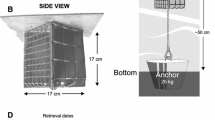
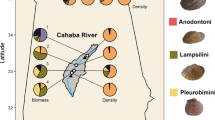
Abstract
Dreissena (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae) species can act as ecosystem engineers, physically altering freshwater ecosystems and changing benthic macro-invertebrate assemblages. The mussel beds they form can provide shelter and food for detritivorous species, whereas fouling can directly impact native bivalves. In this study, we examined the effects of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) and quagga mussel (Dreissena rostriformis) on the macro-invertebrate community in the Meuse River by characterizing the macro-invertebrate assemblage associated with Dreissena clumps on artificial substrates at four sampling sites and by quantifying the infestation of Dreissena on native mussels along six transects. We found that the study site with dense Dreissena clumps on artificial substrates hosted particular macro-invertebrate assemblages that were composed of amphipods, gastropods and some insect larvae. Oligochaeta and Ephemeroptera abundances were low at this site. Non-native Ponto-Caspian amphipods occurred in very high densities in mussel beds, and we report the first records of several new invasive amphipod species in the Meuse River. Our results also revealed that ca. 40 % of sampled Unionidae were infested by Dreissena, although infestation load was low (0.48–2.51 Dreissena per native bivalve). These results suggested that the interactions between Dreissena and other macro-invertebrates ranged between a probably low incapacitating relationship with Unio resulting from a long coexistence which allowed the two species to live in sympatry and a strong facilitation for exotic amphipods native from the same region as Dreissena.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alderstein S, Nalepa TF, Vendrploeg HA, Fahnenstiel GL (2013) Trends in phytoplankton, zooplankton, and macroinvertebrates in Saginaw Bay relative to zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) colonization: a generalized linear model approach. In: Nalepa TF, Schloesser DW (eds) Quagga and zebra mussel: biology, impacts, and control, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 525–544
Armitage P, Moss D, Wright J, Furse M (1983) The performance of a new biological water quality score system based on macroinvertebrates over a wide range of unpolluted running-water sites. Water Res 17:333–347. doi:10.1016/0043-1354(83)90188-4
Beisel JN, Lévêque C (2010) Introductions d’espèces dans les milieux aquatiques: faut-il avoir peur des invasions biologiques?. Edition Quae, Paris
Bially A, MacIsaac HJ (2000) Fouling mussels (Dreissena spp.) colonize soft sediments in Lake Erie and facilitate benthic invertebrates. Freshw Biol 43:85–97. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2427.2000.00526.x
Bódis E, Tóth B, Sousa R (2013) Impact of Dreissena fouling on the physiological condition of native and invasive bivalves: interspecific and temporal variations. Biol Invasions 16:1373–1386. doi:10.1007/s10530-013-0575-z
Bogan AE (2008) Global diversity of freshwater mussels (Mollusca, Bivalvia) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 595:139–147. doi:10.1007/s10750-007-9011-7
Bollache L, Devin S, Wattler R, Chovet Beisel JN, Moreteau JC, Rigaud T (2004) Rapid range extension of the Ponto-Caspian amphipod Dikerogammarus villosus in France: potential consequences. Arch Hydrobiol 111:309–313
Bollache L, Dick JTA, Farnsworth KD, Montgomery WI (2008) Comparison of the functional responses of invasive and native amphipods. Biol Lett 4:166–169
Burlakova LE, Karatayev AY, Padilla DK (2000) The impact of Dreissena polymorpha (PALLAS) invasion on Unionid bivalves. Int Rev Hydrobiol 85:529–5410. doi:10.1002/1522-2632(200011)85:5/6<529:AID-IROH529>3.0.CO;2-O
Chevenet F, Dolédec S, Chessel D (1994) A fuzzy coding approach for the analysis of long-term ecological data. Freshw Biol 31:295–309. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.1994.tb01742.x
Core Team R (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Cristescu MEA, Hebert PDN (2005) The “Crustacean Seas”: an evolutionary perspective on the Ponto-Caspian peracarids. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 62:505–517. doi:10.1139/F04-210
Dermott R, Mitchell J, Murray I, Fear E (1993) Biomass and production of zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) in shallow waters of Northeastern Lake Erie. In: Nalepa TF, Schloesser DW (eds) Zebra mussels: biology, impacts and control. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 399–414
