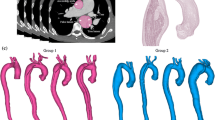
Abstract
Dissection of an artery is characterised by the separation of the layers of the arterial wall causing blood to flow within the wall. The incidence rates of thoracic aortic dissection (AoD) are increasing, despite falls in virtually all other manifestations of cardiovascular disease, including abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). Dissections involving the ascending aorta (Type A) are a medical emergency and require urgent surgical repair. However, dissections of the descending aorta (Type B) are less lethal and require different clinical management whereby the patient may not be offered surgery unless complicating factors are present. But how do we tell if a patient will develop a complication later on? Currently, there is no consensus and the evidence base is limited. There is an opportunity for computational biomechanics to help clinicians decide as to which cases to repair and which to manage with blood pressure control. In this review article, we look at AoD from both the clinical and biomechanical perspective and discuss some of the recent computational studies of both Type A and B AoD. We then focus more on Type B where the real opportunity for patient-specific modelling exists. Finally, we look ahead at some of the promising areas of research that may help clinicians improve the decision-making process surrounding Type B AoD.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azadani, A. N., S. Chitsaz, A. Mannion, A. Mookhoek, A. Wisneski, J. M. Guccione, M. D. Hope, L. Ge, and E. E. Tseng. Biomechanical properties of human ascending thoracic aortic aneurysms. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 96:50–58, 2013.
Beller, C. J., M. R. Labrosse, M. J. Thubrikar, and F. Robicsek. Role of aortic root motion in the pathogenesis of aortic dissection. Circulation 109:763–769, 2004.
Beller, C. J., M. R. Labrosse, M. J. Thubrikar, G. Szabo, F. Robicsek, and S. Hagl. Increased aortic wall stress in aortic insufficiency: clinical data and computer model. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 27:270–275, 2005.
Biasetti, J., T. Gasser, M. Auer, U. Hedin, and F. Labruto. Hemodynamics of the normal aorta compared to fusiform and saccular abdominal aortic aneurysms with emphasis on a potential thrombus formation mechanism. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38:380–390, 2010.
Biasetti, J., F. Hussain, and T. C. Gasser. Blood flow and coherent vortices in the normal and aneurysmatic aortas: a fluid dynamical approach to intra-luminal thrombus formation. J. R. Soc. Interface 8:1449–1461, 2011.
Booher, A. M., E. M. Isselbacher, C. A. Nienaber, S. Trimarchi, A. Evangelista, D. G. Montgomery, J. B. Froehlich, M. P. Ehrlich, J. K. Oh, J. L. Januzzi, P. O’Gara, T. M. Sundt, K. M. Harris, E. Bossone, R. E. Pyeritz, K. A. Eagle, and IRAD Investigators. The IRAD classification system for characterizing survival after aortic dissection. Am. J. Med. 126:730.e719–730.e724, 2013.
Brunkwall, J., and T. Lubke. Part one: for the motion. We do not need level 1 evidence comparing best medical treatment with tevar in patients with uncomplicated type B aortic dissection. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 46:274–277, 2013.
Chen, D., M. Muller-Eschner, D. Kotelis, D. Bockler, Y. Ventikos, and H. von Tengg-Kobligk. A longitudinal study of type-B aortic dissection and endovascular repair scenarios: computational analyses. Med. Eng. Phys. 35:1321–1330, 2013.
Chen, D., M. Muller-Eschner, H. von Tengg-Kobligk, D. Barber, D. Bockler, R. Hose, and Y. Ventikos. A patient-specific study of type-B aortic dissection: evaluation of true-false lumen blood exchange. Biomed. Eng. Online 12:65, 2013.
Cheng, Z., C. Juli, N. B. Wood, R. G. Gibbs, and X. Y. Xu. Predicting flow in aortic dissection: comparison of computational model with PC-MRI velocity measurements. Med. Eng. Phys. 36:1176–1184, 2014.
Cheng, Z., C. Riga, J. Chan, M. Hamady, N. B. Wood, N. J. Cheshire, Y. Xu, and R. G. Gibbs. Initial findings and potential applicability of computational simulation of the aorta in acute type B dissection. J. Vasc. Surg. 57:35S–43S, 2013.
