Abstract
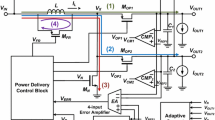
This paper describes a 10-bit 1.8 V 45 mW 100 MHz transmitter chip (TX chip) that is fabricated using 0.18 μm 1P6 M CMOS technology for use in an xDSL modem in a home network. The chip is composed of a 10-bit segmented digital-to-analog converter (DAC) and a fully differential adaptive line driver (LD). In designing the DAC, the switched-current method is used to increase the conversion speed; the anti-process-variation current cell with threshold-voltage compensation is used to reduce the linearity error, and the current cell, with differential input and gain boosting, is used to minimize the feedthrough error and tapered error distribution. The circuit layout of the current source has four-phase symmetry, not only to increase the linearity but also to eliminate the gradient error. To design a fully differential adaptive LD, the feed-forward capacitor and quiescent current control circuit are used to reduce the zero-crossing distortion and to minimize the second-order harmonic. Additionally, the power efficiency is increased using an output-impedance matching circuit. Measurements reveal that, for a TX chip at a differential load of 100 Ω and a supplied voltage of 1.8 V, the efficient number of bits, operating frequency, output voltage, output current, power consumption, differential nonlinearity error and integral nonlinearity error are 9 bits, 100 MHz, ± 0.874 V, ± 10 mA, 45.8 mW, −0.80 to +0.62 LSB, and −0.92 to +0.82 LSB, respectively.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stojkovic, N. (2006). ADSL analog front end. Automatika, 47(1–2), 59–67.
Johns, D. A., & Essig, D. (1997). Integrated circuits for data transmission over twisted-pair channels. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 32(3), 398–406.
Lee, S.S. (2002). Integration and system design trends of ADSL analog front ends and hybrid line interfaces. In Proceedings IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference(CICC), Orlando, Florida (pp. 37-44).
Lin, C. H., & Bult, K. (1998). A 10-b, 500-MSample/s CMOS DAC in 0.6 mm2. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 33(12), 1948–1958.
Bosch, A. V. D., Steyaert, M., & Sansen, W. (2004). Static and dynamic performance limitations for high speed D/A converters. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Miki, T., Nakamura, Y., Nakaya, M., Asai, S., Akasaka, Y., & Horiba, Y. (1986). An 80- MHz 8-bit CMOS D/A converter. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 21(6), 983–988.
Cornil, J.P., Chang, Z.Y., Louagie, F., Overmeive, W., & Vertaille, J. (1999). A 0.5 μm CMOS ADSL analog front-end IC. In Proceedings IEEE International Solid-State Circuit Conference (ISSCC99), San Francisco, California (pp. 238-239).
Tan, N., Caster, F., Eichrodt, C., George, S.O., Horng, B., & Zhao, J. (2003). A universal quad AFE with integrated filters for VDSL, ADSL, and G.SHDSL. In Proceedings IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC 2003), San Jose, California (pp. 599-602).
Gupta, T., Yang, F., Dong, W., Tabatabaei, A., Singh, R., Aslanzadeh, H., Khalili, A., Vats, S., Arno, S., & Campeau, S. (2012). A sub-2 W 10GBase-T analog front-end in 40 nm CMOS process. In Proceedings IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA (pp. 410-412).
Myderrizi, I., & Zeki, A. (2010). A 12-bit 0.35-um CMOS area optimized current-steering hybrid DAC. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 65, 67–75.
Mahadevan, R., & Johns, D. A. (2000). A differential 160-MHz self-terminating adaptive CMOS line driver. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 35(12), 1889–1894.
Conroy, C., Sheng, S., Feldman, A., Uehara, G., Yeung, A., Hung, C.J., Subramanian, V., Chiangj, P., Lai, P., Si, X., Fan, J., Flynn, D., & He, M. (1999). A CMOS analog front-end IC for DMT ADSL. In Proceedings IEEE International Solid-State Circuit Conference (ISSCC99), San Francisco, California (pp. 240-241).
Weinberger, H., Wiesbauer, A., Fleischhacker, C., Hauptmann, J., Ferianz, T., Staber, M., et al. (2002). An ADSL-RT full-rate analog front end IC with integrated line driver. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 37(7), 857–865.
