Abstract
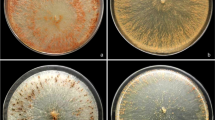
Fungi are the cause of numerous plant diseases. Leading plant pathogens include various species of the genera Curvularia and Bipolaris. In this study of 21 airborne isolates, seven species with pathogenic potential for rice crops were identified (Curvularia aeria, Curvularia clavata, Curvularia pallescens, Curvularia trifolii, Bipolaris australiensis, Bipolaris hawaiiensis and Bipolaris sorghicola). For all isolates, optimum temperatures for mycelial growth and germination of conidia were determined over the 10–40 °C range. All strains were mesophilic, and optimum temperatures for germination of conidia lay within the range favourable for colony growth. In addition to their practical application in protecting the rice crop, these findings are of ecological interest in that they improve awareness of the aeromycological biodiversity of the study area.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrios, G. N. (2005). Plant pathology (5th ed., pp. 386–500). Burlington, MA: Elsevier.
Almaguer, M., Rojas, T. I., Dobal, V., Batista, A., Rives, N., Aira, M. J., Hernández, A. N., & Hernández, A. (2011). Aerobiological dynamics of potentially pathogenic fungi in a rice agroecosystem in La Habana, Cuba. Aerobiologia. doi:10.1007/s10453-011-9222-2.
Barrios, L. M., & Pérez, I. O. (2005). Nuevos registros de hongos en semillas de Oryza sativa en Cuba. Manejo Integrado de Plagas y Agroecología, 75, 64–67.
Cárdenas, R. M., González, L., Parra, Y., Rivero, D., & Cruz, A. (2003). Influencia del manchado del grano de arroz (Oryza sativa L.) en la variedad J-104. nocividad y géneros de hongos presentes. Revista de Protección Vegetal, 18(2), 124–128.
Cardona, R., & González, M. (2008). Caracterización y patogenicidad de hongos del complejo Helmintosporium asociados al cultivo del arroz. Bioagro, 20, 141–145.
Cooney, D. G., & Emerson, R. (1964). Thermophilic Fungi. An account of their biology, activities and classification. San Francisco: Freeman and Company.
Deshmukh, A., & Gawai, D. (2008). Effect of temperature on incidence of storage fungi of some oil seeds. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 2(1), 261–264.
Elliotta, B., & Rayamajhib, N. (2008). Lower temperature during the dark cycle affects disease development on Lygodium microphyllum (old world climbing fern) by Bipolaris sacchari. Biological Control, 45, 56–63.
Ellis, M. B. (1971). Dematiaceous hyphomycetes. England: Commonwealth Mycological Institute. CAB International.
Estrada, G., & Sandoval, I. (2004). Patogenicidad de especies de Curvularia en arroz. Fitosanidad, 8, 23–26.
Falloon, R. E. (1975). Curvularia trifolii as a high-temperature turfgrass pathogen. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research, 19, 243–248.
Farr, D., Bills, G., & Chamuris, G. (2005). Fungi on plants and products in the United States. St. Paul, Minnesota: APS Press.
Freire, S. V. P., Paiva, L. M., Lima, E. A. L. A., & Maia, L. C. (1998). Morphological, cytological, and cultural aspects of Curvularia pallescens. Revista de Microbiologia, 29(3), 56–59.
Gutiérrez, S., & Manzzanti, M. A. (2002). Hongos asociados a granos manchados de Arroz. Arroz, 50, 22–25.
Hassikou, R., Hassikou, K., Ouazzanni, A., Badoc, A., & Doura, A. (2003). Biologie, physiologie et pouvoir pathogène de quelques isolats de Curvularia lunata agent de la curvulariose du riz. Bulletin de la Société Pharmaceutique de Bordeaux, 142, 25–44.
Huang, J., Zheng, L., & Hsiang, T. (2005). First report of leaf spot caused by Curvularia verruculosa on Cynodon sp. in Hubei. China Plant Pathology, 5, 253–257.
