Abstract
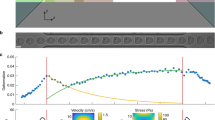
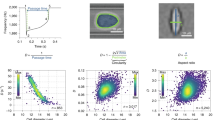
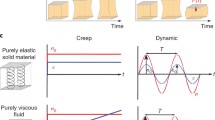
Mechanical deformability of cells is an important property for their function and development, as well as a useful marker of cell state. The classical technique of micropipette aspiration allows single-cell studies and we provide here a method to measure the two basic mechanical parameters, elastic modulus and Poisson’s ratio. The proposed method, developed from finite-element analysis of micropipette aspiration experiments, may be implemented in future technologies for the automated measurement of mechanical properties of cells, based on the micropipette aspiration technique or on the cell transit through flow constrictions. We applied this method to measure the elastic parameters of lymphocytes, in which the mechanical properties depend on their activation state. Additionally, we discuss in this work the accuracy of previous models to estimate the elastic modulus of cells, in particular the analytical model by Theret et al., widely used in the field. We show the necessity of using an improved model, taking into account the finite size of the cells, to obtain new insights that may remain hidden otherwise.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandrov, V. M., and A. D. Pozharskii. Three-dimensional contact problems. Amsterdam: Kluwer, 2001.
Alonso-Fernandez, P., and M. De la Fuente. Role of the immune system in aging and longevity. Curr. Aging Sci. 4:78–100, 2011.
Bao, G., and S. Suresh. Cell and molecular mechanics of biological materials. Nat. Mater. 2:715–725, 2003.
Bernal, A., L. M. Perez, B. De Lucas, N. S. Martin, A. Kadow-Romacker, G. Plaza, K. Raum, and B. G. Galvez. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound improves the functional properties of cardiac mesoangioblasts. Stem Cell Rev. 11:852–865, 2015.
Boal, D. Mechanics of the Cell. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012.
Butler, J. P., and S. M. Kelly. A model for cytoplasmic rheology consistent with magnetic twisting cytometry. Biorheology 35:193–209, 1998.
Cai, X., X. Xing, J. Cai, Q. Chen, S. Wu, and F. Huang. Connection between biomechanics and cytoskeleton structure of lymphocyte and Jurkat cells: an AFM study. Micron 41:257–262, 2010.
Daza, R., J. Cruces, M. Arroyo-Hernandez, N. Mari-Buye, M. De la Fuente, G. R. Plaza, M. Elices, J. Perez-Rigueiro, and G. V. Guinea. Topographical and mechanical characterization of living eukaryotic cells on opaque substrates: development of a general procedure and its application to the study of non-adherent lymphocytes. Phys. Biol. 12:026005, 2015.
Di Carlo, D. A mechanical biomarker of cell state in medicine. J. Lab. Autom. 17:32–42, 2012.
Discher, D. E., D. H. Boal, and S. K. Boey. Simulations of the erythrocyte cytoskeleton at large deformation. II. Micropipette aspiration. Biophys. J. 75:1584–1597, 1998.
Engler, A. J., S. Sen, H. L. Sweeney, and D. E. Discher. Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 126:677–689, 2006.
Evans, E. New membrane concept applied to analysis of fluid shear-deformed and micropipet-deformed red blood-cells. Biophys. J. 13:941–954, 1973.
Evans, E., and A. Yeung. Apparent viscosity and cortical tension of blood granulocytes determined by micropipet aspiration. Biophys. J. 56:151–160, 1989.
Friedmann, A., A. Hoess, A. Cismak, and A. Heilmann. Investigation of cell-substrate interactions by focused ion beam preparation and scanning electron microscopy. Acta Biomater. 7:2499–2507, 2011.
Geissler, E., and A. M. Hecht. The poisson ration in polymer gels. 2. Macromolecules 14:185–188, 1981.
Gossett, D. R., H. T. K. Tse, S. A. Lee, Y. Ying, A. G. Lindgren, O. O. Yang, J. Rao, A. T. Clark, and D. Di Carlo. Hydrodynamic stretching of single cells for large population mechanical phenotyping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109:7630–7635, 2012.
