Abstract
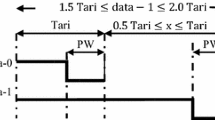
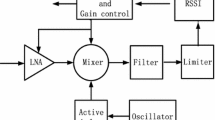
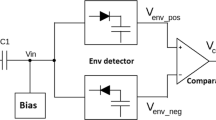
In order to reduce the power consumption of RFID tags and increase the reading range of RFID systems, this paper proposes an ASK demodulator that uses a new approach to reduce the threshold voltage of diode connected MOS transistors as an obstacle in the design of the envelope detector. Also, an ultra low power comparator is used for further power reduction. This circuit has been simulated in a 0.18 μm CMOS technology to satisfy EPC Class 1 Generation 2 standard protocol emphasizing on the reduction of power consumption. The proposed circuit can correctly demodulate the minimum input RF signal amplitude of 180 mV for modulation depths of 55–100 % with 40–160 kb/s data rates. A total power consumption of less than 290 nW is achieved at a 1.2 V power supply. Effects of the input signal additive white noise as well as the process and temperature variations on the signal demodulation is also investigated in this paper.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feldengut, T., Wang, J., Kolnsberg, S., Kokozinski, R. (2008). An Analog Front End for a Passive UHF Transponder with Temperature Sensor. 38th European Microwave Conference, pp. 1200–1203, Amsterdam, The Netherland. doi:10.1109/EUMC.2008.4751675
Wang, Y., Wen, G., Mao, W., He, Y., & Zhu, X. (2011). Design of a passive UHF RFID tag for the ISO18000-6C protocol. Journal of Semiconductors, 32(5), 055009.
Liu, Z., Zhang, C., Li, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, Z. (2009). A Novel Demodulator for Low Modulation Index RF Signal in Passive UHF RFID Tag. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 2109–2112, Taipei, Taiwan. doi:10.1109/ISCAS.2009.5118211
EPC. (2007). Specification for RFID air interface, EPC™ Radio-Frequency Identity protocols Class-1 Generation-2 UHF RFID protocol for communications at 860 MHz–960 MHz Version 1.1.0, EPC Global Inc.
Ahmed, A., et al. (2009). A compact low-power UHF RFID tag. Microelectronics Journal, 40(11), 1–10.
Ma, Changming, wu, Xingjun, Zhang, Chun, & Wang, Zhihua. (2008). A Low-Power RF Front-End of Passive UHF RFID Transponders. IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems, I, 73–76.
Curty, Jari-Pascal, Joehl, Norbert, Dehollain, Catherine, & Declercq, Michel J. (2005). Remotely Powered Addressable UHF RFID Integrated System. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40(11), 2193–2195.
Cantatore, Eugenio. (2007). A 13.56 MHz RFID system based on organic transponders. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 42(1), 84–85.
Usami, M., Sato, A., Sameshima, K., Watanabe, K., Yoshigi, H., Imura, R. (2003). Powder LSI: An Ultra Small RF Identification Chip for Individual Recognition Applications. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, Vol. 1, pp. 398–501, San Francisco, USA. doi:10.1109/ISSCC.2003.1234354
Karthaus, U., & Fischer, M. (2003). Fully integrated passive UHF RFID transponder IC with 16.7-μW minimum RF input power. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(10), 1602–1608.
Umeda, T., et al. (2006). A 950-MHz rectifier circuit for sensor network tags with 10-m distance. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 41(1), 35–41.
Nakamoto, H., et al. (2007). A passive UHF RF identification CMOS tag IC using ferroelectric RAM in 0.35-μm technology. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 42(1), 101–110.
Meng-Lin Hsia, Yu-Sheng Tsai, Oscal T.-C. Chen. (2006). An UHF Passive RFID Transponder Using a Low-Power Clock Generator without Passive Components. 49th IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Vol. 2, pp. 11–15, San Juan, Puerto Rico.
Barnett, R. E. (2007). High Efficiency RF to DC Conversion and Ultra-Low-Power Analog Front End Circuits for Low-Cost Field-Powered UHF RFID. Doctor of Philosophy Dissertation Presented to the Faculty of the University of Texas at Dallas, Richardson, U.S. state of Texas.
Yin, Jun, et al. (2010). A system-on-chip EPC Gen-2 passive UHF RFID tag with embedded temperature sensor. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 45(11), 2404–2420.
Myoeng-Jae, C., Sung-Eon, J. (2010). Design of Low Power ASK CMOS Demodulator Circuit for RFID Tag. IEEE International Conference of Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits, pp. 1–4, Hong Kong, China.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of University of Tehran for this research under grant number 8181013/rp/02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jomehei, M.G., Sheikhaei, S. & Forouzandeh, B. A novel ultra low power ASK demodulator for a passive UHF RFID tag compatible with C1 G2 EPC standard protocol. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 75, 21–29 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0037-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0037-7