Abstract
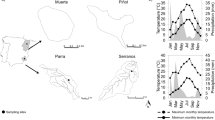
Urban land use has increased dramatically over the past few decades, resulting in high variability in nutrients loading which is likely to alter the biological component of urban streams. Freshwater snails and environmental variables that might structure their diversity and distribution were studied from September 2012 to September 2013 in three contiguous watersheds in Douala. Twelve stations were monitored monthly, two of these are located in a suburban forest area, and the rest situated in urbanized and industrialized zones. Snails were collected using a long-handled net (30 × 30 cm side, 400-µm mesh). Meanwhile, measurements of the environmental variables were taken. Ten species were recorded which are as follows: Melanoides tuberculata (Thiaridae); Gabbiella africana (Bythiniidae); Physa acuta, Aplexa sp. (Physidae); Lymnaea natalensis, Lymnaea stagnalis, Lymnaea columella (Lymnaeidae); Biomphalaria pfeifferi, Bulinus forskalii (Planorbidae) and one undetermined taxon of Bythiniidae. All these snails were identified at nine of the ten urban stations; no species being found in suburban stations. These urban streams have very poor health status with highly polluted waters. Among the species found P. acuta (76.95 %), L. natalensis (19.46 %) and M. tuberculata (2.79 %) were the most abundant. Multiple stepwise regression analysis, Spearman correlation test and redundancy analysis showed that snail occurrences and abundances were probably influenced by water temperature, conductivity, suspended solids, alkalinity, nitrites, nitrates, ammonium, phosphates, oxydability, biochemical oxygen demand, rainfall, encumbrance rate of the riverbed and water width. Moreover, snail dynamics showed a seasonal pattern with peak population abundances and recruitment of young generations during rainy season. This malacological survey spotlighted the impacts of anthropogenic activities on snail’s diversity and distribution, with the proliferation of the invasive pulmonate P. acuta in Douala urban streams.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajeagah GA, Foto MS, Njine T (2012) Experimentation of immunofluorescence technology in the quantification of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia spp. (oo) cysts in surface water in Yaoundé. Cameroon Int J Biosci 2:28–39
Ajeagah G, Wouafo M, Ezenguele G, Nzukam J (2013) Presence of Gastrointestinal Parasites in a Tropical Urban Region (Yaoundé, Cameroon). Comp Parasitol 80:279–283. doi:10.1654/4607.1
Albrecht C, Föller K, Clewing C, Hauffe T, Wilke T (2013) Invaders versus endemics: alien gastropod species in ancient Lake Ohrid. Hydrobiologia 703:165–175. doi:10.1007/s10750-013-1724-1
Alhoniemi E, Himberg J, Parankangas J, Vesanto J (2003) SOM toolbox 2.0. Laboratory of Computer and Information Science, Neural Networks Research Center, Helsinki, Finland
APHA (1998) Standard method for examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Appleton CC (1996) Freshwater mollusks of Southern Africa: with a chapter on bilharzia and its snail hosts. University of Natal Press, Pietermaritzburg
Appleton CC, Brackenbury TD (1998) Introduced freshwater gastropods in Africa with special reference to Physa acuta. In: Madsen H, Appleton CC, Chimbari M (ed) Proceedings of a workshop on medical malacology in Africa, Harare, Zimbabwe, September 1997, pp 45–56
Bernot RJ, Brandenburg M (2013) Freshwater snail vital rates affected by non-lethal concentrations of silver nanoparticles. Hydrobiologia 714:25–34. doi:10.1007/s10750-013-1509-6