Cheng, Z., F. P. Tan, C. V. Riga, C. D. Bicknell, M. S. Hamady, R. G. Gibbs, N. B. Wood, and X. Y. Xu. Analysis of flow patterns in a patient-specific aortic dissection model. J. Biomech. Eng. 132:051007, 2010.
Chiappini, B., M. Schepens, E. Tan, A. Dell’ Amore, W. Morshuis, K. Dossche, M. Bergonzini, N. Camurri, L. B. Reggiani, G. Marinelli, and R. Di Bartolomeo. Early and late outcomes of acute type a aortic dissection: analysis of risk factors in 487 consecutive patients. Eur. Heart J. 26:180–186, 2005.
Di Martino, E., G. Guadagni, A. Fumero, G. Ballerini, R. Spirito, P. Biglioli, and A. Redaelli. Fluid-structure interaction within realistic three-dimensional models of the aneurysmatic aorta as a guidance to assess the risk of rupture of the aneurysm. Med. Eng. Phys. 23:647–655, 2001.
Doyle, B. J., P. R. Hoskins, K. Miller, D. E. Newby, and M. R. Dweck. Biomechanical analysis of the thoracic aorta: could wall stress and 3d geometry help identify patients at risk of acute aortic dissection? In: 3rd International Conference on Mathematical and Computational Biomedical Engineering—CMBE2013, edited by P. Nithiarasu and R. Löhner. Hong Kong, 2013.
Doyle, B., T. McGloughlin, E. Kavanagh, and P. Hoskins. From detection to rupture: a serial computational fluid dynamics case study of a rapidly expanding, patient-specific, ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. In: Computational Biomechanics for Medicine, edited by B. Doyle, K. Miller, A. Wittek and P. M. F. Nielsen. New York: Springer, 2014, pp. 53–68.
Doyle, B. J., A. Callanan, P. E. Burke, P. A. Grace, M. T. Walsh, D. A. Vorp, and T. M. McGloughlin. Vessel asymmetry as an additional diagnostic tool in the assessment of abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 49:443–454, 2009.
Doyle, B. J., A. Callanan, P. A. Grace, and E. G. Kavanagh. On the influence of patient-specific material properties in computational simulations: a case study of a large ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 29:150–164, 2013.
Doyle, B., A. Callanan, and T. McGloughlin. A comparison of modelling techniques for computing wall stress in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Biomed. Eng. Online 6:38, 2007.
Doyle, B. J., T. M. McGloughlin, K. Miller, J. T. Powell, and P. E. Norman. Regions of high wall stress can predict the future location of rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 37:815–818, 2014.
Dweck, M. R., C. Jones, N. V. Joshi, A. M. Fletcher, H. Richardson, A. White, M. Marsden, R. Pessotto, J. C. Clark, W. A. Wallace, D. M. Salter, G. McKillop, E. J. R. van Beek, N. A. Boon, J. H. F. Rudd, and D. E. Newby. Assessment of valvular calcification and inflammation by positron emission tomography in patients with aortic stenosis. Circulation 125:76–U424, 2012.
Erbel, R., V. Aboyans, C. Boileau, E. Bossone, R. D. Bartolomeo, H. Eggebrecht, A. Evangelista, V. Falk, H. Frank, O. Gaemperli, M. Grabenwöger, A. Haverich, B. Iung, A. J. Manolis, F. Meijboom, C. A. Nienaber, M. Roffi, H. Rousseau, U. Sechtem, P. A. Sirnes, R. S. von Allmen, C. J. M. Vrints, J. L. Zamorano, S. Achenbach, H. Baumgartner, J. J. Bax, H. Bueno, V. Dean, C. Deaton, Ç. Erol, R. Fagard, R. Ferrari, D. Hasdai, A. Hoes, P. Kirchhof, J. Knuuti, P. Kolh, P. Lancellotti, A. Linhart, P. Nihoyannopoulos, M. F. Piepoli, P. Ponikowski, P. A. Sirnes, J. L. Tamargo, M. Tendera, A. Torbicki, W. Wijns, S. Windecker, P. Nihoyannopoulos, M. Tendera, M. Czerny, J. Deanfield, C. D. Mario, M. Pepi, M. J. S. Taboada, M. R. van Sambeek, C. Vlachopoulos, and J. L. Zamorano. 2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases. Document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. The task force for the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 35:2873–2926, 2014.