Descy J-P, Kestemont P, Everbecq E, Verniers G, Usseglio-Polatera P, Gérard P, Viroux L, Beisel J-N, Smitz J (2009) The Meuse River Basin. In: Tockner K, Uehlinger U, Robinson CT (eds) Rivers of Europe. Elsevier, London, pp 154–165
Devin S, Piscart C, Beisel JN, Moreteau JC (2003) Ecological traits of the amphipod invader Dikerogammarus villosus on a mesohabitat scale. Arch Hydrobiol 158:43–56
Dobson M (2013) Identifying invasive freshwater shrimps and isopods. Revised edition. Freshwater Biological Association, Ambelside
Dray S, Dufour AB, Chessel D (2007) The ade4 package-II: two-table and K-table methods. R News 7:47–52
Everbecq E, Gosselain V, Viroux L, Descy J-P (2001) Potamon: a dynamic model for predicting phytoplankton composition and biomass in lowland rivers. Water Res 35:901–912. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00360-2
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 3:294–299
Forcellini M (2012) First record of the Ponto-Caspian invasive crustacean Chelicorophium sowinskyi (Marinov, 1924) (Amphipoda, Corophiidae) in the French Rhône River. Crustaceana 85:1781–1785
Gergs R, Rothhaupt KO (2008) Effects of zebra mussels on a native amphipod and the invasive Dikerogammarus villosus: the influence of biodeposition and structural complexity. J N Am Benthol Soc 27:541–548. doi:10.1899/07-151.1
Gittenberger E, Janssen AW, Kuijper WJ, Kuiper JGJ, Meijer T, Van der Velde G, De Vries JN (1998) De Nederlandse zoetwatermollusken: recente en fossiele weekdieren uit zoet en brak water, KNNV uitgeverij & EIS Nederland. Nederlandse Fauna 2:1–288
Greenwood KS, Thorp JH, Summers RB, Guelda DL (2001) Effects of an exotic bivalve mollusc on benthic invertebrates and food quality in the Ohio River. Hydrobiologia 462:169–172. doi:10.1023/A:1013190301967
Griffiths RW (1993) Effects of zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) on benthic fauna of Lake St. Clair. In: Nalepa TF, Schloesser DW (eds) Zebra mussels: biology, impacts and control. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 415–438
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704. doi:10.1080/10635150390235520
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Higgins SN (2013) Meta-analysis of dreissenids effects on freshwater ecosystems. In: Nalepa TF, Schloesser DW (eds) Quagga and zebra mussel: biology, impacts, and control, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 487–494
Josens G, Bij de Vaate A, Usseglio-Polatera P, Cammaerts R, Chérot F, Grisez F, Verboonen P, Vanden Bossche JP (2005) Native and exotic Amphipoda and other Peracarida in the River Meuse: new assemblages emerge from a fast changing fauna. Hydrobiologia 542:203–220. doi:10.1007/s10750-004-8930-9
Karatayev AY, Burlakova LE, Padilla DK (1997) The effects of Dreissena polymorpha (Pallas) invasion on aquatic communities in Eastern Europe. J Shellfish Res 16:187–203
Karatayev AY, Burlakova LE, Padilla DK (2002) Impacts of zebra mussels on aquatic communities and their role as ecosystem engineers. In: Leppäkoski E, Gollasch S, Olenin S (eds) Invasive aquatic species of Europe: distribution, impacts and management. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp 433–446
Karatayev AY, Burlakova LE, Padilla DK (2015) Zebra versus quagga mussels: a review of their spread, population dynamics, and ecosystem impacts. Hydrobiologia 746:97–112. doi:10.1007/s10750-014-1901-x
Kobak J, Kakareko T (2011) The effectiveness of the induced anti-predator behaviour of zebra mussel in the presence of molluscivorous roach. Aquat Ecol 45:357–366. doi:10.1007/s10452-011-9359-7
Kobak J, Zytkowicz J (2007) Preferences of invasive Ponto-Caspian and native European gammarids for zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha, Bivalvia) shell habitat. Hydrobiologia 589:43–54. doi:10.1007/s10750-007-0716-4
Kobak J, Poznanska M, Kakareko T (2012) Behavioural changes of zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha (Bivalvia) induced by Ponto-Caspian gammarids. Biol Invasions 14:1851–1863. doi:10.1007/s10530-012-0197-x
Lobo J, Costa PM, Teixeira MAL, Ferreira MSG, Costa H, Costa FO (2013) Enhanced primers for amplification of DNA barcodes from a broad range of marine metazoans. BMC Ecol 13:34. doi:10.1186/1472-6785-13-34
Lucy FE, Burlakova LE, Karatayev AY, Mastitsky SE, Zanatta DT (2013) Zebra mussel impacts on Unionids: A synthesis of trends in North America and Europe. In: Nalepa TF, Schloesser DW (eds) Quagga and zebra mussel: biology, impacts, and control, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 623–646
Marescaux J, Van Doninck K (2013) Using DNA barcoding to differentiate invasive Dreissena species (Mollusca, Bivalvia). Zookeys 365:235–244. doi:10.3897/zookeys.365.5905