Cresi, M., Hester, R., Maclean, K., Agah, M., Quarfoot, J., Kozak, C., Gibson, N., & Hagen, T. (2001). An ADSL central office analog front-end integrating actively-terminated line driver, receiver and filters. In Proceedings IEEE International Solid-State Circuit Conference (ISSCC 2001), San Francisco, California (pp. 304-305).
Sabouri, F., & Shariadoust, R. (2002). A 740 mW ADSL line driver for central office with 75 dB MTPR. In Proceedings IEEE International Solid-State Circuit Conference (ISSCC 2002), San Francisco, California (pp. 322-323).
Ingels, M., Bojja, S., & Wouters, P. (2002). A 0.5 μm CMOS low-distortion low-power line driver with embedded digital adaptive bias algorithm for integrated ADSL analog front-ends. In Proceedings IEEE International Solid-State Circuit Conference (ISSCC 2002), San Francisco, California (pp. 324-325).
Bosch, A.V.D., Borremans, M., Steyaert, M., & Sansen, W. (2001). A 12 b 500 MSample/s current-steering CMOS D/A converter. In Proceedings IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, California (pp. 366-367).
Bastos, J., Marques, A. M., Steyaert, S. J., & Sansen, W. (1998). A 12-bit intrinsic accuracy high-speed CMOS DAC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 33(12), 1959–1969.
Chin, S. Y., & Wu, C. Y. (1994). A 10-b 125-MHz CMOS digital-to-analog converter (DAC) with threshold-voltage compensated current sources. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 29(11), 1374–1380.
Razavi, B. (2001). Design of Analog CMOS Integrated Circuits. New York (NY): McGraw-Hill.
Schafferer, B., & Adams, R. (2004). A 3 V CMOS 400mW 14b 1.4GS/s DAC for multi-carrier applications. In Proceedings IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC 2004), San Francisco, California (pp. 360-369).
Lu, C. W., & Huang, Y. C. (2004). 1.5 V large-driving class-AB buffer amplifier with quiescent current control. Electronics Letters, 40(1), 1–2.
You, F., Embadi, S. H. K., & Sanchez-Sinencio, E. (1998). Low-voltage class AB buffer with quiescent current control. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 33(6), 915–920.
Babanezhad, J. N. (1999). A 100-MHz, 50 ohm, −45-dB distortion, 3.3-V CMOS line driver for Ethernet and fast Ethernet networking application. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 34(8), 1044–1049.
Jinup, L., Sungwon, N., Kwangoh, K., & Joongho, C. (2003). A 3.3-V ISDN U-interface line driver with a new IQ-control circuit. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(8), 1421–1424.
Serneels, B., Steyaert, M., & Dehaene, W. (2007). A 237mW ADSL2 + CO line driver in standard 1.2 V 0.13-μm CMOS. In Proceedings IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, California (pp. 524–619).
Hogervorst, R., Tourette, B., Monier, N., Metayer, O., Afifi, E., Delefosse, J.C., & Michel, J.Y. (2004). A 3 V CMOS quad-spectrum ADSL CPE analog front-end with 5 V integrated line driver. In Proceedings IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, California (pp. 332–333).
Mehrmanesh, S., Atarodi, M., Aslanzadeh, H. A., Saeedi, S., & Safarian, A. Q. (2004). A new full COMS 2.5-V two-stage line driver with variable gain for ADSL applications. In Proceedings International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Vancouver, Canada (pp. IV-405–IV-408).
Nam, C., Pu, Y. G., Kim, S. W., & Lee, K. Y. (2009). Full CMOS single supply PLC SoC ASIC with integrated analog front-end. Journal of Semiconductor Technology and Science, 9(2), 85–90.
Lu, C.W., Yin, P.Y., Hsiao, C.M., & Frank Chang, M.C. (2011). A 10b resistor–resistor-string DAC with current compensation for compact LCD driver ICs. In IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC-2011), San Francisco, California (pp. 318–319).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sung, GM., Chou, WD. & Yu, CP. A 10-bit 1.8 V 45 mW 100 MHz CMOS transmitter chip for use in an XDSL modem in a home network. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 81, 515–527 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0398-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0398-6