Fattori, R., P. Cao, P. De Rango, M. Czerny, A. Evangelista, C. Nienaber, H. Rousseau, and M. Schepens. Interdisciplinary expert consensus document on management of type B aortic dissection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 61:1661–1678, 2013.
Fielden, S. W., B. K. Fornwalt, M. Jerosch-Herold, R. L. Eisner, A. E. Stillman, and J. N. Oshinski. A new method for the determination of aortic pulse wave velocity using cross-correlation on 2D PCMR velocity data. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 27:1382–1387, 2008.
Fukui, T., T. Matsumoto, T. Tanaka, T. Ohashi, K. Kumagai, H. Akimoto, K. Tabayashi, and M. Sato. In vivo mechanical properties of thoracic aortic aneurysmal wall estimated from in vitro biaxial tensile test. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 15:295–305, 2005.
Gao, F., Z. Guo, M. Sakamoto, and T. Matsuzawa. Fluid-structure interaction within a layered aortic arch model. J. Biol. Phys. 32:435–454, 2006.
Gao, F., M. Watanabe, and T. Matsuzawa. Stress analysis in a layered aortic arch model under pulsatile blood flow. Biomed. Eng. Online 5:25, 2006.
Gasser, T. C., M. Auer, F. Labruto, J. Swedenborg, and J. Roy. Biomechanical rupture risk assessment of abdominal aortic aneurysms: model complexity versus predictability of finite element simulations. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 40:176–185, 2010.
Hagan, P. G., C. A. Nienaber, E. M. Isselbacher, D. Bruckman, D. J. Karavite, P. L. Russman, A. Evangelista, R. Fattori, T. Suzuki, J. K. Oh, A. G. Moore, J. F. Malouf, L. A. Pape, C. Gaca, U. Sechtem, S. Lenferink, H. J. Deutsch, H. Diedrichs, J. Marcos y Robles, A. Llovet, D. Gilon, S. K. Das, W. F. Armstrong, G. M. Deeb, and K. A. Eagle. The international registry of acute aortic dissection (IRAD): new insights into an old disease. JAMA 283:897–903, 2000.
Hardman, D., B. J. Doyle, S. I. Semple, J. M. Richards, D. E. Newby, W. J. Easson, and P. R. Hoskins. On the prediction of monocyte deposition in abdominal aortic aneurysms using computational fluid dynamics. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H. 227:1114–1124, 2013.
Hiratzka, L. F., G. L. Bakris, J. A. Beckman, R. M. Berson, V. F. Carr, D. E. Casey, Jr, K. A. Eagle, L. K. Herman, E. M. Isselbacker, E. A. Kazerooni, N. T. Kouchoukos, B. W. Lytle, D. M. Milewicz, D. L. Reich, S. Sen, J. A. Shinn, L. G. Svensson, and D. M. Williams. ACCF/AHA/AATS/ACR/ASA/SCA/SCAI/SIR/STS/SVM guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with Thoracic Aortic Disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American College of Radiology, American Stroke Association, Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, and Society for Vascular Medicine. Circulation 121:e266–369, 2010.
Hirst, A. E., Jr., V. J. Johns, Jr., and S. W. Kime, Jr. Dissecting aneurysm of the aorta: a review of 505 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 37:217–279, 1958.
Holzapfel, G. A., G. Sommer, M. Auer, P. Regitnig, and R. W. Ogden. Layer-specific 3D residual deformations of human aortas with non-atherosclerotic intimal thickening. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 35:530–545, 2007.
Jaussaud, N., S. Chitsaz, A. Meadows, M. Wintermark, N. Cambronero, A. N. Azadani, D. A. Saloner, T. A. Chuter, and E. E. Tseng. Acute type a aortic dissection intimal tears by 64-slice computed tomography: a role for endovascular stent-grafting? J. Cardiovasc. Surg. (Torino) 2012.
Joldes, G., K. Miller, A. Wittek, and B. Doyle. A simplified and effective method of computing wall stress in abdominal aortic aneurysms. In: 2nd Workshop on Soft Tissue Modelling, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK, June 10–12, 2015.
