Abstract
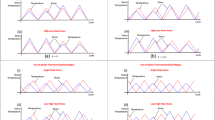
In this paper, the synergistic effects of temperature, oxidation and multicracking modes on damage evolution and life prediction in 2D woven ceramic-matrix composites (CMCs) have been investigated. The damage parameter of fatigue hysteresis dissipated energy and the interface shear stress were used to monitor the damage evolution inside of CMCs. Under cyclic fatigue loading, the fibers broken fraction was determined by combining the interface/fiber oxidation model, interface wear model and fibers statistical failure model at elevated temperature, based on the assumption that the fiber strength is subjected to two-parameter Weibull distribution and the load carried by broken and intact fibers satisfy the Global Load Sharing (GLS) criterion. When the broken fibers fraction approaches to the critical value, the composite fatigue fractures. The evolution of fatigue hysteresis dissipated energy, the interface shear stress and broken fibers fraction versus cycle number, and the fatigue life S–N curves of SiC/SiC at 1000, 1200 and 1300 °C in air and steam condition have been predicted. The synergistic effects of temperature, oxidation, fatigue peak stress, and multicracking modes on the evolution of interface shear stress and fatigue hysteresis dissipated energy versus cycle numbers curves have been analyzed.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Naslain, R.: Design, preparation and properties of non-oxide CMCs for application in engines and nuclear reactors: an overview. Compos. Sci. Technol. 64, 155–170 (2004). doi:10.1016/S0266-3538(03)00230-6
Reynaud, P.: Cyclic fatigue of ceramic-matrix composites at ambient and elevated temperatures. Compos. Sci. Technol. 56, 809–814 (1996). doi:10.1016/0266-3538(96)00025-5
Michael, K.: Fatigue behavior of a SiC/SiC composite at 1000°C in air and steam. Master Thesis, Air Force Institute of Technology, Wright-Patterson Air Force base, Ohio, USA. (2010)
Jacob, D.: Fatigue behavior of an advanced SiC/SiC composite with an oxidation inhibited matrix at 1200°C in air and in steam. Master Thesis, Air Force Institute of Technology, Wright-Patterson Air Force base, Ohio, USA. (2010)
Zhu, S.J., Mizuno, M., Nagano, Y., Cao, J.W., Kagawa, Y., Kaya, H.: Creep and fatigue behavior in an enhanced SiC/SiC composite at high temperature. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81, 2269–2277 (1998). doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1998.tb02621.x
Gowayed, Y., Ojard, G., Santhosh, U., Jefferso, G.: Modeling of crack density in ceramic matrix composites. J. Compos. Mater. 49, 2285–2294 (2015). doi:10.1177/0021998314545188
Evans, A.G., Zok, F.W., McMeeking, R.M.: Fatigue of ceramic matrix composites. Acta Metall. Mater. 43, 859–875 (1995). doi:10.1016/0956-7151(94)00304-Z
Fantozzi, G., Reynaud, P.: Mechanical hysteresis in ceramic matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. Part A. Struct. 521–522, 18–23 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.msea.2008.09.128
Li, L.B., Song, Y.D., Sun, Z.G.: Influence of interface de-bonding on the fatigue hysteresis loops of ceramic matrix composites. Chin. J. Solid Mech. 30, 8–14 (2009)
Li, L.B., Song, Y.D., Sun, Z.G.: Effect of fiber Poisson contraction on fatigue hysteresis loops of ceramic matrix composites. J. Nanjing Univ. Aero. Astro. 41, 181–186 (2009)
Li, L.B., Song, Y.D.: Influnece of fiber failure on fatigue hysteresis loops of ceramic matrix composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 30, 12–25 (2011). doi:10.1177/0731684410386273
Li, L.B.: Modeling the effect of interface wear on fatigue hysteresis behavior of carbon fiber-reinforced ceramic-matrix composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 22, 887–920 (2015). doi:10.1007/s10443-015-9442-7
Li, L.B., Song, Y.D., Sun, Y.C.: Estimate interface shear stress of unidirectional C/SiC ceramic matrix composites from hysteresis loops. Appl. Compos. Mater. 20, 693–707 (2013). doi:10.1007/s10443-012-9297-0
Kuo, W.S., Chou, T.W.: Multiple cracking of unidirectional and cross-ply ceramic matrix composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 78, 745–755 (1995). doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1995.tb08242.x
Lamon, J.: A micromechanics-based approach to the mechanical behavior of brittle-matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 61, 2259–2272 (2001). doi:10.1016/S0266-3538(01)00120-8
Lamouroux, F., Camus, G., Thebault, J.: Kinetics and mechanisms of oxidation of 2D woven C/SiC composites: I, experimental approach. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 77, 2049–2057 (1994). doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1994.tb07096.x
Halbig, M.C., McGuffin-Cawley, J.D., Eckel, A.J., Brewer, D.N.: Oxidation kinetics and stress effects for the oxidation of continuous carbon fibers within a microcracked C/SiC ceramic matrix composite. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 519–526 (2008). doi:10.1111/j.1551-2916.2007.02170.x
Filipuzzi, L., Naslain, R.: Oxidation mechanisms and kinetics of 1D-SiC/C/SiC composite materials: II. Model. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 77, 467–480 (1994). doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1994.tb07016.x
Naslain, R., Guette, A., Rebillat, F., Gallet, S., Lamouroux, F., Filipuzzi, L., Louchet, C.: Oxidation mechanisms and kinetics of SiC-matrix composites and their constituents. J. Mater. Sci. 39, 7303–7316 (2004). doi:10.1023/B:JMSC.0000048745.18938.d5
Lara-Curzio, E.: Analysis of oxidation-assisted stress-rupture of continuous fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites at intermediate temperatures. Compos. Part A 30, 549–554 (1999). doi:10.1016/S1359-835X(98)00148-1
Casas, L., Martinez-Esnaola, J.M.: Modelling the effect of oxidation on the creep behavior of fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites. Acta Mater. 51, 3745–3757 (2003). doi:10.1016/S1359-6454(03)00189-7
Evans, A.G.: Design and life prediction issues for high-temperature engineering ceramics and their composites. Acta Mater. 45, 23–40 (1997). doi:10.1016/S1359-6454(96)00143-7
Curtin, W.A., Ahn, B.K., Takeda, N.: Modeling brittle and tough stress-strain behavior in unidirectional ceramic matrix composites. Acta Mater. 46, 3409–3420 (1998). doi:10.1016/S1359-6454(98)00041-X
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the Science and Technology Department of Jiangsu Province for the funding that made this research study possible
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study has received the support from the Science and Technology Department of Jiangsu Province through the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20140813), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. NS2016070).
Conflict of Interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Longbiao, L. Synergistic Effects of Temperature, Oxidation and Multicracking Modes on Damage Evolution and Life Prediction of 2D Woven Ceramic-Matrix Composites under Tension-Tension Fatigue Loading. Appl Compos Mater 24, 965–981 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-016-9567-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-016-9567-3