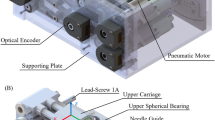
Abstract
This paper presents the design, modeling and experimental evaluation of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-compatible concentric tube continuum robotic system. This system enables MRI-guided deployment of a precurved and steerable concentric tube continuum mechanism, and is suitable for clinical applications where a curved trajectory is needed. This compact 6 degree-of-freedom (DOF) robotic system is piezoelectrically-actuated, and allows simultaneous robot motion and imaging with no visually observable image artifact. The targeting accuracy is evaluated with optical tracking system and gelatin phantom under live MRI-guidance with Root Mean Square (RMS) errors of 1.94 and 2.17 mm respectively. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the robot has kinematic redundancy to reach the same target through different paths. This was evaluated in both free space and MRI-guided gelatin phantom trails, with RMS errors of 0.48 and 0.59 mm respectively. As the first of its kind, MRI-guided targeted concentric tube needle placements with ex vivo porcine liver are demonstrated with 4.64 mm RMS error through closed-loop control of the piezoelectrically-actuated robot.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergeles, C., A. H. Gosline, N. V. Vasilyev, P. J. Codd, P. J. del Nido, and P. E. Dupont. Concentric tube robot design and optimization based on task and anatomical constraints. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31(1):67–84, 2015.
Bergeles, C., and G.-Z. Yang. From passive tool holders to microsurgeons: safer, smaller, smarter surgical robots. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61(5):1565–1576, 2014.
Chen, Y., K.-W. Kwok, and Z. T. H. Tse. An MR-conditional high-torque pneumatic stepper motor for MRI-guided and robot-assisted intervention. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 42(9):1823–1833, 2014.
Diederich, C., R. Stafford, W. Nau, E. Burdette, R. Price, and J. Hazle. Transurethral ultrasound applicators with directional heating patterns for prostate thermal therapy: in vivo evaluation using magnetic resonance thermometry. Med. Phys. 31:405, 2004.
Duerig, T., A. Pelton, and D. Stöckel. An overview of nitinol medical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 273:149–160, 1999.
Dupont, P., J. Lock, B. Itkowitz, and E. Butler. Design and control of concentric-tube robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 26(2):209–225, 2010.
Fischer, G. S., A. Krieger, I. Iordachita, C. Csoma, L. L. Whitcomb, and G. Fichtinger. MRI compatibility of robot actuation techniques—a comparative study. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, 2008, pp. 509–517.
Gilbert, H., J. Neimat, and R. Webster. Concentric tube robots as steerable needles: achieving follow-the-leader deployment. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31:246–258, 2015.
Glozman, D., and M. Shoham. Image-guided robotic flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans. Robot. 23:459 –467, 2007.
Ho, M., A. McMillan, J. Simard, R. Gullapalli, and J. Desai. Toward a SMA-actuated MRI-compatible neurosurgical robot. IEEE Trans. Robot. 28:213–222, 2012.
Iranpanah, B., M. Chen, A. Patriciu, and S. Sirouspour. A pneumatically actuated target stabilization device for MRI-guided breast biopsy. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 20:1288–1300.
Krieger, A., S. Song, N. Bongjoon Cho, I. Iordachita, P. Guion, G. Fichtinger, and L. L. Whitcomb. Development and evaluation of an actuated MRI-compatible robotic system for MRI-guided prostate intervention. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron., (99):1–12, 2012.
Lathrop, R., D. C. Rucker, R. J. Webster III, et al.. Guidance of a steerable cannula robot in soft tissue using preoperative imaging and conoscopic surface contour sensing. In: 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 5601–5606, IEEE, 2010.
Li, G., H. Su, G. Cole, W. Shang, K. Harrington, A. Camilo, J. G. Pilitsis, and G. S. Fischer. Robotic system for MRI-guided stereotactic neurosurgery. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 62(4):1077–1088, 2015.
Lock, J., G. Laing, M. Mahvash, and P. E. Dupont. Quasistatic modeling of concentric tube robots with external loads. In: 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), IEEE, 2010, pp. 2325–2332.
Okazawa, S., R. Ebrahimi, J. Chuang, S. E. Salcudean, and R. Rohling. Hand-held steerable needle device. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 10(3):285–296, 2005.