Joldes, G., A. Wittek, M. Couton, S. Warfield, and K. Miller. Real-time prediction of brain shift using nonlinear finite element algorithms. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist Interv. 12:300–307, 2009.
Joldes, G. R., A. Wittek, and K. Miller. Real-time nonlinear finite element computations on GPU—application to neurosurgical simulation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199:3305–3314, 2010.
Karmonik, C., J. X. Bismuth, M. G. Davies, and A. B. Lumsden. Computational hemodynamics in the human aorta: a computational fluid dynamics study of three cases with patient-specific geometries and inflow rates. Technol. Health Care 16:343–354, 2008.
Karmonik, C., J. Bismuth, M. G. Davies, D. J. Shah, H. K. Younes, and A. B. Lumsden. A computational fluid dynamics study pre- and post-stent graft placement in an acute type B aortic dissection. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 45:157–164, 2011.
Karmonik, C., J. Bismuth, D. J. Shah, M. G. Davies, D. Purdy, and L. A. B. Computational study of haemodynamic effects of entry- and exit-tear coverage in a debakey type III aortic dissection: technical report. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 42:172–177, 2011.
Karmonik, C., J. Bismuth, T. Redel, J. E. Anaya-Ayala, M. G. Davies, D. J. Shah, and A. B. Lumsden. Impact of tear location on hemodynamics in a type B aortic dissection investigated with computational fluid dynamics. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010, pp. 3138–3141, 2010.
Karmonik, C., S. Partovi, M. Muller-Eschner, J. Bismuth, M. G. Davies, D. J. Shah, M. Loebe, D. Bockler, A. B. Lumsden, and H. von Tengg-Kobligk. Longitudinal computational fluid dynamics study of aneurysmal dilatation in a chronic DeBakey type III aortic dissection. J. Vasc. Surg. 56:260–263.e261, 2012.
Karmonik, C., M. Muller-Eschner, S. Partovi, P. Geisbusch, M. K. Ganten, J. Bismuth, M. G. Davies, D. Bockler, M. Loebe, A. B. Lumsden, and H. von Tengg-Kobligk. Computational fluid dynamics investigation of chronic aortic dissection hemodynamics versus normal aorta. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 47:625–631, 2013.
Kato, K., A. Nishio, N. Kato, H. Usami, T. Fujimaki, and T. Murohara. Uptake of 18F-FDG in acute aortic dissection: a determinant of unfavorable outcome. J. Nucl. Med. 51:674–681, 2010.
Khandheria, B. K. Aortic dissection. The last frontier. Circulation 87:1765–1768, 1993.
Kunov, M. J., D. A. Steinman, and C. R. Ethier. Particle volumetric residence time calculations in arterial geometries. J. Biomech. Eng. 118:158–164, 1996.
Les, A. S., S. C. Shadden, C. A. Figueroa, J. M. Park, M. M. Tedesco, R. J. Herfkens, R. L. Dalman, and C. A. Taylor. Quantification of hemodynamics in abdominal aortic aneurysms during rest and exercise using magnetic resonance imaging and computational fluid dynamics. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38:1288–1313, 2010.
Li, M., K. Miller, G. R. Joldes, B. Doyle, R. R. Garlapati, R. Kikinis, and A. Wittek. Patient-specific biomechanical model as whole-body CT image registration tool. Med. Image Anal. 22:22–34, 2015.
Li, Z. Y., U. Sadat, U. K.-I. J, T. Y. Tang, D. J. Bowden, P. D. Hayes, and J. H. Gillard. Association between aneurysm shoulder stress and abdominal aortic aneurysm expansion: a longitudinal follow-up study. Circulation 122:1815–1822, 2010.
Liu, Y., S. M. Sadowski, A. B. Weisbrod, E. Kebebew, R. M. Summers, and J. Yao. Patient specific tumor growth prediction using multimodal images. Med. Image Anal. 18:555–566, 2014.
Lu, J., X. Zhou, and M. L. Raghavan. Inverse elastostatic stress analysis in pre-deformed biological structures: demonstration using abdominal aortic aneurysms. J. Biomech. 40:693–696, 2007.
