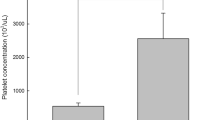
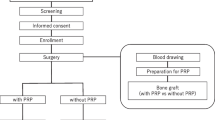
Abstract
Spinal fusion is one of the most commonly performed procedures for the treatment of spinal instability caused by a multitude of pathologies. However, despite significant advances in spinal instrumentation, failed fusion, or pseudoarthrosis, remains a significant challenge. Therefore, other additives such as bone graft extenders and growth factors have been explored as a method to augment fusion rates. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) represents an additional approach, as it has shown some promise in bone regeneration. While the general use of PRP in orthopedic applications has been reviewed previously, its use in spinal fusion has not been systematically analyzed. The objective of this review is to systematically discuss the role of PRP in augmentation of bone regeneration for the purpose of spinal fusion. Background information on PRP, including a discussion of its preparation, activation, and growth factors, is included. Additionally, data from in vitro studies utilizing PRP in bone tissue engineering strategies is analyzed, and the available animal and clinical studies are systematically reviewed in order to provide guidance on future research pathways as well as the potential role of PRP in spinal fusion surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACDF:
-
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion
- ALIF:
-
Anterior lumbar interbody fusion
- β-TCP:
-
Beta-tricalcium phosphate
- CaCl2 :
-
Calcium chloride
- CaCO3 :
-
Calcium carbonate
- HA:
-
Hydroxyapatite
- MSC:
-
Mesenchymal stem cell
- PDGF:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor
- PRP:
-
Platelet-rich plasma
- rhBMP:
-
Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor beta
- TLIF:
-
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion
References
Acebal-Cortina, G., M. A. Suarez-Suarez, C. Garcia-Menendez, L. Moro-Barrero, R. Iglesias-Colao, and A. Torres-Perez. Evaluation of autologous platelet concentrate for intertransverse lumbar fusion. Eur. Spine J. 20(Suppl 3):361–366, 2011.
Alsousou, J., M. Thompson, P. Hulley, A. Noble, and K. Willett. The biology of platelet-rich plasma and its application in trauma and orthopaedic surgery: a review of the literature. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 91:987–996, 2009.
Auerbach, J. D., K. B. McGowan, M. Halevi, M. C. Gerling, A. D. Sharan, P. G. Whang, et al. Mitigating adverse event reporting bias in spine surgery. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 95:1450–1456, 2013.
Boden, S. D., J. Kang, H. Sandhu, and J. G. Heller. Use of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 to achieve posterolateral lumbar spine fusion in humans: a prospective, randomized clinical pilot trial: 2002 Volvo Award in clinical studies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 27:2662–2673, 2002.
Bose, B., and M. A. Balzarini. Bone graft gel: autologous growth factors used with autograft bone for lumbar spine fusions. Adv. Ther. 19:170–175, 2002.
Bydon Macki, M., N. B. Abt, T. F. Witham, J. P. Wolinsky, Z. L. Gokaslan, et al. The cost-effectiveness of interbody fusions versus posterolateral fusions in 137 patients with lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine J. 15:492–498, 2015.
Carragee, E. J., E. L. Hurwitz, and B. K. Weiner. A critical review of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 trials in spinal surgery: emerging safety concerns and lessons learned. Spine J. 11:471–491, 2011.
Carreon, L. Y., S. D. Glassman, Y. Anekstein, and R. M. Puno. Platelet gel (AGF) fails to increase fusion rates in instrumented posterolateral fusions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30:E243–246, 2005; (discussion E247).
Castro, Jr., F. P. Role of activated growth factors in lumbar spinal fusions. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 17:380–384, 2004.
Cinotti, G., A. Corsi, B. Sacchetti, M. Riminucci, P. Bianco, and G. Giannicola. Bone ingrowth and vascular supply in experimental spinal fusion with platelet-rich plasma. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38:385–391, 2013.
Cmolik, B. L., J. A. Spero, G. J. Magovern, and R. E. Clark. Redo cardiac surgery: late bleeding complications from topical thrombin-induced factor V deficiency. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 105:222–227, 1993; (discussion 227–228).
Coseo, N. M., N. Saldua, and J. Harrop. Current use of biologic graft extenders for spinal fusion. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 56:203–207, 2012.
