Abstract
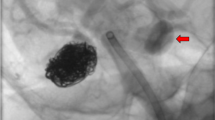
In vitro simulations of the trajectory and lodgement locations of emboli within the circle of Willis (CoW) are crucial in understanding the associated hemodynamic effects in stroke patients. A clot was fabricated from the hemolymph of a crustacean species. Clots were injected into the internal carotid artery via a cerebral flow facility housing a manufactured CoW human model. The trajectory of the clot was tracked and its hemodynamic effects monitored. The clots traveled with an average velocity of 88 mm/s along the ipsilateral side with momentary pauses along high curvature regions before finally lodging within the distal branches of the ipsilateral middle cerebral artery (MCA). These clots either elongated along the branching vessels or compressed against a bifurcation point. A blocked M1-segment of the MCA reduced the efferent blood pressure and flow rates by (15–77%) and (20–100%) respectively with a re-distribution of the flow towards the other efferent vessels. Mimicking blood clots with crustacean hemolymph provides a much lower biohazard risk than using human or mammalian blood clots and a superior alternative to synthetic materials. The geometry of the distal MCA vasculature will determine the end morphology of the lodged clot. Clotting severely reduces the distal flow rates and pressures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Chebl, A. Endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke may be safely performed with no time window limit in appropriately selected patients. Stroke. 41:1996–2000, 2010.
Asakura, F., H. Yilmaz, G. Sekoranja, et al. Preclinical testing of a new clot-retrieving wire device using polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel vascular models. Neuroradiology. 49(3):243–251, 2007.
Buijs, P. C., M. J. Krabbe-Hartkamp, C. J. Bakker, E. E. de Lange, L. M. Ramos, M. M. Breteler, and W. P. Mali. Effect of age on cerebral blood flow: measurement with ungated two-dimensional phase-contrast MR angiography in 250 adults. Radiology. 209(3):667–674, 1998.
Cao, C., S. C. Ang, P. Indraratna, C. Manganas, P. Bannon, D. Black, D. Tian, and T. D. Yan. Systematic review and meta-analysis of transcatheter aortic valve implantation versus surgical aortic valve replacement for severe aortic stenosis. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2(1):10–23, 2013.
Carlisle, C. R., E. A. Sparks, C. Der Loughlian, and M. Guthold. Strength and failure of fibrin fibre branchpoints. J. Thromb. Haemost. 8:1135–1138, 2010.
Chueh, J. K., A. K. Wakhloo, G. H. Hendricks, C. F. Silva, J. P. Weaver, and M. J. Gounis. Mechanical characterisation of thromboemboli in acute ischemic stroke and laboratory embolus analogs. Am. J. Neurodiol. 32:1237–1244, 2011.
Chung, E. M. L., J. P. Hague, M.-A. Chanrion, K. V. Ramnarine, E. Katsogridakis, and D. H. Evans. Embolus trajectory through a physical replica of the major cerebral arteries. Stroke. 41(4):647–652, 2010.
Cloft, H. J., A. Rabinstein, G. Lanzino, and D. F. Kallmes. Intra-arterial stroke therapy: an assessment of demand and available work force. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 30(3):453–458, 2009.
Ene, F., C. Gachon, P. Delassus, R. Carroll, F. Stefanov, P. O’Flynn, and L. Morris. In vitro evaluation of the effects of intraluminal thrombus on abdominal aortic aneurysm wall dynamics. Med. Eng. Phys. 33(8):957–966, 2011.
Fahy, P., P. Delassus, P. McCarthy, S. Sultan, N. Hynes, and L. Morris. An in vitro assessment of the cerebral hemodynamcis through three patient specific circle of willis geometries. J. Biomech. Eng. 136(1):011007, 2013. doi:10.1115/1.402577.
Fahy, P., P. Delassus, P. O’Flynn, and L. Morris. An experimental study of the effects anatomical variations have on collateral flows within the circle of willis. Farmington, VA: Proceedings of the ASME Summer Bioengineering Conference, 2011.
Fahy, P., P. McCarthy, S. Sultan, N. Hynes, P. Delassus, and L. Morris. An experimental investigation of the hemodynamic variations due to aplastic vessels within three-dimensional phantom models of the circle of willis. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 42(1):123–128, 2014.
Ford, M. D., N. Alperin, S. H. Lee, D. W. Holdsworth, and D. A. Steinman. Characterization of volumetric flow rate waveforms in the normal internal carotid and vertebral arteries. Physiol. Meas. 26(4):477–488, 2005.