Guck, J., S. Schinkinger, B. Lincoln, F. Wottawah, S. Ebert, M. Romeyke, D. Lenz, H. M. Erickson, R. Ananthakrishnan, D. Mitchell, J. Kas, S. Ulvick, and C. Bilby. Optical deformability as an inherent cell marker for testing malignant transformation and metastatic competence. Biophys. J. 88:3689–3698, 2005.
Haase, K., and A. E. Pelling. Investigating cell mechanics with atomic force microscopy. J. R. Soc. Interface 12:20140970, 2015.
Hochmuth, R. M. Micropipette aspiration of living cells. J. Biomech. 33:15–22, 2000.
Ip, J. E., Y. Wu, J. Huang, L. Zhang, R. E. Pratt, and V. J. Dzau. Mesenchymal stem cells use integrin beta 1 not CXC chemokine receptor 4 for myocardial migration and engraftment. Mol. Biol. Cell 18:2873–2882, 2007.
Janeway, C., P. Travers, M. Walport, and M. Shlomchik. Immunobiology: the immune system in health and disease. Curr. Biol. 1:11, 2001.
Lange, J. R., J. Steinwachs, T. Kolb, L. A. Lautscham, I. Harder, G. Whyte, and B. Fabry. Microconstriction arrays for high-throughput quantitative measurements of cell mechanical properties. Biophys. J. 109:26–34, 2015.
Lois, C., and A. Alvarezbuylla. Long-distance neuronal migration in the adult mammalian brain. Science 264:1145–1148, 1994.
Luo, T., K. Mohan, P. A. Iglesias, and D. N. Robinson. Molecular mechanisms of cellular mechanosensing. Nat. Mater. 12:1064–1071, 2013.
Majstoravich, S., J. Y. Zhang, S. Nicholson-Dykstra, S. Linder, W. Friedrich, K. A. Siminovitch, and H. N. Higgs. Lymphocyte microvilli are dynamic, actin-dependent structures that do not require Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASp) for their morphology. Blood 104:1396–1403, 2004.
Needham, D., and R. M. Hochmuth. Rapid flow of passive neutrophils into a 4 Mu-M pipette and measurement of cytoplasmic viscosity. J. Biomech. Eng. Trans. ASME 112:269–276, 1990.
Nishino, M., H. Tanaka, H. Ogura, Y. Inoue, T. Koh, K. Fujita, and H. Sugimoto. Serial changes in leukcocyte deformability and whole blood rheology in patients with sepsis or trauma. J. Trauma Injury Infect. Crit. Care 59:1425–1431, 2005.
Phillips, R., J. Kondev, J. Theriot, and H. Garcia. Physical Biology of the Cell. New York: Garland Science, 2012.
Plaza, G. R., and T. Q. P. Uyeda. Contraction speed of the actomyosin cytoskeleton in the absence of the cell membrane. Soft Matter 9:4390–4400, 2013.
Plaza, G. R., N. Marí, B. G. Gálvez, A. Bernal, G. V. Guinea, R. Daza, J. Pérez-Rigueiro, C. Solanas, and M. Elices. Simple measurement of the apparent viscosity of a cell from only one picture: application to cardiac stem cells. Phys. Rev. E 90:052715, 2014.
Plaza, G. R., T. Q. P. Uyeda, Z. Mirzaei, and C. A. Simmons. Study of the influence of actin-binding proteins using linear analyses of cell deformability. Soft Matter 11:5435–5446, 2015.
Poschl, J. M. B., P. Ruef, and O. Linderkamp. Deformability of passive and activated neutrophils in children with Gram-negative septicemia. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 65:333–339, 2005.
Rodriguez, M. L., P. J. McGarry, and N. J. Sniadecki. Review on cell mechanics: experimental and modeling approaches. Appl. Mech. Rev. 65:060801, 2013.
Stewart, M. P., J. Helenius, Y. Toyoda, S. P. Ramanathan, D. J. Muller, and A. A. Hyman. Hydrostatic pressure and the actomyosin cortex drive mitotic cell rounding. Nature 469:226–230, 2011.