Bode RW, Novak MA, Abele LE, Heitzman D L, Smith AJ (2002) Quality Assurance Work Plan for Biological Stream Monitoring in New York State, Albany (New York), Stream Biomonitoring Unit, Bureau of Water Assessment and Management, Division of Water, NYS Department of Environmental Conservation
Bony YK (2007) Biodiversité et écologie des mollusques gastéropodes d’eau douce en milieu continental ivoirien (bassins de la Mé, de l’Agnéby et du Banco). Traits d’histoire de vie d’une espèce invasive Indoplanorbis exustus (Deshayes, 1834). Thèse de Doctorat, Ecole Pratique des Hautes Etudes, Perpignan France
Bony YK, Kouassi NC, Diomandé D, Gourène G, Verdoit-Jarraya M, Pointier JP (2008) Ecological conditions for the spread of the invasive snail Physa marmorata (Pulmonata: physidae) in Ivory Coast. Afr Zool 43:53–60. doi:10.3377/1562-7020(2008)43[53:ECFSOT]2.0.CO;2
Brackenbury TD, Appleton CC (1993) Recolonization of the Umsinduzi River, Natal, South Africa, by the invasive gastropod Physa acuta (Basommatophora: physidae). J Med Appl Malacol 5:39–44
Brown DS (1994) Freshwater snails of Africa and their medical importance. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis, London
Brown KM, Alexander JE, Thorp JH (1998) Differences in the ecology and distribution of lotic pulmonate and prosobranch gastropods. Am Malacol Bull 14:91–101
Bukowski SJ, Auld JR (2014) The effects of calcium in mediating the inducible morphological defenses of a freshwater snail, Physa acuta. Aquat Ecol 48:85–90. doi:10.1007/s10452-013-9468-6
Callisto M, Moreno P, Barbosa FAR (2001) Habitat diversity and benthic trophic functional groups at Serra do Cipo, southern Brazil. Braz J Biol 61:259–266
Camara IA, Bony YK, Diomandé D, Edia EO, Konan FK, Kouassi CN, Gourène G, Pointier JP (2012) Freshwater snail distribution related to environmental factors in Banco National Park, an urban reserve in the Ivory Coast (West Africa). Afr Zool 47:160–168. doi:10.3377/004.047.0106
Chapman EJ, Prezant RS, Shell R (2012) Temporal variation in Molluscan community structure in an Urban New Jersey Pond. Northeast. Nat 19:373–390. doi:10.1656/045.019.0302
Colas F, Vigneron A, Felten V, Devin S (2014) The contribution of a niche-based approach to ecological risk assessment: using macroinvertebrate species under multiple stressors. Environ Pollut 185:24–34. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2013.09.033
Cope NJ, Winterbourn MJ (2004) Competitive interactions between two successful molluscan invaders of freshwaters: an experimental study. Aquat Ecol 38:83–91. doi:10.1023/B%3AAECO.0000021018.20945.9d
Dajoz R (2000) Précis d’Écologie, 7e édition. Dunod, Paris
Dana P, Appleton CC (2007) Observations on the population dynamics of the invasive freshwater snail Aplexa marmorata (Pulmonata: Physidae) in Durban, South Africa. S Afr J Sci 103:493–496
Djuikom E, Temgoua E, Jugnia LB, Nola M, Baane M (2009) Pollution bactériologique des puits d’eau utilisés par les populations dans la Communauté Urbaine de Douala—Cameroun. Int J Biol Chem Sci 3:967–978. doi:10.4314/ijbcs.v3i5.51076
Evans RR, Ray SJ (2010) Distribution and Environmental Influences on Freshwater Gastropods from lotic systems and springs in Pennsylvania, USA, with Conservation Recommendations. Am Malacol Bull 28:135–150. doi:10.4003/006.028.0207
Feumba R, Ngounou Ngatcha B, Tabue Youmbi JG, Ekodeck GE (2011) Relationship between climate and groundwater recharge in the Besseke watershed (Douala–Cameroun). JWARP 3:607–619. doi:10.1007/s00027-011-0218-3
Foto Menbohan S (2012) Recherche écologique sur le réseau hydrographique du Mfoundi (Yaoundé): Essai de biotypologie. Thèse de Doctorat d’Etat, Faculté des Sciences, Université de Yaoundé I