Gács, G., F. T. Mérei, and M. Bodosi. Balloon catheter as a model of cerebral emboli in humans. Stroke. 13(1):39–42, 1982.
Ghanem, A., J. Kocurek, J. M. Sinning, M. Weber, C. Hammersting, M. Wagner, M. Vasa-Nicotera, E. Grube, N. Werner, and G. Nickenig. Novel approaches for prevention of stroke related to transcather aortic valve implantation. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 11(10):1311–1320, 2013.
Gralla, J., M. Burkhardt, G. Schroth, M. EI-Koussy, M. Reinert, K. Nedeltchev, J. Slotboom, and C. Brekenfeld. Occlusion length is a crucial determinant of efficiency and complication rate in thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 29(2):247–252, 2008.
Hart, R. G., J. L. Halperin, L. A. Pearce, D. C. Anderson, R. A. Kronmal, et al. Lessons from the stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation trials. Ann. Intern. Med. 138(10):831–838, 2003.
Hauton, C. The scope of the crustacean immune system for disease control. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 110(2):251–260, 2012.
Hossmann, K. A. Experimental models for the investigation of brain ischemia. Cardiovasc. Res. 39:106–120, 1998.
Hussain, S. I., O. O. Zaidar, and B. F. M. Fitzsimmons. The penumbra system for mechanical thrombectomy in endovascular acute ischemic stroke therapy. Neurology. Suppl. 1:S135–S141, 2012.
Hylek, E. M., A. S. Go, Y. Chang, N. G. Jensvold, L. E. Henault, et al. Effect of intensity of oral anticoagulation on stroke severity and mortality in atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 349:1019–1026, 2003.
Jou, L.-D., D. H. Lee, and M. E. Mawad. Cross-flow at the anterior communicating artery and its implication in cerebral aneurysm formation. J. Biomech. 43(11):2189–2195, 2010.
Krings, T., D. M. Mandell, T.-R. Kiehl, S. Geibprasert, M. Tymianski, H. Alvarez, K. G. Terbrugge, and F.-J. Hans. Intracranial aneurysms: from vessel wall pathology to therapeutic approach. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 7(10):547–559, 2011.
Leon, M. B., C. R. Smith, M. Mack, C. Miller, et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve implantation for aortic stenosis in patients who cannot undergo surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 363(17):1597–1607, 2010.
Lin, J. K., and W. C. Shyu. Middle cerebral artery occlusion compromising the sensory and motor cortices. Tzu Chi Med. 18:382–384, 2006.
Liu, W., C. R. Carlisle, E. A. Sparks, and M. Guthold. The mechanical properties of single fibrin fibres. J. Thromb. Haemost. 8:1030–1036, 2010.
Maas, S. J., and J. E. Safdieh. Ischemic stroke: pathophysiology and principles of localization. Hosp. Physician Neurol. Board Rev. Man. 13(2):1–17, 2009.
Makkar, R. R., P. G. Fontana, H. Jilaihawi, S. Kapadia, et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement for inoperable severe aortic stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 366(18):1696–1704, 2012.
Marder, V. J., D. J. Chute, S. Starkman, A. M. Abolian, et al. Analysis of thrombi retrieved from cerebral arteries of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 37(8):2086–2093, 2006.
Masuda, J., C. Yutani, J. Ogata, Y. Kuriyama, and T. Yamaguchi. Atheromatous embolism in the brain: a clinicopathologic analysis of 15 autopsy cases. Neurology. 44:1231–1237, 1994.
Monson, K. L., W. Goldsmith, N. M. Barbaro, and G. T. Manley. Axial mechanical properties of fresh human cerebral blood vessels. J Biomech. Eng. 125(2):288–294, 2003.
Monson, K. L., W. Goldsmith, N. M. Barbaro, and G. T. Manley. Significance of source and size in the mechanical response of human cerebral blood vessels. J. Biomech. 38(4):737–744, 2005.
Moore, S., T. David, J. G. Chase, J. Arnold, and J. Fink. 3D models of blood flow in the cerebral vasculature. J. Biomech. 39(8):1454–1463, 2006.
Morris, L., P. O’Donnell, P. Delassus, and T. McGloughlin. Experimental assessment of stress patterns in abdominal aortic aneurysms using the photoelastic method. Strain. 40(4):165–172, 2004.
