply nanowatt resistorless sub-bandgap curvature-compensated CMOS voltage reference. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 88, 333–345 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0722-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-016-0722-4