Abstract
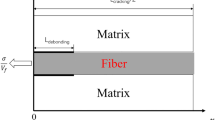
Crack deflection along the fiber/matrix interface for fiber-reinforced composites is an important condition upon which the toughening mechanisms depend. Sound control for the interface debonding of composites contributes to improving the fracture toughness of composites. Combined with the virtual crack closure technique, a finite element model of composites is proposed to predict the competition between the matrix crack deflection along the interface and the matrix crack penetration into the fibers under the thermomechanical coupling fields. For C/C composites, the effects of the geometry size, fiber volume fraction, fiber coating materials and thermal mismatch on the energy release rate and the crack deflection mechanisms are studied. Results show the fiber coating increases the ability to deflect at large thermal mismatch and small crack sizes, and the TaC coating shows larger effect than the SiC coating. The research provides fundamental method for promoting the toughening design of C/C composites.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Launey, M.E., Ritchie, R.O.: On the fracture toughness of advanced materials. Adv. Mater. 21, 1–8 (2009)
Christensen, R.M.: Mechanics of composite materials. Wiley, New York (1979)
Ahn, B.K., Curtin, W.A., Parthasarathy, T.A., Dutton, R.E.: Criteria for crack deflection/penetration criteria for fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 58(11), 1775–1784 (1998)
Kumar, S., Curtin, W.A.: Crack interaction with microstructure. Mater. Today 10(9), 34–44 (2007)
He, M.Y., Hutchinson, J.W.: Crack deflection at an interface between dissimilar elastic materials. Inter. J. Solids Struct. 25(9), 1053–1067 (1989)
Martin, E., Peters, P.W.M., Leguillon, D., Quenisset, J.M.: Conditions for matrix crack deflection at an interface in ceramic matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 250(2), 291–302 (1998)
Martin, E., Leguillon, D.: Energetic conditions for interfacial failure in the vicinity of a matrix crack in brittle matrix composites. Inter. J. Solids Struct. 41(24–25), 6937–6948 (2004)
Kumar, S., Singh, R.N.: Effects of fiber coating properties on the crack deflection and penetration in fiber-reinforced ceramic composites. Acta Mater. 45(11), 4721–4731 (1997)
Carrère, N., Martin, E., Lamon, J.: The influence of the interphase and associated interfaces on the deflection of matrix cracks in ceramic matrix composites. Compos. Part A 31(11), 1179–1190 (2000)
Rybicki, E.F., Kanninen, M.F.: A finite element calculation of stress intensity factors by a modified crack closure integral. Eng. Fract. Mech. 9, 931–938 (1977)
Irwin, G.R.: Fracture dynamics, fracturing of metals. Cleveland: Am. Soc. Met. 147–166 (1948)
Krueger, R.: Virtual crack closure technique: history, approach, and applications. Appl. Mech. Rev. 57, 109–143 (2004)
Zak, A.R., Williams, M.L.: Crack point stress singularities at a bimaterial interface. J. Appl. Mech. 30, 142–143 (1963)
Dundurs, J.: Edge bonded dissimilar orthogonal elastic wedges under normal and shear loading. J. Appl. Mech. 36, 650–662 (1968)
Li, Z., Xiao, P., Xiong, X., Yang, Y., Kuang, W.M.: Form mechanism of cracks in fabricated process of C/C-SiC frictional composites through warm compacted-in situ reacted process. J Cent. South Univ (Science and Technology) 39(3), 506–511 (2008). [In Chinese]
López-de-la-Torrea, L., Winkler, B., Schreuer, J., Knorr, K., Avalos-Borja, M.: Elastic properties of tantalum carbide (TaC). Solid State Commu. 134, 245–250 (2005)
Liao, X.L., Li, H.J., Xu, W.F., Li, K.Z.: Study on the thermal expansion properties of C/C composites. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 3435–3439 (2007)
Tsang, D.K.L., Marsden, B.J., Fok, S.L., Hall, G.: Graphite thermal expansion relationship for different temperature ranges. Carbon 43, 2902–2906 (2005)
Xiong, X., Wang, Y.L., Chen, Z.K., Li, G.D.: Mechanical properties and fracture behaviors of C/C composites with PyC/TaC/PyC, PyC/SiC/TaC/PyC multi-interlayers. Solid State Sci. 11, 1386–1392 (2009)
Rice, J.R.: A path independent integral and the approximate analysis of strain concentration by notches and cracks. J. Appl. Mech. 35(2), 379–386 (1968)
Cai, D.Y., Li, D.C.: Eeffect of carbon fiber content on the mechanical properties of C/C composites. Carbon Tech. 1(1), 16–18 (2001). [In Chinese]
Zhao, J.G., Li, K.Z., Li, H.G.: Influence of fiber volume and heat treatment on the properties of C/C composites. Chinese J. Mater. Res. 19, 293–298 (2009) [In Chinese]
Liu, P.F., Wang, S.L., Tao, W.M., Guo, Y.M.: Finite element analysis of matrix crack deflection mechanisms in fiber-reinforced composites. Acta Mater. Compos Sinica 23(3), 146–152 (2006). [In Chinese]
Wang, Y.L., Xiong, X., Li, G.D., Xiao, P., Chen, Z.K.: Microstructure and mechanical performance of advanced C/C-Tac composites. Chinese J. Nonfer. Metal 18, 608–613 (2008) [In Chinese]
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Funding of China (No. 51375435), the Natural Science Funding of Zhejiang Province of China (No. LY13E050002) and the Specialized Fund for the Basic Research Operating expenses Program of Central Colleges (2013XZZX005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P.F., Yang, Y.H. Finite Element Analysis of the Competition Between Crack Deflection and Penetration of Fiber-Reinforced Composites Using Virtual Crack Closure Technique. Appl Compos Mater 21, 759–771 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-013-9375-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10443-013-9375-y