Foto Menbohan S, Tchakonté S, AJeagah G, Zébazé Togouet SH, Bilong Bilong CF, Njine T (2013) Water quality assessment using benthic macroinvertebrates in a periurban stream (Cameroon). TIJB 2:91–104
Garcia-Roger EM, Sanchez-Montoya MDM, Gomez R, Suarez ML, Vidal-Abarca R, Latron J, Rieradevall M, Prat N (2011) Do seasonal changes in habitat features influence aquatic macroinvertebrate assemblages in perennial versus temporary Mediterranean streams? Aquat Sci 73:567–579. doi:10.1007/s00027-011-0218-3
Kohonen T (2001) Self-organizing maps, 3rd edn. Springer Series in Information Sciences, Springer, New York
Kramkimel JD, Grifoni U, Kabeya Mukenyi R (2004) Profil Environnemental du Cameroun, Rapport Provisoire des services de coopération dans le Secteur de l’Environnement. Commission Européenne, Contrat-cadre AMS/451
Machena C, Kaujsky N (1988) A quantitative diving survey of benthic vegetation and fauna in Lake Kariba, a tropical man-made lake. Freshw Biol 19:1–14. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427
Marsden ID, Swinscoe I (2014) Does population structure and growth of an intertidal pulmonate snail reflect environmental conditions within a small estuary? Hydrobiologia 724:141–155. doi:10.1007/s10750-013-1730-3
Martinez MA, Rogowski DL (2011) Use and apparent partitioning of habitat by an imperiled Spring snail (hydrobiidae) and a cosmopolitan pond snail (Physidae). Southwest Nat 56:216–223. doi:10.1894/F11-JS-34.1
Moisan J (2010) Guide d’identification des principaux macroinvertébrés benthiques d’eau douce du Québec, surveillance volontaire des cours peu profonds, Direction du Suivi de l’Etat de l’Environnement, Ministère du développement durable, de l’Environnement et des Parcs
Moor IJ, Day JA (2002) Guides to the Freshwater Invertebrates of Southern Africa, Volume 6: Arachnida & Mollusca. Water Research Commission Report, No. TT 182/02, Pretoria-South Africa
Morrissey CA, Boldt A, Mapstone A, Newton J, Ormerod SJ (2013) Stable isotopes as indicators of wastewater effects on the macroinvertebrates of urban rivers. Hydrobiologia 700:231–244. doi:10.1007/s10750-012-1233-7
Olivry JC (1986) Fleuve et rivières du Cameroun. Collection Monographie Hydrologie, MESRE/ORSTOM
Platts WS, Megahan WF, Minshall GW (1983) Methods for evaluating stream, riparian and biotic conditions. General technical report 138, US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Intermountain Forest and Range Experiment Station
Pointier JP, Theron A, Borel G (1993) Ecology of the introduced snail Melanoides tuberculata (Gastropoda: Thiaridae) in relation to Biomphalaria glabrata in the marshy forest zone of guadeloupe, French west indies. J Mollus Stud 59:421–428. doi:10.1093/mollus/59.4.421
Pointier JP, Facon B, Jarne P, David P (2004) Les thiaridés, des Gastéropodes envahisseurs des eaux douces tropicales. Xenophora 104:14–20
Prezant RS, Chapman EJ (2004) Freshwater mollusks of the United States Military Academy drainages (West Point, NY) and comparative regional biodiversity of gastropods. Northeast Nat 11:273–294. doi:10.1656/1092-6194(2004)011[0273:FMOTUS]2.0.CO;2
Rios SL, Bailey RC (2006) Relationships between riparian vegetation and stream benthic communities at three spatial scales. Hydrobiologia 553:153–160. doi:10.1007/s10750-005-0868-z
Rodier J, Legube B, Marlet N, Brunet R (2009) L’analyse de l’eau. 9e édition, DUNOD, Paris
Sachs L (1997) Angewandte Statistik, 8th edn. Springer, Berlin
Same Ekobo A (1984) Faune malacologique du Cameroun (description, répartition des mollusques dulçaquicoles et foyers de trématodoses humaines). Thèse de Doctorat d’Etat, Université de Rennes I
Scherrer B (1984) Biostatistiques. Gaëtan Morin Edition, Boucherville, Canada