Marescaux J, Bij de Vaate A, Van Doninck K (2012) First records of Dreissena rostriformis bugensis (Andrusov, 1897) in the Meuse River. BioInvasions Rec 1:119–124. doi:10.3391/bir.2012.1.2.05
Marescaux J, Boets P, Lorquet J, Sablon R, Van Doninck K, Beisel J-N (2015) Sympatric Dreissena species in the Meuse River: towards a dominance shift from zebra to quagga mussels. Aquat Invasions 10:287–298. doi:10.3391/ai.2015.10.3.04
Matthews J, van der Velde G, bij de Vaate A, Leuven RSEW (2012) Key factors for spread, impact and management of quagga mussels in the Netherlands. Reports Environmental Science nr.404, Department of Environmental Science, Faculty of Science, Institute for Water and Wetland Research, Radboud University Nijmegen, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
Messiaen M, Lock K, Gabriels W, Vercauteren T, Wouters K, Boets P, Goethals PLM (2010) Alien macrocrustaceans in freshwater ecosystems in the eastern part of Flanders (Belgium). Belg J Zool 140:30–39
Mills EL, Rosenberg G, Spidle AP, Ludyanskiy M, Pligin Y, May B (1996) A review of the biology and ecology of the quagga mussel (Dreissena bugensis), a second species of freshwater Dreissenid introduced to North America. Am Zool 36:271–286. doi:10.1093/icb/36.3.271
Mondy CP, Villeneuve B, Archaimbault V, Usseglio-Polatera P (2012) A new macroinvertebrate-based multimetric index (I2M2) to evaluate ecological quality of French wadeable streams fulfilling the WFD demands: a taxonomical and trait approach. Ecol Indic 18:452–467. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.12.013
Mörtl M, Rothhaupt KO (2003) Effects of adult Dreissena polymorpha on settling juveniles and associated macroinvertebrates. Int Rev Hydrobiol 88:561–569. doi:10.1002/iroh.200310640
Nalepa TF (1994) Decline of native bivalves (Unionidae: Bivalvia) in Lake St. Clair after infestation by the zebra mussels Dreissena polymorpha. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 51:2227–2233. doi:10.1139/f94-225
Nalepa TF, Fanslow DL, Lang GA (2009) Transformation of the offshore benthic community in Lake Michigan: recent shift from the native amphipod Diporeia spp. to the invasive mussel Dreissena rostriformis bugensis. Freshw Biol 54:466–479. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2008.02123.x
Nijs E, Van Goethem JL (1995) Distributional data of the unionids in Belgium (Mollusca, Bivalvia, Unionidae). Bull Inst R Sci Nat Belg 65:83–87
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Henry M, Stevens H, Wagner H (2013) Vegan: community ecology Package, R package version 2.0-7
Palmer ME, Ricciardi A (2005) Community interactions affecting the relative abundances of native and invasive amphipods in the St. Lawrence River. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 62:1111–1118. doi:10.1139/F05-012
Pathy DA, Mackie GL (1993) Comparative shell morphology of Dreissena polymorpha, Mytilopsis leucophaeata and the “quagga” mussel (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae) in North America. Can J Zool 71:1012–1023. doi:10.1139/z93-135
Petit M (1978) Ecologie et répartition spatiale des macroinvertébrés benthiques de la Haute Meuse belge. Master Thesis, Facultés Universitaires Notre-Dame de la Paix, Namur
Pigneur L-M, Falisse E, Roland K, Everbecq E, Deliège J-F, Smitz JS, Van Doninck K, Descy J-P (2014) Impact of invasive Asian clams, Corbicula spp., on a large river ecosystem. Freshw Biol 59:573–583. doi:10.1111/fwb.12286
Piscart C, Bollache L (2012) Practical introduction to the systematic of the organisms of French continental waters. Epigean, Crustacea, Amphipoda. Association Française de Limnologie, Bordeaux
Piscart C, Genoel R, Doledec S, Chauvet E, Marmonier P (2009) Effects of intense agricultural practices on heterotrophic processes in streams. Environ Pollut 157:1011–1018. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2008.10.010
Posada D (2008) jModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol 25:1253–1256. doi:10.1093/molbev/msn083
Reynolds CS, Descy J-P (1996) The production, biomass and structure of phytoplankton in large rivers. Arch Hydrobiol 113:161–187
Ricciardi A, Whoriskey FG, Rasmussen JB (1996) Impact of the Dreissena invasion on native unionid bivalves in the upper St. Lawrence River. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 53:1434–1444. doi:10.1139/f96-068
Ricciardi A, Whoriskey FG, Rasmussen JB (1997) The role of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) in structuring macroinvertebrate communities on hard substrata. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 54:2596–2608. doi:10.1139/f97-174
Sablon R, Vercauteren T, Jacobs P (2010) De quaggamossel (Dreissena rostriformis bugensis (Andrusov, 1897)), een recent gevonden invasieve zoetwatermossel in Vlaanderen. Antenne 4:32–36
