Abstract
Blood coagulation is regulated through a complex network of biochemical reactions of blood factors. The main acting enzyme is thrombin whose propagation in blood plasma leads to fibrin clot formation. Spontaneous clot formation is normally controlled through the action of different plasma inhibitors, in particular, through the thrombin binding by antithrombin. In the current study we develop a mathematical model of clot formation both in quiescent plasma and in blood flow and determine the analytical conditions on the antithrombin concentration corresponding to different regimes of blood coagulation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butenas S, Mann KG (2001) Blood coagulation. Biochem (Mosc) 61(3):3–12
Chorin A (1968) Numerical solution of the Navier–Stokes equations. Math Comput 22(104):745–762. doi:10.1090/S0025-5718-1968-0242392-2
Dashkevich NM, Ovanesov MV, Balandina N, Karamzin SS, Shestakov PI, Soshitova NP, Tokarev AA, Panteleev MA, Ataullakhanov FI (2012) Thrombin activity propagates in space during blood coagulation as an excitation wave. Biophys J 103(10):2233–2240. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2012.10.011
Galochkina T, Bouchnita A, Kurbatova P, Volpert V (2016) Reaction–diffusion waves of blood coagulation. arXiv:160407635
Ilyashenko V, Solovyov S, Pojman J (1995) Theoretical aspects of self-propagating reaction fronts in condensed medium. AIChE J 41(12):2631–2636
Neeves KB, Onasoga AA, Wufsus AR (2013) The use of microfluidics in hemostasis: clinical diagnostics and biomimetic models of vascular injury. Curr Opin Hematol 20(5):417–423. doi:10.1097/MOH.0b013e3283642186
Pieters J, Willems G, Hemker HC, Lindhout T (1988) Inhibition of factor Xa and factor X, by antithrombin III/heparin during factor X activation. J Biol Chem 263(30):15,313–15,318
Quinsey NS, Greedy AL, Bottomley SP, Whisstock JC, Pike RN (2004) Antithrombin: in control of coagulation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36(3):386–389. doi:10.1016/S1357-2725(03)00244-9
Rosenberg RD (1989) Biochemistry of heparin antithrombin interactions, and the physiologic role of this natural anticoagulant mechanism. Am J Med 87(3B):2S–9S. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(89)80523-6
Rosenberg RD, Damus PS (1973) The purification and mechanism of action of human antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem 248(18):6490–6505
Souter PJ, Thomas S, Hubbard AR, Poole S, Römisch J, Gray E (2001) Antithrombin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced tissue factor and interleukin-6 production by mononuclear cells, human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and whole blood. Crit Care Med 29(1):134–139
Volpert AI, Volpert VA, Volbert VA (1994) Traveling wave solutions of parabolic systems, Translation of mathematical monographs, vol 140
Wufsus AR, Macera NE, Neeves KB (2013) The hydraulic permeability of blood clots as a function of fibrin and platelet density. Biophys J 104(8):1812–1823. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2013.02.055
Zarnitsina VI, Pokhilko AV, Ataullakhanov FI (1996) A mathematical model for the spatio-temporal dynamics of intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. I. The model description. Thromb Res 84(4):225–236. doi:10.1016/S0049-3848(96)00182-X
Zarnitsina VI, Ataullakhanov FI, Lobanov AI, Morozova OL (2001) Dynamics of spatially nonuniform patterning in the model of blood coagulation. Chaos 11(1):57–70. doi:10.1063/1.1345728
Zeldovich YB, Frank-Kamenetskii DA (1938) A theory of thermal propagation of flame. Acta Physicochim USSR 9:341–350
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
1.1 Model of the Intrinsic Pathway Functioning
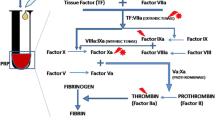
We model the reactions of coagulation cascade presented in the Fig. 8. Straight arrows indicate factors activation, curved arrows indicate the catalytic actions of factors on other factors activation reactions. Ia, IIa, Va, VIIIa, IXa, Xa, XIa denote the concentrations of activated factor forms and I, II, V, VIII, IX, X, XI denote the inactivated forms. Coagulation cascade is launched when sufficient initial amount of thrombin (IIa) is formed and starts the positive feedback loops. As the result we have the conversion of fibrinogen (I) to fibrin (Ia) and fibrin polymerization (Ip). Fibrin polymer finally forms the clot scaffold.
1.2 Parameter Values for Numerical Simulations
Parameter values are taken from Zarnitsina et al. (2001), and Butenas and Mann (2001) (Table 1).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouchnita, A., Galochkina, T. & Volpert, V. Influence of Antithrombin on the Regimes of Blood Coagulation: Insights from the Mathematical Model. Acta Biotheor 64, 327–342 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10441-016-9291-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10441-016-9291-2