Cunningham, B. W., J. C. Sefter, N. Hu, and P. C. McAfee. Autologous growth factors versus autogenous graft for anterior cervical interbody fusion: an in vivo caprine model. J. Neurosurg. Spine 13:216–223, 2010.
Eppley, B. L., J. E. Woodell, and J. Higgins. Platelet quantification and growth factor analysis from platelet-rich plasma: implications for wound healing. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 114:1502–1508, 2004.
Feiz-Erfan, I., M. Harrigan, V. K. Sonntag, and T. R. Harrington. Effect of autologous platelet gel on early and late graft fusion in anterior cervical spine surgery. J. Neurosurg. Spine 7:496–502, 2007.
Gullung, G. B., J. W. Woodall, M. A. Tucci, J. James, D. A. Black, and R. A. McGuire. Platelet-rich plasma effects on degenerative disc disease: analysis of histology and imaging in an animal model. Evid. Based Spine Care J. 2:13–18, 2011.
Han, B., J. Woodell-May, M. Ponticiello, Z. Yang, and M. Nimni. The effect of thrombin activation of platelet-rich plasma on demineralized bone matrix osteoinductivity. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 91:1459–1470, 2009.
Hartmann, E. K., T. Heintel, R. H. Morrison, and A. Weckbach. Influence of platelet-rich plasma on the anterior fusion in spinal injuries: a qualitative and quantitative analysis using computer tomography. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 130:909–914, 2010.
Hee, H. T., M. E. Majd, R. T. Holt, and L. Myers. Do autologous growth factors enhance transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion? Eur. Spine J. 12:400–407, 2003.
Helm, G. A., H. Dayoub, and J. A. Jane, Jr. Bone graft substitutes for the promotion of spinal arthrodesis. Neurosurg. Focus 10:E4, 2001.
Hsu, W. K., R. E. Hashimoto, S. H. Berven, and A. Nassr. Biological substitutes/extenders for spinal arthrodesis: which agents are cost-effective? Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 39:S86–98, 2014.
Hsu, W. K., A. Mishra, S. R. Rodeo, F. Fu, M. A. Terry, P. Randelli, et al. Platelet-rich plasma in orthopaedic applications: evidence-based recommendations for treatment. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 21:739–748, 2013.
Intini, G. The use of platelet-rich plasma in bone reconstruction therapy. Biomaterials 30:4956–4966, 2009.
Jenis, L. G., R. J. Banco, and B. Kwon. A prospective study of Autologous Growth Factors (AGF) in lumbar interbody fusion. Spine J. 6:14–20, 2006.
Kaiser, M. G., M. W. Groff, W. C. Watters, 3rd, Z. Ghogawala, P. V. Mummaneni, A. T. Dailey, et al. Guideline update for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 16: bone graft extenders and substitutes as an adjunct for lumbar fusion. J. Neurosurg. Spine 21:106–132, 2014.
Kamoda, H., S. Ohtori, T. Ishikawa, M. Miyagi, G. Arai, M. Suzuki, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on posterolateral lumbar fusion in a rat model. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 95:1109–1116, 2013.
Kasten, P., J. Vogel, I. Beyen, S. Weiss, P. Niemeyer, A. Leo, et al. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on the in vitro proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on distinct calcium phosphate scaffolds: the specific surface area makes a difference. J. Biomater. Appl. 23:169–188, 2008.
Kasten, P., J. Vogel, R. Luginbuhl, P. Niemeyer, S. Weiss, S. Schneider, et al. Influence of platelet-rich plasma on osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and ectopic bone formation in calcium phosphate ceramics. Cells Tissues Organs 183:68–79, 2006.
Kelly, A. M., J. N. Batke, N. Dea, D. P. Hartig, C. G. Fisher, and J. T. Street. Prospective analysis of adverse events in surgical treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine J. 14:2905–2910, 2014.
Kim, E. S., J. J. Kim, and E. J. Park. Angiogenic factor-enriched platelet-rich plasma enhances in vivo bone formation around alloplastic graft material. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2:7–13, 2010.
Klaassen, M. A., and W. S. Pietrzak. Platelet-rich plasma application and heterotopic bone formation following total hip arthroplasty. J. Invest. Surg. 24:257–261, 2011.
Kurz, L. T., S. R. Garfin, and R. E. Booth, Jr. Harvesting autogenous iliac bone grafts. A review of complications and techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 14:1324–1331, 1989.