Schuetze T, Chelleri L (2013) Integrating decentralized rainwater management in urban planning and design: flood resilient and sustainable water management using the example of coastal cities in The Netherlands. Water 5:593–616. doi:10.3390/w5020593
Schuwirth N, Reichert P (2012) Prévoir la présence des organismes dans les rivières. Eawag News 72:14–17
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1995) Biometry, 3rd edn. Freeman, New York
Song MY, Leprieur F, Thomas A, Lek-Ang S, Chon TS, Lek S (2009) Impact of agricultural land use on aquatic insect assemblages in the Garonne river catchment (SW France). Aquat Ecol 43:999–1009. doi:10.1007/s10452-008-9218-3
Stark JD, Boothroyd KG, Harding JS, Maxted JR, Scarsbrook MR (2001) Protocols for Sampling Macroinvertebrates in Wadeable Streams. New Zealand Macroinvertebrates working group, report no. 1, Ministry for the Environment, Sustainable Management fund project no. 5103
Strong EE, Glaubrecht M (2007) Anatomy and systematics of the minute syrnolopsine gastropods from Lake Tanganyika (Caenogastropoda, Cerithioidea, Paludomidae). Acta Zool-Stockholm 88:1–22. doi:10.1111/j.1463-6395.2007.00318.x
Suchel JB (1972) Le climat du Cameroun. Thèse de Doctorat 3eme cycle, Université de Bordeaux III
Tening AS, Chuyong GB, Asongwe GA, Fonge BA, Lifongo LL, Tandia BK (2013) Nitrate and ammonium levels of some water bodies and their interaction with some selected properties of soils in Douala metropolis, Cameroon. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 7:648–656. doi:10.5897/AJEST12.082
Tolley-Jordan LR, Owen JM (2008) Habitat influences snail community structure and trematode infection levels in a spring-fed river, Texas, USA. Hydrobiologia 600:29–40. doi:10.1007/s10750-007-9173-3
Wang B, Liu D, Liu S, Zhang Y, Lu D, Wang L (2012) Impacts of urbanization on stream habitats and macroinvertebrate communities in the tributaries of Qiangtang River, China. Hydrobiologia 680:39–51. doi:10.1007/s10750-011-0899-6
Xu M, Wang Z, Duan X, Pan B (2013) Effects of pollution on macroinvertebrates and water quality bio-assessment. Hydrobiologia 703:176–189. doi:10.1007/s10750-013-1504-y
Yapi Y, N’goran KE, Salia D, Cunin P, Bellec C (1994) Population dynamics of Indoplanorbis exustus (Deshayes, 1834) (Gastropoda: Planorbidae), an exotic freshwater snail recently discovered at Yamoussoukro (Ivory Coast). J Mollus Stud 60:83–95. doi:10.1093/mollus/60.1.83
Zalizniak L, Kefford BJ, Nugegoda D (2009a) Effects of pH on salinity tolerance of selected freshwater invertebrates. Aquat Ecol 43:135–144. doi:10.1007/s10452-007-9148-5
Zalizniak L, Kefford BJ, Nugegoda D (2009b) Effects of different ionic compositions on survival and growth of Physa acuta. Aquat Ecol 43:145–156. doi:10.1007/s10452-007-9144-9
Acknowledgments
This malacological survey was achieved thanks to the financial support of the Intra-African Mobility Program (PIMASO) and the International Foundation for Sciences (IFS). Authors would like to gratefully acknowledge Pr. Jean Pierre POINTIER and Dr. Norbert Kouakou KOUADIO for their help in taxonomic verifications of the biological material. Authors also express their gratitude to Dr. Olive Vivien NOAH EWOTI and Mr. Henry Bruno DOMCHE TEHAM for their help during the sampling campaigns.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Piet Spaak.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tchakonté, S., Ajeagah, G.A., Diomandé, D. et al. Diversity, dynamic and ecology of freshwater snails related to environmental factors in urban and suburban streams in Douala–Cameroon (Central Africa). Aquat Ecol 48, 379–395 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-014-9491-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-014-9491-2