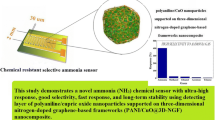
Abstract
Activated carbons, either synthetic, developed in our laboratory, or commercial were prepared or further modified, in order to introduce specific heteroatoms such as oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur to their matrix. Chips with thin layers of active materials were prepared and used for ammonia or hydrogen sulfide sensing. They showed high sensitivity and their response was selective. They also responded linearly to changes in various ammonia concentrations. The incorporation of specific heteroatoms to the carbons matrices was an effective means to control the type of the charge carriers, and thus the electronic and transport properties. Depending on the specific chemical arrangement of heteroatoms, materials exhibiting n- or p-type conduction were obtained. Pyridines and nitropyridines played an important role. A small amount of ammonia was oxidized to NO2 on the surface of sulfur and nitrogen co-doped carbons, due to their ability to generate superoxide ions. When adsorbed in the pore system of the carbons, it affected the electrical signal due to an increase in the population of holes as charge carriers. The synergistic effect between the heteroatoms greatly enhanced the electrical response of the chips. The mechanism governing the reversible sensing involved several processes, including specific interactions between NH3 and surface functional groups, pore-filling with NH3/NO2, and electron–hole conductivity. The structural and chemical features of the carbons were found to act either synergistically or competitively. Surface acidity, by enhancing the affinity of the carbons towards NH3 adsorption, contributed to an ammonia selective detection.




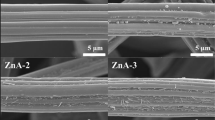
Copyright 2016, Elsevier (Travlou et al. 2016b)

Copyright 2016, Elsevier (Travlou et al. 2016b)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agmon, N.: The Grotthuss mechanism. Chem. Phys. Lett. 244, 456–462 (1995)
Bandosz, T.J.: On the adsorption/oxidation of hydrogen sulfide on activated carbons at ambient temperatures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 246, 1–20 (2002)
Ghosh, R., Singh, A., Santra, S., Ray, S.K., Chandra, A., Guha, P.K.: Highly sensitive large area multi-layered graphene based flexible ammonia sensor. Sens. Actuators B. 205, 67–73 (2014)
Gonçalves, M., Sánchez-García, L., Oliveira Jardim, E. De, Silvestre-Albero, J., Rodríguez-Reinoso, F.: Ammonia removal using activated carbons: effect of the surface chemistry in dry and moist conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 10605–10610 (2011)
Huang, X., Hu, N., Gao, R., Yu, Y., Wang, Y., Yang, Z., Siu-Wai Kong, E., Wei, H., Zhang, Y.: Reduced graphene oxide–polyaniline hybrid: Preparation, characterization and its applications for ammonia gas sensing. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 22488 (2012)
Jagiello, J., Olivier, J.P.: Carbon slit pore model incorporating surface energetical heterogeneity and geometrical corrugation. Adsorption. 19, 777–783 (2013a)
Jagiello, J., Olivier, J.P.: 2D-NLDFT adsorption models for carbon slit-shaped pores with surface energetical heterogeneity and geometrical corrugation. Carbon. 55, 70–80 (2013b)
Johnson, J.L., Behnam, A., An, Y., Pearton, S.J., Ural, A.: Experimental study of graphitic nanoribbon films for ammonia sensing. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 124301 (2011)
Kiciński, W., Szala, M., Bystrzejewski, M.: Sulfur-doped porous carbons: Synthesis and applications. Carbon. 68, 1–32 (2014)
Liang, J., Jiao, Y., Jaroniec, M., Qiao, S.Z.: Sulfur and nitrogen dual-doped mesoporous graphene electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction with synergistically enhanced performance. Angew. Chemie. Int. Ed. 51, 11496–11500 (2012)
Lide, D.R.: Handbook of chemistry and physics, 85th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2005)
Liu, C.C., Walters, A.B., Vannice, M.A.: Measurement of electrical properties of a carbon black. Carbon. 33, 1699–1708 (1995)
Luo, G., Liu, L., Zhang, J., Li, G., Wang, B., Zhao, J.: Hole defects and nitrogen doping in graphene: Implication for super capacitor applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 11184–11193 (2013)
Mangu, R., Rajaputra, S., Singh, V.P.: MWCNT-polymer composites as highly sensitive and selective room temperature gas sensors. Nanotechnology. 22, 215502 (2011)
Nguyen, L.Q., Phan, P.Q., Duong, H.N., Nguyen, C.D., Nguyen, L.H.: Enhancement of NH3 gas sensitivity at room temperature by carbon nanotube-based sensor coated with Co nanoparticles. Sensors. 13, 1754–62 (2013)
Ni, S., Li, Z.Y., Yang, J.L.: Oxygen molecule dissociation on carbon nanostructures with different types of nitrogen doping. Nanoscale. 4, 1184–1189 (2012)
OSHA online. https://www.osha.gov/dts/chemicalsampling/data/CH_218300.html. Accessed 12 June 2016
Ostafiychuk, B.K., Budzulyak, I.M., Rachiy, B.I., Kuzyshyn, M.M., Shyyko, L.O.: Nanoporous nitrogen-containing coal for electrodes of supercapacitors. 1, 17–22 (2013)
