Abstract
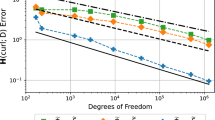
In this paper, we use the integral-identity argument to obtain asymptotic error expansions for the mixed finite element approximation of the Maxwell equations on a rectangular mesh. The extrapolation method is applied to improve the accuracy of the approximation via an interpolation postprocessing technique. With the extrapolation, the approximation accuracy can be improved from O(h) to O(h 4) in the L 2-norm. Illustrative numerical results are given to demonstrate the higher order accuracy of the extrapolation method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bank, R.E., Xu, J.: Asymptotic exact a posteriori error estimators, Part I: grids with superconvergence. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41(6), 2294–2312 (2003)
Bank, R.E., Xu, J.: Asymptotic exact a posteriori error estimators, Part II: general unstructured grids. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41(6), 2312–2332 (2003)
Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: Mixed and Hybrid Finite Element Methods. Springer-Verlag, New York (1991)
Brandts, J.: Superconvergence of mixed finite element semi-discretization of two time-dependent problems. Appl. Math. 44(1), 43–53 (1999)
Ciarlet, P.G.: The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problem. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1978)
Douglas, J., Roberts, J.E.: Mixed finite element methods for second order elliptic problems. Mat. Apl. Comput. 1, 91–103 (1982)
Douglas, J., Roberts, J.E.: Global estimates for mixed methods for second order elliptic equations. Math. Comp. 44, 39–52 (1985)
Fairweather, G., Lin, Q., Lin, Y., Wang, J., Zhang, S.: Asymptotic expansion and Richardson extrapolation of approximate solutions for second order elliptic problems by mixed finite element methods. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44(3), 1122–1149 (2006)
Falk, R.S., Osborn, J.E.: Error estimates for mixed methods. RAIRO Anal. Numer. 14, 309–324 (1980)
Girault, V., Raviart, P.: Finite Element Methods for Navier-Stokes Equations. Springer-Verlag, New York (1980)
Lin, J., Lin, Q.: Extrapolation of the Hood–Taylor element for the Stokes problem. Adv. Comput. Math. 22, 115–123 (2005)
Lin, J., Lin, Q.: Global superconvergence of the mixed finite element methods for 2-D Maxwell equation. J. Comput. Math. 21(5), 637–646 (2003)
Lin, Q., Lin, J.: High accuracy approximation of mixed finite element for 2-d Maxwell equation. Acta Math. 23(4), 499–503 (2003)
Lin, Q., Yan, N.: The Construction and Analysis of High Efficiency Finite Element Methods. HeBei University Publishers (1995)
Lin, Q., Yan, N.: Gloabal superconvergence for Maxwell’s equation. Math. Comp. 69(229), 159–176 (1999)
Lin, Q., Zhang, S., Yan, N.: Extrapolation and defect correction for diffusion equation with boundary integral conditions. Acta Math. Sci. 17(4), 405–412 (1997)
Monk, P.: A mixed finite element for approximating Maxwell’s equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 28(6), 1610–1634 (1991)
Monk, P.: A comparision of three mixed methods for the time-dependent Maxwell’s equations. SIAM J. Statist. Comput. 13(5), 1097–1122 (1992)
Monk, P.: Analysis of a finite element method for Maxwell’s equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 29(3), 714–729 (1992)
Monk, P.: Superconvergence of finite element approximation to Maxwell’s equation. Numer. Methods Partial Differential Equations 10, 793–812 (1994)
Monk, P.: Finite Element Methods for Maxwell Equations. Clarendon Press, Oxford (2003)
Wang, J.: Mixed finite element methods: a chapter in numerical methods. In: Cai, W., Shi, Z., Shu, C., Xu, J. (eds.) Scientific and Engineering Computing. Academic, New York (1996)
Wang, J.: Superconvergence and extrapolation for mixed finite element method on rectangular domains. Math. Comp. 56, 447–503 (1991)
Zhou, A.: Global superconvergence approximation of the mixed finite element method for the Stokes problem and the linear elasticity equation. RAIRO Modél. Math. Anal. Numér. 30, 401–411 (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Zhou.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.10471103), Social Science Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (06JA630047), Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (07JCYBJC14300).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, H. Extrapolation of the Nédélec element for the Maxwell equations by the mixed finite element method. Adv Comput Math 29, 135–145 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-007-9047-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-007-9047-2
Keywords
- Maxwell equations
- Mixed finite element methods
- Nédélec elements
- Interpolation postprocessing
- Extrapolation