Patel, N. A., T. van Katwijk, G. Li, P. Moreira, W. Shang, S. Misra, and G. S. Fischer. Closed-loop asymmetric-tip needle steering under continuous intraoperative MRI guidance. In: Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBC, Annual International Conference of the IEEE, pp. 6687 –6690, 2015.
Patriciu, A., A. Patriciu, D. Petrisor, M. Muntener, D. Mazilu, M. Schar, and D. Stoianovici. Automatic brachytherapy seed placement under MRI guidance. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 54(8):1499–1506, 2007.
Rucker, D. C., R. J. Webster, G. S. Chirikjian, and N. J. Cowan. Equilibrium conformations of concentric-tube continuum robots. Int. J. Robot. Res. 29(10):1263–1280, 2010.
Rucker, D., B. Jones, and R. J. Webster III. A geometrically exact model for externally loaded concentric-tube continuum robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 26:769 –780, 2010.
Shang, W., and G. S. Fischer. A high accuracy multi-image registration method for tracking MRI-guided robots. In: SPIE Medical Imaging (Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions, and Modeling Conference), (San Diego, USA), 2012.
Stoianovici, D., D. Stoianovici, A. Patriciu, D. Petrisor, D. Mazilu, and L. Kavoussi. A new type of motor: pneumatic step motor. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 12(1):98–106, 2007.
Su, H., W. Shang, G. Cole, G. Li, K. Harrington, A. Camilo, J. Tokuda, C. M. Tempany, N. Hata, and G. S. Fischer. Piezoelectrically-actuated robotic system for MRI-guided prostate percutaneous therapy. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 99(3):1–13, 2015.
Su, H., D. Cardona, W. Shang, A. Camilo, G. Cole, D. Rucker, R. Webster, and G. Fischer. MRI-guided concentric tube continuum robot with piezoelectric actuation: a feasibility study. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2012, pp. 1939–1945.
Sutherland, G. R., I. Latour, A. D. Greer, T. Fielding, G. Feil, and P. Newhook. An image-guided magnetic resonance-compatible surgical robot. Neurosurgery 62:286–292, 2008, discussion 292–3.
Tsekos, N., A. Khanicheh, E. Christoforou, and C. Mavroidis. Magnetic resonance-compatible robotic and mechatronics systems for image-guided interventions and rehabilitation: a review study. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 9:351–387, 2007.
Vandini, A., C. Bergeles, F.-Y. Lin, and G.-Z. Yang. Vision-based intraoperative shape sensing of concentric tube robots. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2015, pp. 3505–3510.
Webster, R. J. III, J. S. Kim, N. Cowan, G. Chirikjian, and A. Okamura. Nonholonomic modeling of needle steering. Int. J. Robot. Res. 25(5–6):509–525, 2006.
Webster, R. J., J. M. Romano, and N. J. Cowan. Mechanics of precurved-tube continuum robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 25(1):67–78, 2009.
Wu, K., L. Wu, and H. Ren. An image based targeting method to guide a tentacle-like curvilinear concentric tube robot. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO). IEEE, 2014.
Yakar, D., M. G. Schouten, D. G. H. Bosboom, J. O. Barentsz, T. W. J. Scheenen, and J. J. Futterer. Feasibility of a pneumatically actuated MR-compatible robot for transrectal prostate biopsy guidance. Radiology 260(1):241–247, 2011.
Yang, B., U.-X. Tan, A. B. McMillan, R. Gullapalli, and J. P. Desai. Design and control of a 1-DOF MRI-compatible pneumatically actuated robot with long transmission lines. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 16(6):1040–1048, 2011.
Yang, B., S. Roys, U.-X. Tan, M. Philip, H. Richard, R. P. Gullapalli, and J. P. Desai. Design, development, and evaluation of a master–slave surgical system for breast biopsy under continuous MRI. Int. J.Robot. Res., 616–630, 2013.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs Prostate Cancer Research Program New Investigator Award W81XWH-09-1-0191, NSF CAREER Award IIS-1054331, NIH Bioengineering Research Partnership R01CA111288, NIH award R01CA166379, and the Link Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Xiaoxiang Zheng oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, H., Li, G., Rucker, D.C. et al. A Concentric Tube Continuum Robot with Piezoelectric Actuation for MRI-Guided Closed-Loop Targeting. Ann Biomed Eng 44, 2863–2873 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-016-1585-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-016-1585-7