Lu, J., X. Zhou, and M. L. Raghavan. Inverse method of stress analysis for cerebral aneurysms. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 7:477–486, 2008.
Maier, A., M. Essler, M. W. Gee, H.-H. Eckstein, W. A. Wall, and C. Reeps. Correlation of biomechanics to tissue reaction in aortic aneurysms assessed by finite elements and [18f]–fluorodeoxyglucose–PET/CT. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 28:456–471, 2012.
Maier, A., M. W. Gee, C. Reeps, J. Pongratz, H. H. Eckstein, and W. A. Wall. A comparison of diameter, wall stress, and rupture potential index for abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture risk prediction. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38:3124–3134, 2010.
Morris, L., P. Delassus, A. Callanan, M. Walsh, F. Wallis, P. Grace, and T. McGloughlin. 3D numerical simulation of blood flow through models of the human aorta. J. Biomech. Eng. 127:767–775, 2005.
Morris, L., P. Delassus, M. Walsh, and T. McGloughlin. A mathematical model to predict the in vivo pulsatile drag forces acting on bifurcated stent grafts used in endovascular treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA). J. Biomech. 37:1087–1095, 2004.
Nathan, D. P., C. Xu, J. H. Gorman, 3rd, R. M. Fairman, J. E. Bavaria, R. C. Gorman, K. B. Chandran, and B. M. Jackson. Pathogenesis of acute aortic dissection: a finite element stress analysis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 91:458–463, 2011.
Nathan, D. P., C. Xu, T. Plappert, B. Desjardins, J. H. Gorman, 3rd, J. E. Bavaria, R. C. Gorman, K. B. Chandran, and B. M. Jackson. Increased ascending aortic wall stress in patients with bicuspid aortic valves. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 92:1384–1389, 2011.
Nchimi, A., J. P. Cheramy-Bien, T. C. Gasser, G. Namur, P. Gomez, L. Seidel, A. Albert, J. O. Defraigne, N. Labropoulos, and N. Sakalihasan. Multifactorial relationship between 18f-Fluoro-Deoxy-Glucose positron emission tomography signaling and biomechanical properties in unruptured aortic aneurysms. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 7:82–91, 2014.
Nichols, W. W., and M. F. O’Rourke. Mcdonald’s Blood Flow in Arteries (4th ed.). New York: Oxfrod University Press, 1998.
Nienaber, C. A., and J. T. Powell. Management of acute aortic syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 33:26–35, 2012.
O’Leary, S. A., E. G. Kavanagh, P. A. Grace, T. M. McGloughlin, and B. J. Doyle. The biaxial mechanical behaviour of abdominal aortic aneurysm intraluminal thrombus: classification of morphology and the determination of layer and region specific properties. J. Biomech. 47:1430–1437, 2014.
O’Leary, S. A., D. A. Healey, E. G. Kavanagh, M. T. Walsh, T. M. McGloughlin, and B. J. Doyle. The biaxial biomechanical behavior of abdominal aortic aneurysm tissue. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 42:2440–2450, 2014.
O’Leary, S. A., J. J. Mulvihill, H. E. Barrett, E. G. Kavanagh, M. T. Walsh, T. M. McGloughlin, and B. J. Doyle. Determining the influence of calcification on the failure properties of abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) tissue. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 42:154–167, 2015.
Olufsen, M. S., C. S. Peskin, W. Y. Kim, E. M. Pedersen, A. Nadim, and J. Larsen. Numerical simulation and experimental validation of blood flow in arteries with structured-tree outflow conditions. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 28:1281–1299, 2000.
Pasta, S., J. A. Phillippi, T. G. Gleason, and D. A. Vorp. Effect of aneurysm on the mechanical dissection properties of the human ascending thoracic aorta. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 143:460–467, 2012.
Pasta, S., A. Rinaudo, A. Luca, M. Pilato, C. Scardulla, T. G. Gleason, and D. A. Vorp. Difference in hemodynamic and wall stress of ascending thoracic aortic aneurysms with bicuspid and tricuspid aortic valve. J. Biomech. 46:1729–1738, 2013.
Patel, D. J., J. C. Greenfield, Jr, W. G. Austen, A. G. Morrow, and D. L. Fry. Pressure-flow relationships in the ascending aorta and femoral artery of man. J. Appl. Physiol. 20:459–463, 1965.