Schloesser DW, Kovalak WP, Longton GD, Ohnesorg KL, Smithee RD (1998) Impact of zebra and quagga mussels (Dreissena spp.) on freshwater unionids (Bivalvia: Unionidae) in the Detroit River of the Great Lakes. Am Midl Nat 140:299–313
Schloesser DW, Metcalfe-Smith JL, Kovalak WP, Longton GD, Smithee RD (2006) Extirpation of freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Unionidae) following the invasion of dreissenid mussels in an interconnecting river of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Am Midl Nat 155:307–320
Sousa R, Pilotto F, Aldrigde DC (2011) Fouling of European freshwater bivalves (Unionidae) by the invasive zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Freshw Biol 56:867–876. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2010.02532.x
Sousa R, Novais A, Costa R, Strayer DL (2013) Invasive bivalves in fresh waters: impacts from individuals to ecosystems and possible control strategies. Hydrobiologia 735:233–251. doi:10.1007/s10750-012-1409-1
Stewart TW, Haynes JM (1994) Benthic macroinvertebrate communities of Southwestern Lake Ontario following invasion of Dreissena. J Great Lakes Res 20:479–493. doi:10.1016/S0380-1330(94)71164-3
Stewart TW, Miner JG, Lowe RL (1998a) Macroinvertebrate communities on hard substrates in Western Lake Erie: structuring effects of Dreissena. J Great Lakes Res 24:868–879. doi:10.1016/S0380-1330(98)70868-8
Stewart TW, Miner JG, Lowe RL (1998b) Quantifying mechanisms for zebra mussel effects on benthic macroinvertebrates: organic matter production and shell-generated habitat. J North Am Benthol Soc 17:84–94
Strayer DL, Smith LC (1996) Relationships between zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) and unionid clams during the early stages of the zebra mussel invasion of the Hudson River. Freshw Biol 36:771–778
Strayer DL, Smith DR (2003) A guide to sampling freshwater mussel population. American Fisheries Society, Monograph 8, Bethesda, Maryland
Strayer DL, Cid N, Malcom HM (2011) Long-term changes in a population of an invasive bivalve and its effects. Oecologia 165:1063–1072. doi:10.1007/s00442-010-1792-0
Tachet H, Richoux P, Bournaud M, Usseglio-Polatera P (2010) Invertébrés d’eau Douce. Systématique, Biologie, Ecologie. CNRS Editions, Paris
Usseglio-Polatera P, Beisel JN (2002) Longitudinal changes in macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Meuse River: anthropogenic effects versus natural change. River Res Applic 18:197–211. doi:10.1002/rra.651
Van der Velde G, Leuven RSEW, Platvoet D, Bacela K, Huijbregts MAJ, Hendriks HWM, Kruijt D (2009) Environmental and morphological factors influencing predatory behaviour by invasive non-indigenous gammaridean species. Biol Invasions 11:2043–2054. doi:10.1007/s10530-009-9500-x
Vanden Bossche JP (2002) First records and fast spread of five new (1995–2000) alien species in the River Meuse in Belgium: Hypania invalida, Corbicula fluminea, Hemimysis anomala, Dikerogammarus villosus and Crangonyx pseudogracilis. Bull Inst R Sci Nat Belg 72:73–78
Vaughn CC (2012) Life history traits and abundance can predict local colonization and extinction rates of freshwater mussels. Freshw Biol. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2012.02759.x
Ward JM, Ricciardi A (2013) Impacts of Dreissena on benthic macroinvertebrate communities: predictable patterns revealed by invasion history. In: Nalepa TF, Schloesser DW (eds) Quagga and zebra mussel: biology, impacts, and control, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 599–610
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Voies Navigables de France (VNF), and especially Frédéric Rogissart, for authorization to work on the French dams. We also thank the two anonymous reviewers and the editor for their suggestions, which greatly improved an early version of this manuscript. This study received financial support from the University of Namur, from the European Fisheries Fund (FEP 32-1109-004) and from the European Cooperation in Science and Technology (COST Action TD1209). Adrien Latli is funded by an assistant PhD grant from the University of Namur. Jonathan Marescaux is funded by a PhD grant from the Belgian National Fund for Scientific Research (FRS-FNRS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Michael T. Monaghan.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marescaux, J., Latli, A., Lorquet, J. et al. Benthic macro-invertebrate fauna associated with Dreissena mussels in the Meuse River: from incapacitating relationships to facilitation. Aquat Ecol 50, 15–28 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-015-9540-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-015-9540-5