Lacoste, E., I. Martineau, and G. Gagnon. Platelet concentrates: effects of calcium and thrombin on endothelial cell proliferation and growth factor release. J. Periodontol. 74:1498–1507, 2003.
Landi, A., R. Tarantino, N. Marotta, A. G. Ruggeri, M. Domenicucci, L. Giudice, et al. The use of platelet gel in postero-lateral fusion: preliminary results in a series of 14 cases. Eur. Spine J. 20(Suppl 1):S61–S67, 2011.
Li, H., X. Zou, Q. Xue, N. Egund, M. Lind, and C. Bunger. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion with carbon fiber cage loaded with bioceramics and platelet-rich plasma. An experimental study on pigs. Eur. Spine J. 13:354–358, 2004.
Liao, H. T., K. G. Marra, and J. P. Rubin. Application of platelet-rich plasma and platelet-rich fibrin in fat grafting: basic science and literature review. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 20:267–276, 2014.
Lowery, G. L., S. Kulkarni, and A. E. Pennisi. Use of autologous growth factors in lumbar spinal fusion. Bone 25:47S–50S, 1999.
Marlovits, S., M. Mousavi, C. Gabler, J. Erdos, and V. Vecsei. A new simplified technique for producing platelet-rich plasma: a short technical note. Eur. Spine J. 13(Suppl 1):S102–S106, 2004.
Martin, Jr., G. J., S. D. Boden, M. A. Marone, M. A. Marone, and P. A. Moskovitz. Posterolateral intertransverse process spinal arthrodesis with rhBMP-2 in a nonhuman primate: important lessons learned regarding dose, carrier, and safety. J. Spinal Disord. 12:179–186, 1999.
Marx, R. E. Platelet-rich plasma: evidence to support its use. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 62:489–496, 2004.
Marx, R. E., E. R. Carlson, R. M. Eichstaedt, S. R. Schimmele, J. E. Strauss, and K. R. Georgeff. Platelet-rich plasma: growth factor enhancement for bone grafts. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 85:638–646, 1998.
Miyazaki, M., H. Tsumura, J. C. Wang, and A. Alanay. An update on bone substitutes for spinal fusion. Eur. Spine J. 18:783–799, 2009.
Morone, M. A., S. D. Boden, G. Hair, G. J. Martin, Jr., M. Racine, L. Titus, et al. The Marshall R. Urist Young Investigator Award. Gene expression during autograft lumbar spine fusion and the effect of bone morphogenetic protein 2. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 351:252–265, 1998.
Obata, S., K. Akeda, T. Imanishi, K. Masuda, W. Bae, R. Morimoto, et al. Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma-releasate on intervertebral disc degeneration in the rabbit anular puncture model: a preclinical study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 14:R241, 2012.
Okamoto, S., T. Ikeda, K. Sawamura, M. Nagae, H. Hase, Y. Mikami, et al. Positive effect on bone fusion by the combination of platelet-rich plasma and a gelatin beta-tricalcium phosphate sponge: a study using a posterolateral fusion model of lumbar vertebrae in rats. Tissue Eng. Part A 18:157–166, 2012.
Rajaee, S. S., H. W. Bae, L. E. Kanim, and R. B. Delamarter. Spinal fusion in the United States: analysis of trends from 1998 to 2008. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 37:67–76, 2012.
Rao, R. D., K. Gourab, V. B. Bagaria, V. B. Shidham, U. Metkar, and B. C. Cooley. The effect of platelet-rich plasma and bone marrow on murine posterolateral lumbar spine arthrodesis with bone morphogenetic protein. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 91:1199–1206, 2009.
Rodeo, S. A., S. D. Boden, M. M. Murray, and T. A. Einhorn. 2011 AOA Symposium: tissue engineering and tissue regeneration: AOA critical issues. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 95:e109, 2013.
Rodriguez, I. A., E. A. Growney Kalaf, G. L. Bowlin, and S. A. Sell. Platelet-rich plasma in bone regeneration: engineering the delivery for improved clinical efficacy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014:392398, 2014.
Scholz, M., P. Schleicher, T. Eindorf, F. Friedersdorff, M. Gelinsky, U. Konig, et al. Cages augmented with mineralized collagen and platelet-rich plasma as an osteoconductive/inductive combination for interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35:740–746, 2010.