Suresh, S., J. Spatz, J. P. Mills, A. Micoulet, M. Dao, C. T. Lim, M. Beil, and T. Seufferlein. Connections between single-cell biomechanics and human disease states: gastrointestinal cancer and malaria. Acta Biomater. 1:15–30, 2005.
Svetina, S., G. Kokot, T. S. Kebe, B. Zeks, and R. E. Waugh. A novel strain energy relationship for red blood cell membrane skeleton based on spectrin stiffness and its application to micropipette deformation. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 15:745–758, 2016.
Swift, J., I. L. Ivanovska, A. Buxboim, T. Harada, P. C. D. P. Dingal, J. Pinter, J. D. Pajerowski, K. R. Spinler, J. Shin, M. Tewari, F. Rehfeldt, D. W. Speicher, and D. E. Discher. Nuclear Lamin-A scales with tissue stiffness and enhances matrix-directed differentiation. Science 341:1240104, 2013.
Theret, D. P., M. J. Levesque, M. Sato, R. M. Nerem, and L. T. Wheeler. The application of a homogeneous half-space model in the analysis of endothelial-cell micropipette measurements. J. Biomech. Eng. Trans. ASME 110:190–199, 1988.
Trepat, X., L. Deng, S. S. An, D. Navajas, D. J. Tschumperlin, W. T. Gerthoffer, J. P. Butler, and J. J. Fredberg. Universal physical responses to stretch in the living cell. Nature 447:592, 2007.
Trickey, W. R., G. M. Lee, and F. Guilak. Viscoelastic properties of chondrocytes from normal and osteoarthritic human cartilage. J. Orthop. Res. 18:891–898, 2000.
Urayama, K., T. Takigawa, and T. Masuda. Poisson ratio of poly(vinyl alcohol) gels. Macromolecules 26:3092–3096, 1993.
Villora, E. G., K. Shimamura, and G. R. Plaza. Ultraviolet-visible optical isolators based on CeF3 Faraday rotator. J. Appl. Phys. 117:233101, 2015.
Wang, N., J. D. Tytell, and D. E. Ingber. Mechanotransduction at a distance: mechanically coupling the extracellular matrix with the nucleus. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10:75–82, 2009.
Worthen, G. S., B. Schwab, E. L. Elson, and G. P. Downey. Mechanics of stimulated neutrophils—cell stiffening induces retention in capillaries. Science 245:183–186, 1989.
Yeung, A., and E. Evans. Cortical shell-liquid core model for passive flow of liquid-like spherical cells into micropipets. Biophys. J. 56:139–149, 1989.
YongSheng, Li, and Chen WeiYi. Finite element analysis of micropipette aspiration considering finite size and compressibility of cells. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 56:2208–2215, 2013.
Zahalak, G. I., W. B. Mcconnaughey, and E. L. Elson. Determination of cellular mechanical-properties by cell poking, with an application to leukocytes. J. Biomech. Eng. Trans. ASME 112:283–294, 1990.
Zhou, E. H., C. T. Lim, and S. T. Quek. Finite element simulation of the micropipette aspiration of a living cell undergoing large viscoelastic deformation. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 12:501–512, 2005.
Zhou, E. H., F. D. Martinez, and J. J. Fredberg. Cell rheology mush rather than machine. Nat. Mater. 12:184–185, 2013.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank M. Carmen Álvarez for her help in preparing microscopy samples. Blanca González-Bermúdez received a research grant from the Consejería de Educación, Juventud y Deporte de la Comunidad de Madrid. The authors received support from the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad, Spain, througth the project MAT2016-76847-R.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Konstantinos Konstantopoulos oversaw the review of this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esteban-Manzanares, G., González-Bermúdez, B., Cruces, J. et al. Improved Measurement of Elastic Properties of Cells by Micropipette Aspiration and Its Application to Lymphocytes. Ann Biomed Eng 45, 1375–1385 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-017-1795-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-017-1795-7