Qiao, A., and Y. Liu. Medical application oriented blood flow simulation. Clin. Biomech. 23(Supplement 1):S130–S136, 2008.
Rajagopal, K., C. Bridges, and K. R. Rajagopal. Towards an understanding of the mechanics underlying aortic dissection. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 6:345–359, 2007.
Reeps, C., J. Pelisek, R. A. Bundschuh, M. Gurdan, A. Zimmermann, S. Ockert, M. Dobritz, H. H. Eckstein, and M. Essler. Imaging of acute and chronic aortic dissection by 18F-FDG PET/CT. J. Nucl. Med. 51:686–691, 2010.
Sakalihasan, N., C. A. Nienaber, R. Hustinx, P. Lovinfosse, M. El Hachemi, J. P. Cheramy-Bien, L. Seidel, J. P. Lavigne, J. Quaniers, M. A. Kerstenne, A. Courtois, A. Ooms, A. Albert, J. O. Defraigne, and J. B. Michel. (Tissue PET) vascular metabolic imaging and peripheral plasma biomarkers in the evolution of chronic aortic dissections. Eur. Heart. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 16:626–633, 2015.
Sakalihasan, N., H. Van Damme, P. Gomez, P. Rigo, C. M. Lapiere, B. Nusgens, and R. Limet. Positron emission tomography (PET) evaluation of abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 23:431–436, 2002.
Sankaran, S., L. J. Grady, and C. A. Taylor. Real-time sensitivity analysis of blood flow simulations to lumen segmentation uncertainty. Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv. 17:1–8, 2014.
Shang, E. K., D. P. Nathan, S. R. Sprinkle, R. M. Fairman, J. E. Bavaria, R. C. Gorman, J. H. Gorman, and B. M. Jackson. Impact of wall thickness and saccular geometry on the computational wall stress of descending thoracic aortic aneurysms. Circulation 128:S157–S162, 2013.
Sheikh, A. S., K. Ali, and S. Mazhar. Acute aortic syndrome. Circulation 128:1122–1127, 2013.
Shim, V. B., R. P. Pitto, R. M. Streicher, P. J. Hunter, and I. A. Anderson. Development and validation of patient-specific finite element models of the hemipelvis generated from a sparse CT data set. J. Biomech. Eng. 130:051010, 2008.
Sokolis, D. P., E. P. Kritharis, and D. C. Iliopoulos. Effect of layer heterogeneity on the biomechanical properties of ascending thoracic aortic aneurysms. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 50:1227–1237, 2012.
Song, H. K., M. Kindem, J. E. Bavaria, H. C. Dietz, D. M. Milewicz, R. B. Devereux, K. A. Eagle, C. L. Maslen, B. L. Kroner, R. E. Pyeritz, K. W. Holmes, J. W. Weinsaft, V. Menashe, W. Ravekes, and S. A. LeMaire. Long-term implications of emergency versus elective proximal aortic surgery in patients with marfan syndrome in the genetically triggered thoracic aortic aneurysms and cardiovascular conditions consortium registry. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 143:282–286, 2012.
Stone, P. H., S. Saito, S. Takahashi, Y. Makita, S. Nakamura, T. Kawasaki, A. Takahashi, T. Katsuki, S. Nakamura, A. Namiki, A. Hirohata, T. Matsumura, S. Yamazaki, H. Yokoi, S. Tanaka, S. Otsuji, F. Yoshimachi, J. Honye, D. Harwood, M. Reitman, A. U. Coskun, M. I. Papafaklis, and C. L. Feldman. Prediction of progression of coronary artery disease and clinical outcomes using vascular profiling of endothelial shear stress and arterial plaque characteristics: the PREDICTION study. Circulation 126:172–181, 2012.
Sueyoshi, E., I. Sakamoto, K. Hayashi, T. Yamaguchi, and T. Imada. Growth rate of aortic diameter in patients with type B aortic dissection during the chronic phase. Circulation 110(Suppl 1):II256–II261, 2004.
Thubrikar, M. J., P. Agali, and F. Robicsek. Wall stress as a possible mechanism for the development of transverse intimal tears in aortic dissections. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 23:127–134, 1999.