Islam, S. M. M., Masum, M. M. I., & Fakir, M. G. A. (2009). Prevalence of seed-borne fungi in sorghum of different locations of Bangladesh. Scientific Research and Essay, 4(3), 175–179.
Jones, A., & Harrison, R. (2004). The effects of meteorological factors on atmospheric bioaerosol concentrations—A review. Science of the Total Environment, 326, 151–180.
Mena, J. (2004). Taxonomía del complejo Bipolaris, Curvularia, Drechslera y Exserohilum en Cuba. Phd Thesis, Instituto de Ecología y Sistemática, CITMA. La Habana, Cuba.
Motlagh, M., & Kaviani, B. (2008). Characterization of new Bipolaris spp: The agent causal of rice brown spot disease in the North of Iran. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 10, 638–642.
Neninger, H., Hidalgo, E., Barrios, L. M., & Puedo, M. (2003). Hongos presentes en semillas de arroz (Oryza sativa L) en Cuba. Fitosanidad, 7(3), 7–11.
Niaz, I., & Dawar, S. (2009). Detection of seed borne mycoflora in maize (Zea mays L.). Pakistan Journal of Botany, 41(1), 443–451.
Ojeda, A., & Subero, L. (2006). Crecimiento y esporulación de Bipolaris oryzae (Breda de Hann) Shoem en diferentes medios de cultivo, condiciones de luz y temperatura. Mycopathologia, 13(1), 19–24.
Olufolaji, B. (1985). Comparative studies of the effect of Helminthosporium maydis and Curvularia pallescens infection on total nitrogen of maize leaves. Cryptogamie Mycology, 6(3), 97–200.
Picco, A. M., Lorenzi, E., Rodino, D., Rodolfi, M., & Biloni, M. (2004). Airspores detection or Pyricularia grisea (Cooke) Sacc. and Bipolaris spp. A three years monitoring in different rice fields in Northern Italy. Aerobiologia, 47(2), 133–137.
Picco, A. M., & Rodolfi, M. (2002). Pyricularia grisea and Bipolaris oryzae: A preliminary study on the occurrence of airborne spores in a rice field. Aerobiologia, 18(2), 163–167.
Pratt, R. G. (2005). Variation in occurrence of dematiaceous hyphomycetes on forage bermudagrass over years, sampling times, and locations. Phytopathology, 95(10), 1183–1190.
Rashid, M. (2001). Detection of Curvularia species on boro rice seeds of Dinajpur. Journal of Biological Sciences, 7, 591–592.
Salar, R. K., & Aneja, K. R. (2007). Thermophilic Fungi: Taxonomy and biogeography. Journal of Agricultural Technology, 3(1), 77–107.
Sharma, K. (2010). Seasonal variation of aeromycoflora over Ocimum sanctum plant with special reference to winter season. Journal of Phytology, 2(8), 1–5.
Sivanesan, A. (1987). Graminicolous species of Bipolaris, Curvularia, Drechslera, Exserohilum, and their teleomorphs. Mycological Papers, 158, 1–261.
Taylor, B. M., & Khan, A. (2010). Germination, radial growth and virulence of Metarhizium anisopliae and Paecilomyces fumoso-roseus on Bemisia Tabaci Gennadius (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae). Pakistan Entomologist, 32(2), 148–154.
Webster, J., & Weber, R. W. S. (2007). Introduction to Fungi. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Yeo, H., Pell, J., Clark, S., & Pye, B. (2003). Laboratory evaluation of temperature effects on the germination and growth of entomopathogenic fungi and on their pathogenicity to two aphid species. Pest Management Science, 59, 156–165.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almaguer, M., Rojas, T.I., Dobal, V. et al. Effect of temperature on growth and germination of conidia in Curvularia and Bipolaris species isolated from the air. Aerobiologia 29, 13–20 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-012-9257-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-012-9257-z