Petit, C., Kante, K., Bandosz, T.J.: The role of sulfur-containing groups in ammonia retention on activated carbons. Carbon. 48, 654–667 (2010)
Scardamaglia, M., Struzzi, C., Aparicio Rebollo, F.J., De Marco, P., Mudimela, P.R., Colomer, J.F., Amati, M., Gregoratti, L., Petaccia, L., Snyders, R., Bittencourt, C: Tuning electronic properties of carbon nanotubes by nitrogen grafting: chemistry and chemical stability. Carbon. 83, 118–127 (2015)
Seredych, M., Bandosz, T.J.: S-doped micro/mesoporous carbon–graphene composites as efficient supercapacitors in alkaline media. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 11717 (2013)
Seredych, M., Rodríguez-Castellón, E., Biggs, M.J., Skinner, W., Bandosz, T.J.: Effect of visible light and electrode wetting on the capacitive performance of S- and N-doped nanoporous carbons: importance of surface chemistry. Carbon. 78, 540–558 (2014)
Sheng, Z.H., Shao, L., Chen, J.J., Bao, W. J., Wang, F. B., Xia, X.H.: Catalyst-free synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene via thermal annealing graphite oxide with melamine and its excellent electrocatalysis. ACS Nano 5, 4350–4358 (2011)
Singh, K., Travlou, N.A., Bashkova, S., Rodríguez-Castellón, E., Bandosz, T.J.: Nanoporous carbons as gas sensors: Exploring the surface sensitivity. Carbon. (2014)
Strelko, V.V., Kartel, N.T., Dukhno, I.N., Kuts, V.S., Clarkson, R.B., Odintsov, B.M.: Mechanism of reductive oxygen adsorption on active carbons with various surface chemistry. Surf. Sci. 548, 281–290 (2004)
Travlou, N.A., Seredych, M., Rodríguez-Castellón, E., Bandosz, T.J.: Activated carbon-based gas sensors: effects of surface features on the sensing mechanism. J. Mater. Chem. A. 3, 3821–3831 (2015)
Travlou, N.A., Rodríguez-Castellón, E., Bandosz, T.J.: Sensing of NH3 on heterogeneous nanoporous carbons in the presence of humidity. Carbon. 100, 64–73 (2016a)
Travlou, N.A., Seredych, M., Rodríguez-Castellón, E., Bandosz, T.J.: Insight into ammonia sensing on heterogeneous S- and N- co-doped nanoporous carbons. Carbon. 96, 1014–1021 (2016bb)
Travlou, N.A., Ushay, C., Seredych, M., Rodríguez-Castellón, E., Bandosz, T. J.: Nitrogen-Doped Activated Carbon-Based Ammonia Sensors: Effect of Specific Surface Functional Groups on Carbon Electronic Properties. ACS Sensors. 1, 591–599 (2016c)
Tsubota, T., Takenaka, K., Murakami, N., Ohno, T.: Performance of nitrogen- and sulfur-containing carbon material derived from thiourea and formaldehyde as electrochemical capacitor. J. Power Sources. 196, 10455–10460 (2011)
Usachov, D., Vilkov, O., Grüneis, A., Haberer, D., Fedorov, A., Adamchuk, V.K., Preobrajenski, A.B., Dudin, P., Barinov, A., Oehzelt, M., Laubschat, C., Vyalikh, D.V.: Nitrogen-doped graphene: Efficient growth, structure, and electronic properties. Nano Lett. 11, 5401–5407 (2011)
Wang, Y., Shao, Y., Matson, D.W., Li, J., Lin, Y.: Nitrogen-doped graphene and its biosensing. ACS Nano. 4, 1790–1798 (2010)
Wang, D.W., Li, F., Yin, L.C., Lu, X., Chen, Z.G., Gentle, I.R., Lu, G.Q., Cheng, H.M.: Nitrogen-doped carbon monolith for alkaline supercapacitors and understanding nitrogen-induced redox transitions. Chem. Eur. J. 18, 5345–51 (2012)
Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Hu, N., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhou, Z., Liu, Y., Shen, S., Peng, C.: Ammonia gas sensors based on chemically reduced graphene oxide sheets self-assembled on Au electrodes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9, 251 (2014)
Xiang, C., Jiang, D., Zou, Y., Chu, H., Qiu, S., Zhang, H., Xu, F., Sun, L., Zheng, L.: Ammonia sensor based on polypyrrole–graphene nanocomposite decorated with titania nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 41, 6432–6438 (2015).
Yavari, F., Chen, Z., Thomas, A.V., Ren, W., Cheng, H. M., Koratkar, N.: High sensitivity gas detection using a macroscopic three-dimensional graphene foam network. Sci. Rep. 1, 166 (2011)
Zhang, R., Alecrim, V., Hummelgård, M., Andres, B., Forsberg, S., Andersson, M., Olin, H.: Thermally reduced kaolin-graphene oxide nanocomposites for gas sensing. Sci. Rep. 5, 7676 (2015)
Zhao, X., Zhang, Q., Chen, C.-M., Zhang, B., Reiche, S., Wang, A., Zhang, T., Schlögl, R., Sheng Su, D.: Aromatic sulfide, sulfoxide, and sulfone mediated mesoporous carbon monolith for use in supercapacitor. Nano. Energy. 1, 624–630 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the ARO (Army Research Office Grant W911NF-13-1-0225, and NSF collaborative CBET Grant No. 1133112). Special thanks are addressed to Drs. E. Rodriguez-Castellon, M. Seredych and Mr. Anmol Jadvani for their contributions to our understanding of toxic gas sensing on porous carbons.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Travlou, N.A., Bandosz, T.J. Toxic gas sensing on nanoporous carbons. Adsorption 23, 271–280 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-016-9848-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-016-9848-z