Tong, J., T. Cohnert, P. Regitnig, and G. A. Holzapfel. Effects of age on the elastic properties of the intraluminal thrombus and the thrombus-covered wall in abdominal aortic aneurysms: biaxial extension behaviour and material modelling. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 42:207–219, 2011.
Trimarchi, S., C. A. Nienaber, V. Rampoldi, T. Myrmel, T. Suzuki, R. H. Mehta, E. Bossone, J. V. Cooper, D. E. Smith, L. Menicanti, A. Frigiola, J. K. Oh, M. G. Deeb, E. M. Isselbacher, and K. A. Eagle. Contemporary results of surgery in acute type a aortic dissection: the international registry of acute aortic dissection experience. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 129:112–122, 2005.
Trimarchi, S., J. L. Tolenaar, F. H. Jonker, B. Murray, T. T. Tsai, K. A. Eagle, V. Rampoldi, H. J. Verhagen, J. A. van Herwaarden, F. L. Moll, B. E. Muhs, and J. A. Elefteriades. Importance of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection prognosis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012.
Tsai, T. T., A. Evangelista, C. A. Nienaber, T. Myrmel, G. Meinhardt, J. V. Cooper, D. E. Smith, T. Suzuki, R. Fattori, A. Llovet, J. Froehlich, S. Hutchison, A. Distante, T. Sundt, J. Beckman, J. L. Januzzi, Jr, E. M. Isselbacher, and K. A. Eagle. Partial thrombosis of the false lumen in patients with acute type B aortic dissection. N. Engl. J. Med. 357:349–359, 2007.
Tsai, T. T., M. S. Schlicht, K. Khanafer, J. L. Bull, D. T. Valassis, D. M. Williams, R. Berguer, and E. K. A. Tear. Size and location impacts false lumen pressure in an ex vivo model of chronic type B aortic dissection. J. Vasc. Surg. 47:844–851, 2008.
Tsai, T. T., S. Trimarchi, and C. A. Nienaber. Acute aortic dissection: perspectives from the international registry of acute aortic dissection (IRAD). Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 37:149–159, 2009.
Tse, K. M., P. Chiu, H. P. Lee, and P. Ho. Investigation of hemodynamics in the development of dissecting aneurysm within patient-specific dissecting aneurismal aortas using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. J. Biomech. 44:827–836, 2011.
Vande Geest, J. P., M. S. Sacks, and D. A. Vorp. The effects of aneurysm on the biaxial mechanical behavior of human abdominal aorta. J. Biomech. 39:1324–1334, 2006.
Weisbecker, H., D. M. Pierce, P. Regitnig, and G. A. Holzapfel. Layer-specific damage experiments and modeling of human thoracic and abdominal aortas with non-atherosclerotic intimal thickening. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 12:93–106, 2012.
Wen, C. Y., A. S. Yang, L. Y. Tseng, and J. W. Chai. Investigation of pulsatile flowfield in healthy thoracic aorta models. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38:391–402, 2010.
Xu, X. Y., A. Borghi, A. Nchimi, J. Leung, P. Gomez, Z. Cheng, J. O. Defraigne, and N. Sakalihasan. High levels of 18F-FDG uptake in aortic aneurysm wall are associated with high wall stress. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 39:295–301, 2010.
Zhang, S., L. Gu, W. Liang, P. Huang, J. Boehm, and J. Xu. The framework for real-time simulation of deformable soft-tissue using a hybrid elastic model. In: Biomedical Simulation, edited by M. Harders and G. Székely. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2006, pp. 75–83.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Eileen Wiryadinata, Adam Byass, Grand Joldes and Adam Wittek from The University of Western Australia, and Peter Hoskins, David Newby, Marc Dweck and Scott Semple from The University of Edinburgh. We would also like to thank our funding sources; The University of Western Australia and the National Health and Medical Research Council (Grants: APP1063986, APP1083572).
Conflict of Interest
The authors have nothing to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Karol Miller oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doyle, B.J., Norman, P.E. Computational Biomechanics in Thoracic Aortic Dissection: Today’s Approaches and Tomorrow’s Opportunities. Ann Biomed Eng 44, 71–83 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1366-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1366-8