Abstract
The pursuit for energy and area efficient circuits has become greater than ever. Low power and small area integrated circuits are in high demand today. Reference voltage circuitry for analog-to-digital conversion comprises 20–30 % of the overall power and area of the ADC. To this end, a fully differential 1.5-bit multiplying digital-to-analog converter (MDAC) precluding reference voltages, that can be employed in MDAC-based ADCs, is presented. Reference shifting is performed in current-mode and the gain of two is obtained by associating charged capacitors in series in the opamp’s feedback loop, achieving a unity feedback factor. Theoretical analyses of various nonideal effects of the reference shifting and gain of two are presented and confirmed with electrical level simulations. Furthermore, to avoid reference voltages in the local quantizers, an architecture with built-in thresholds is used. A proof of concept 1.5-bit/stage 7-bit 500 MS/s pipeline ADC is designed using the proposed MDAC in a standard digital 0.13 μm CMOS technology. The ADC achieves a peak SNDR and SFDR of 36.1 and 48.7 dB, respectively, while dissipating 12.7 mW from a single 1.2 V supply voltage, and it does not require external reference circuitry.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
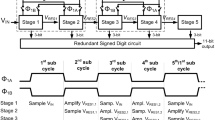
MDAC-based ADCs are composed of the multi-step flash, the multi-stage algorithmic, and the pipeline architectures.
In [9] it is demonstrated that reference voltage circuits can have 1-bit lower accuracy than the resolution of the ADC.
The capacitor mismatch-insensitivity advantage is validated theoretically here, but not emphasized in the prototype ADC because the objective of this paper is to demonstrate how the proposed MDAC solves system-level issues.
If I P and I N are not exactly matched, a current error (I e ) arises and results in an additive term appearing at the end of (3). It only affects the capacitor mismatch error (5), depending mainly on an I e /I REF term. For values of I e /I REF up to 20 %, I e may be neglected. Small I e is easily achieved using nonminimum transistor lengths.
This is true assuming an equal C L for both the proposed and conventional MDACs. However, in a pipeline ADC employing the proposed MDAC in all stages, the β enhancement factor reduces to 2, because of the extra sampling capacitor, C 3j .
The model of the opamp used in these simulations has A 0 = 106 dB, GBW = 3.2 GHz, and a load capacitance, C L , of 2 pF is considered.
References
Hsu, C. C., Huang, C. C., Lin, Y. H., Lee, C. C., Soe, Z., Aytur, T., & Yan, R. H. (2007). A 7b 1.1GS/s reconfigurable time-interleaved ADC in 90nm CMOS. In Symposium on VLSI circuits. Digest on techical papers (pp. 66–67).
Jussila, J., Ryynanen, J., Kivekas, K., Sumanen, L., Parssinen, A., & Halonen, K. (2001). A 22-mA 3.0-dB NF direct conversion receiver for 3G WCDMA. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 36, 2025–2029.
Khorram, S., Darabi, H., Zhou, Z., Li, Q., Marholev, B., Chiu, J., Castaneda, J., Chien, H. M., Anand, S., Wu, S., Pan, M. A., Roofougaran, R., Kim, H. J., Lettieri, P., Ibrahim, B., Rael, J., Tran, L., Geronaga, E., Yeh, H., Frost, T., Trachewsky, J., & Rofougaran, A. (2005). A fully integrated SOC for 802.11b in 0.18-μm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40, 2492–2501.
Tu, W. H., Kang, & T. H. (2008). A 1.2V 30mW 8b 800MS/s time-interleaved ADC in 65nm CMOS. In Symposium on VLSI circuits. Digest of technical papers (pp. 72–73).
Singer, L., Ho, S., Timko, M., & Kelly, D. (2000). A 12 b 65 MSample/s CMOS ADC with 82 dB SFDR at 120 MHz. In IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC). Digest of technical papers (pp. 38–39).
Bult, K. (2009). Embedded analog-to-digital converters. In Proceedings of European solid-state circuits conference (ESSCIRC) (pp. 52–64).
Kuppambatti, J., & Kinget, P. (2012). A current reference pre-charged zero-crossing pipeline-SAR ADC in 65nm CMOS. In Proceedings of IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC).
Lewis, S. H., Fetterman, H. S., Gross, Jr G. F., Ramachandran, R., & Viswanathan, T. R. (1992). A 10-b 20-M sample/s analog-to-digital converter. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 27, 351–358.
Mok, W. I., Mak, P. I., U, S. P., & Martins, R. P. (2004). Modeling of noise sources in reference voltage generator for very-high-speed pipelined ADC. In Proceedings of IEEE midwest symposium on circuits systems (Vol. 1, pp. I–5–8).
Sumanen, L., Waltari, M., & Halonen, K. A. I. (2001). A 10-bit 200-MS/s CMOS parallel pipeline A/D converter. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 36(7), 1048–1055.
Cho, Y. J., & Lee, S. H. (2005). An 11b 70-MHz 1.2-mm2 49-mW 0.18-μm CMOS ADC with on-chip current/voltage references. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems—Part I: Regular Papers, 52(10), 1989–1995.
Gulati, K., Peng, M. S., Pulincherry, A., Munoz, C. E., Lugin, M., Bugeja, A. R., Jipeng, L., & Chandrakasan, A. P. (2006). A highly integrated CMOS analog baseband transceiver with 180 MSPS 13-bit pipelined CMOS ADC and dual 12-bit DACs. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 41(8), 1856–1866.