Morris, L., F. Stefanov, and T. McGloghlin. Stent graft performance in the treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms: the influence of compliance and geometry. J. Biomech. 46(2):383–395, 2013.
Ng, Y. S., J. Stein, M. M. Ning, and R. M. Black-Schaffer. Comparison of clinical characteristics and functional outcomes of ischemic stroke in different vascular territories. Stroke. 38:2309–2314, 2007.
Nogueira, R. G., L. H. Schwamm, and J. Hirsch. Endovascular approaches to acute stroke, part 1: drugs, devices, and data. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 30(4):649–661, 2009.
O’Brien, T., L. Morris, M. O’Donnell, M. Walsh, and T. McGloughlin. Injection-moulded models of major and minor arteries: the variability of model wall thickness owing to casting technique. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H. 219(H5):381–386, 2005.
Ringelstein, E. B., R. Biniek, C. Weiller, B. Ammeling, P. N. Nolte, and A. Thorn. Type and extent of hemispheric brain infarctions and clinical outcome in early and delayed middle cerebral artery recanalization. Neurology. 42:289–298, 1992.
Ruland, S., and A. Venkatesh. Cerebral autoregulation and blood pressure lowering. Hypertension. 49:977–978, 2007.
Schwaigner, B. J., F. Kober, A. S. Gersing, J. F. Kleine, S. Wunderlich, C. Zimmer, H. Poppert, and S. Prothmann. The pREset stent retriever for endovascular treatment of stroke caused by MCA occlusion: safety and clinical outcome. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2014. doi:10.1007/s00062-014-0329-z.
Seitz, R. J., P. Hoflick, F. Binkofski, L. Tellmann, H. Herzog, and H. J. Freund. Role of the premotor cortex in recover from middle cerebral artery infarction. Arch. Neurol. 55:1081–1088, 1998.
Shrive, A. K., A. M. Metcalfe, J. R. Cartwright, and T. J. Greenhough. C-reactive protein and SAP-like pentraxin are both present in Limulus polyphemus hemolymph: crystal structure of Limulus SAP. J. Mol. Biol. 290(5):997–1008, 1999.
Steinman, D. A., Y. Hoi, P. Fahy, L. Morris, et al. Variability of CFD solutions for pressure and flow in a giant aneurysm: the SBC2012 CFD challenge. J. Biomech. Eng. 135(2):021016, 2013. doi:10.1115/1.4023382.
Tanaka, H., N. Fujita, T. Enoki, et al. Relationship between variations in the circle of Willis and flow rates in internal carotid and basilar arteries determined by means of magnetic resonance imaging with semiautomated lumen segmentation: reference data from 125 healthy volunteers. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 27:1770–1775, 2006.
Taussky, P., R. G. Tawk, W. P. Daugherty, and R. A. Hanel. Medical therapy for ischemic stroke: review of intravenous and intra-arterial treatment methods. World Neurosurg. 76(6):S9–S15, 2011.
Tennuci, C., G. Pearce, J. Wong, S. Nayak, T. Jones, F. Lally, and C. Roffe. Comparison of the effectiveness of three methods of recanalization in a model of the middle cerebral artery: thrombus aspiration via a 4F Catheter, thrombus aspiration via the GP thromboaspiration device, and mechanical thrombectomy using the solitaire thrombectomy device. Stroke Res. Treat. 2011:186424, 2011.
Tenser, M. S., A. P. Amar, and W. J. Mack. Mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke using the MERCI retriever and penumbra aspiration systems. World Neurosurg. 76(6):S16–S23, 2011.
Torvik, A., and K. Skullerud. Watershed infarcts in the brain caused by microemboli. Clin. Neuropathol. 1:99–105, 1982.
Weisel, J. W. Structure of fibrin: impact on clot stability. J. Thromb. Haemost. 5(1):116–124, 2007.
Zhu, L., D. S. Liebeskind, R. Jahan, S. Starkman, N. Salamon, G. Duckwiler, et al. Thrombus branching and vessel curvature are important determinants of middle cerebral artery trunk recanalization with merci thrombectomy devices. Stroke. 43:787–792, 2014.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by Strands I and III from the Department of Education in Ireland.
Conflict of interest
We have no conflict of interest issues.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Andreas Anayiotos oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fahy, P., Malone, F., McCarthy, E. et al. An In Vitro Evaluation of Emboli Trajectories Within a Three-Dimensional Physical Model of the Circle of Willis Under Cerebral Blood Flow Conditions. Ann Biomed Eng 43, 2265–2278 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1250-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1250-6