Sethi, P. M., J. J. Miranda, S. Kadiyala, T. Patel, M. Panjabi, N. Troiano, et al. Evaluation of autologous platelet concentrate for intertransverse process lumbar fusion. Am. J. Orthop. (Belle Mead NJ) 37:E84–E90, 2008.
Simman, R., A. Hoffmann, R. J. Bohinc, W. C. Peterson, and A. J. Russ. Role of platelet-rich plasma in acceleration of bone fracture healing. Ann. Plast. Surg. 61:337–344, 2008.
Slater, M., J. Patava, K. Kingham, and R. S. Mason. Involvement of platelets in stimulating osteogenic activity. J. Orthop. Res. 13:655–663, 1995.
Sys, J., J. Weyler, T. Van Der Zijden, P. Parizel, and J. Michielsen. Platelet-rich plasma in mono-segmental posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Eur. Spine J. 20:1650–1657, 2011.
Tarantino, R., P. Donnarumma, C. Mancarella, M. Rullo, G. Ferrazza, G. Barrella, et al. Posterolateral arthrodesis in lumbar spine surgery using autologous platelet-rich plasma and cancellous bone substitute: an osteoinductive and osteoconductive effect. Glob. Spine J. 4:137–142, 2014.
Tsai, C. H., H. C. Hsu, Y. J. Chen, M. J. Lin, and H. T. Chen. Using the growth factors-enriched platelet glue in spinal fusion and its efficiency. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 22:246–250, 2009.
Vadala, G., A. Di Martino, M. C. Tirindelli, L. Denaro, and V. Denaro. Use of autologous bone marrow cells concentrate enriched with platelet-rich fibrin on corticocancellous bone allograft for posterolateral multilevel cervical fusion. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2:515–520, 2008.
Walsh, W. R., A. Loefler, S. Nicklin, D. Arm, R. E. Stanford, Y. Yu, et al. Spinal fusion using an autologous growth factor gel and a porous resorbable ceramic. Eur. Spine J. 13:359–366, 2004.
Wang, D., H. Jiang, S. Wang, H. Li, H. Zhang, L. Zhao, et al. Construction of tissue-engineered bone using a bioreactor and platelet-rich plasma. Exp. Ther. Med. 8:413–418, 2014.
Wang, S. Z., Y. F. Rui, Q. Tan, and C. Wang. Enhancing intervertebral disc repair and regeneration through biology: platelet-rich plasma as an alternative strategy. Arthritis Res. Ther. 15:220, 2013.
Wang, C., D. Zhong, X. Zhou, K. Yin, Q. Liao, L. Kong, et al. Preparation of a new composite combining strengthened beta-tricalcium phosphate with platelet-rich plasma as a potential scaffold for the repair of bone defects. Exp. Ther. Med. 8:1081–1086, 2014.
Weibrich, G., T. Hansen, W. Kleis, R. Buch, and W. E. Hitzler. Effect of platelet concentration in platelet-rich plasma on peri-implant bone regeneration. Bone 34:665–671, 2004.
Weibrich, G., W. K. Kleis, G. Hafner, and W. E. Hitzler. Growth factor levels in platelet-rich plasma and correlations with donor age, sex, and platelet count. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 30:97–102, 2002.
Weibrich, G., W. K. Kleis, M. Kunz-Kostomanolakis, A. H. Loos, and W. Wagner. Correlation of platelet concentration in platelet-rich plasma to the extraction method, age, sex, and platelet count of the donor. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 16:693–699, 2001.
Weiner, B. K., and M. Walker. Efficacy of autologous growth factors in lumbar intertransverse fusions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 28:1968–1970, 2003; (discussion 1971).
Wu, R. H., J. F. Fraser, and R. Hartl. Minimal access versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: meta-analysis of fusion rates. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35:2273–2281, 2010.
Acknowledgments
This article reflects the views of the author and should not be construed to represent the US Food and Drug Administration’s views or policies.
Conflict of interest
The senior author (TW) has received prior donations of research materials from Eli Lily and Company for research indirectly related to the subject of this manuscript. Additionally, TW receives research support from the Gordon and Marilyn Macklin Foundation. No other benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Eric M. Darling oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elder, B.D., Holmes, C., Goodwin, C.R. et al. A Systematic Assessment of the Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Spinal Fusion. Ann Biomed Eng 43, 1057–1070 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1300-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1300-0