Choi, H. C., Kim, Y. J., Yoo, S. W., Hwang, S. Y., & Lee, S. H. (2008). A programmable 0.8-V 10-bit 60-MS/s 19.2-mW 0.13-μm CMOS ADC operating down to 0.5 V. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Part II: Express Briefs, 55(4), 319–323
Ishii, H., Tanabe, K., & Iida, T. (2005). A 1.0 V 40 mW 10b 100 MS/s pipeline ADC in 90 nm CMOS. In Proceedings on IEEE custom integrated circuits (CICC). (pp. 395–398).
Gulati, K., Munoz, C., Cho, S., Manganaro, G., Lugin, M., Peng, M., Pulincherry, A., Jipeng, L., Bugeja, A., Chandrakasan, A., & Shoemaker, D. (2004) A highly integrated analog baseband transceiver featuring a 12-bit 180MSPS pipelined A/D converter for multi-channel wireless LAN. In Symposium on VLSI circuits. Digest on Techical Papers (pp. 428–431).
Nezuka, T., Misawa, K., Azami, J., Majima, Y., & Okamura, J. I. (2006). A 10-bit 200MS/s pipeline A/D converter for high-speed video signal digitizer. In IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (ASSCC) (pp. 31–34).
Chandrashekar, K., & Bakkaloglu, B. (2011). A 10 b 50 MS/s opamp-sharing pipeline A/D with current-reuse OTAs. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration Systems, 19, 1610–1616.
Verma, A., & Razavi, B. (2009). A 10-Bit 500-MS/s 55-mW CMOS ADC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44(11), 3039–3050.
Kim, M. Y., Kim, J., Lee, T., & Kim, C. (2011). 10-bit 100-MS/s pipelined ADC using input-swapped opamp sharing and self-calibrated V/I converter. IIEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration Systems, 19, 1438–1447.
Figueiredo, M., Santin, E., Goes, J., Paulino, N., Barúqui, F., & Petraglia, A. (2011). Flipped-around multiply-by-two amplifier with unity feedback factor. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 68(1), 133–138.
Sepke, T., Holloway, P., Sodini, C., & Lee, H. S. (2009). Noise analysis for comparator-based circuits. Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 56, 541–553.
Quinn, P., & Pribytko, M. (2003). Capacitor matching insensitive 12-bit 3.3 MS/s algorithmic ADC in 0.25 μm CMOS. In Proceedings of IEEE custom integrated circuits conference (CICC) (pp. 425–428).
Chiu, Y. (2000). Inherently linear capacitor error-averaging techniques for pipelined A/D conversion. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, 47, 229–232.
Saberi, M., & Lotfi, R. (2007). A capacitor mismatch-and nonlinearity-insensitive 1.5-bit residue stage for pipelined ADCs. In Proceedings of IEEE international conferece on electronics, circuits and systems (ICECS) (pp. 677–680).
Zhian Tabasy, E., Kamarei, M., & Ashtiani, S. (2009). 1.5-bit mismatch-insensitive MDAC with reduced input capacitive loading. IET Electronics Letters, 45(23), 1157–1158.
Keramat, A., & Tao, Z. (2000). A capacitor mismatch and gain insensitive 1.5-bit/stage pipelined A/D converter. In Proceedings of IEEE midwest symposium on circuits systems (Vol 1, pp. 48–51).
Chen, H. S., Song, B. S., & Bacrania, K. (2001). A 14-b 20-Msamples/s CMOS pipelined ADC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 36(6), 997–1001.
Figueiredo, M., Goes, J., Oliveira, L. B., & Steiger-Garção, A. (2011). Low voltage low power fully differential self-biased 1.5-bit quantizer with built-in thresholds.International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications (early view).
Figueiredo, M., Santos-Tavares, R., Santin, E., Ferreira, J., Evans, G., & Goes, J. (2011). A two-stage fully differential inverter-based self-biased CMOS amplifier with high efficiency. Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 58, 1591–1603.
Kim, J., Limotyrakis, S., & Yang, C. K. K. (2011). Multilevel power optimization of pipelined A/D converters. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration Systems, 19, 832–845.
Brooks, L., & Lee, H. S. (2007). A zero-crossing-based 8-bit 200 MS/s pipelined ADC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 42, 2677–2687.
Kim, H. C., Jeong, D. K., & Kim, W. (2005). A 30mW 8b 200MS/s pipelined CMOS ADC using a switched-opamp technique. In IEEE international solid-state circuits conference (ISSCC). Digest of technical papers (Vol. 1, pp. 284–598).
Jiang, S., Do, M. A., Yeo, K. S., & Lim, W. M. (2008). An 8-bit 200-MSample/s pipelined ADC with mixed-mode front-end S/H circuit. In Transactions on circuits and systems I: regular papers 55.
Chen, H. W., Chen, I. C., Tseng, H. C., & Chen, H. S. (2009). A 1-GS/s 6-bit two-channel two-step ADC in 0.13-μm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 44, 3051–3059.
Malcovati, P., Picolli, L., Crespi, L., Chaahoub, F., & Baschirotto, A. (2010). A 90-nm CMOS, 8-bit pipeline ADC with 60-MHz bandwidth and 125-MS/s or 250-MS/s sampling frequency. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 64, 159–172.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology under projects IMPACT (PTDC/EEA-ELC/101421/2008), OBiS FRET (PTDC/CTM/099511/2008), and Ph.D. grants BD/41524/2007 and BD/62568/2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Figueiredo, M., Santin, E., Goes, J. et al. A reference-free 7-bit 500 MS/s pipeline ADC using current-mode reference shifting and quantizers with built-in thresholds. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 75, 53–65 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0030-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-013-0030-1