Abstract
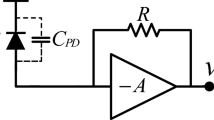
This work presents the design and the measured performance of a 8 Gb/s transimpedance amplifier (TIA) fabricated in a 90 nm CMOS technology. The introduced TIA uses an inverter input stage followed by two common-source stages with a 1.5 kΩ feedback resistor. The TIA is followed by a single-ended to differential converter stage, a differential amplifier and a 50 Ω differential output driver to provide an interface to the measurement setup. The optical receiver shows a measured optical sensitivity of −18.3 dBm for a bit error rate = 10−9. A gain control circuitry is integrated with the TIA to increase its input photo-current dynamic range (DR) to 32 dB. The TIA has an input photo-current range from 12 to 500 μA without overloading. The stability is guaranteed over the whole DR. The optical receiver achieves a transimpedance gain of 72 dBΩ and 6 GHz bandwidth with 0.3 pF total input capacitance for the photodiode and input PAD. The TIA occupies 0.0036 mm2 whereas the complete optical receiver occupies a chip area of 0.46 mm2. The power consumption of the TIA is only 12 mW from a 1.2 V single supply voltage. The complete chip dissipates 60 mW where a 1.6 V supply is used for the output stages.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, C. Y., Wang, C. S., & Wang, C. K. (2007). An 18-mW two-stage CMOS transimpedance amplifier for 10 Gb/s optical application. In IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference, A-SSCC, pp. 412–415.
Lu, Z., Yeo, K. S., Ma, J., Do, M. A., Lim, W. M., & Chen, X. (2007). Broad-band design techniques for transimpedance amplifiers. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 54(3), 590–600.
Park, K., Oh, W. S., Choi, B. Y., Han, J. W., & Park, S. M. (2007). A 4-channel 12.5 Gb/s common-gate transimpedance amplifier array for DVI/HDMI applications. In Proceedings—IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 2192–2195.
Park, S. M., & Yoo, H. J. (2004). 1.25-Gb/s regulated cascode CMOS transimpedance amplifier for gigabit ethernet applications. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 39(1), 112–121.
Chan, C. T., & Chen, O. T. C. (2006). Inductor-less 10 Gb/s CMOS transimpedance amplifier using source-follower regulated cascode and double three-order active feedback. In Proceedings—IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 5487–5490.
Atef, M., & Zimmermann, H. (2012). 10 Gbit/s 2 mW inductorless transimpedance amplifier. In IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), May 2012, pp. 1728–1731.
Säckinger, E. (2005). Broadband circuits for optical fiber communication. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley–Interscience.
Schneider, K., & Zimmermann, H. (2006). Highly sensitive optical receivers. Springer series in advanced microelectronics, Berlin.
Atef, M., Swoboda, R., & Zimmermann, H. (2010). Optical receiver for multicarrier modulation in short-reach communication. Electronics Letters, 46(3), 233–234.
Schneider, K., & Zimmermann, H. (2006). Three-stage burst-mode transimpedance amplifier in deep-sub-μm CMOS technology. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 53(7), 1458–1467.
Aznar, F., Gaberl, W., & Zimmermann, H. (2011). A 0.18 μm CMOS transimpedance amplifier with 26 dB dynamic range at 2.5 Gb/s. Microelectronics Journal, 42(10), 1136–1142.
Ingels, M., Van Der Plas, G., Crols, J., & Steyaert, M. (1994). A CMOS 18 THzΩ 248 Mb/s transimpedance amplifier and 155 Mb/s LED-driver for low cost optical fiber links. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 29(12), 1552–1559.
Vivien, L., Polzer, A., Marris-Morini, D., Osmond, J., Hartmann, J., Crozat, P., et al. (2012). Zero-bias 40 Gbit/s germanium waveguide photodetector on silicon. Optics Express, 20, 1096–1101.
Shammugasamy, B, & Zulkifli, T. Z. A. (2008). A 10-Gb/s fully balanced differential output transimpedance amplifier in 0.18-μm CMOS technology for SDH/SONET application. In IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems (APCCAS), pp. 684–687.
Chen, H. L., Chen, C. H., Yang, W. B., & Chiang, J. S. (2009). Inductorless CMOS receiver front-end circuits for 10-Gb/s optical communications. Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, 12(4), 449–458.
Momeni, O., Hashemi, H., & Afshari, E. (2010). A 10-Gb/s inductorless transimpedance amplifier. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 57(12), 926–930.
Hassan, M., & Zimmermann, H. (2011). An 85 dB dynamic range transimpedance amplifier in 40 nm CMOS technology. In NORCHIP 2011, pp. 1–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atef, M., Aznar, F., Schidl, S. et al. 8 Gbits/s inductorless transimpedance amplifier in 90 nm CMOS technology. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 79, 27–36 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0242-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0242-4