Abstract
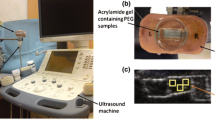
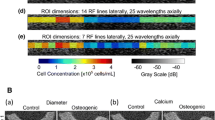
Histology and biochemical assays are standard techniques for estimating cell concentration in engineered tissues. However, these techniques are destructive and cannot be used for longitudinal monitoring of engineered tissues during fabrication processes. The goal of this study was to develop high-frequency quantitative ultrasound techniques to nondestructively estimate cell concentration in three-dimensional (3-D) engineered tissue constructs. High-frequency ultrasound backscatter measurements were obtained from cell-embedded, 3-D agarose hydrogels. Two broadband single-element transducers (center frequencies of 30 and 38 MHz) were employed over the frequency range of 13–47 MHz. Agarose gels with cell concentrations ranging from 1 × 104 to 1 × 106 cells mL−1 were investigated. The integrated backscatter coefficient (IBC), a quantitative ultrasound spectral parameter, was calculated and used to estimate cell concentration. Accuracy and precision of this technique were analyzed by calculating the percent error and coefficient of variation of cell concentration estimates. The IBC increased linearly with increasing cell concentration. Axial and lateral dimensions of regions of interest that resulted in errors of less than 20% were determined. Images of cell concentration estimates were employed to visualize quantitatively regional differences in cell concentrations. This ultrasound technique provides the capability to rapidly quantify cell concentration within 3-D tissue constructs noninvasively and nondestructively.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubry, A., and A. Derode. Multiple scattering of ultrasound in weakly inhomogeneous media: application to human soft tissues. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 129:225–233, 2011.
Bamber, J. C. Ultrasonic properties of tissues. In: Ultrasound in Medicine, edited by F. A. Duck, A. C. Baker, and H. C. Starritt. Bristol, UK: Institute of Physics Publishing, 1998, pp. 57–88.
Bendat, J. S., and A. G. Piersol. Random Data Analysis and Measurement Procedures. New York: Whiley, p. 93, 2000.
Brand, S., E. C. Weiss, R. M. Lemor, and M. C. Kolios. High frequency ultrasound tissue characterization and acoustic microscopy of intracellular changes. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 34:1396–1407, 2008.
Couture, O. Ultrasound Echoes from Targeted Contrast Agents. Ph.D. Thesis, Graduate Department in Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, 2007.
Fite, B. Z., M. Decaris, Y. Sun, Y. Sun, A. Lam, C. K. Ho, J. K. Leach, and L. Marcu. Noninvasive multimodal evaluation of bioengineered cartilage constructs combining time-resolved fluorescence and ultrasound imaging. Tissue Eng. Part C 17:495–504, 2011.
Franceschini, E., and R. Guillermin. Experimental assessment of four ultrasound scattering models for characterizing concentrated tissue-mimicking phantoms. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 132:3735–3747, 2012.
Garvin, K. A., D. C. Hocking, and D. Dalecki. Controlling the spatial organization of cells and extracellular matrix proteins in engineered tissues using ultrasound standing wave fields. Ultrasound Med Biol. 36:1919–1932, 2010.
Ghoshal, G., M. L. Oelze, and W. D. O’Brien. Quantitative ultrasound history and successes. In: Quantitative Ultrasound in Soft Tissues, edited by J. Mamou, and M. L. Oelze. New York: Springer, 2013, pp. 21–42.
Gudur, M., R. R. Rao, Y. S. Hsiao, A. W. Peterson, C. X. Deng, and J. P. Stegemann. Noninvasive, quantitative, spatiotemporal characterization of mineralization in three-dimensional collagen hydrogels using high-resolution spectral ultrasound imaging. Tissue Eng. Part C 18:935–946, 2012.
Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation. F. D. A. US Department of Health and Human Services, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Rockville, MD, 2001.
Insana, M. F., and T. J. Hall. Parametric ultrasound imaging from backscatter coefficient measurements: image formation and interpretation. Ultrason. Imaging 12:245–267, 1990.
Insana, M. F., R. F. Wagner, D. G. Brown, and T. J. Hall. Describing small-scale structure in random media using pulse-echo ultrasound. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 87:179–192, 1990.
Tissue Engineering. Advancing tissue science and engineering: a foundation for the future. A multi-agency strategic plan. Tissue Eng. 13:2825–2826, 2007.
Katouzian, A., S. Sathyanarayana, B. Baseri, E. E. Konofagou, and S. G. Carlier. Challenges in atherosclerotic plaque characterization with intravascular ultrasound (IVUS): from data collection to classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 12:315–327, 2008.
Kemmerer, J. P., and M. L. Oelze. Quantitative ultrasound assessment of thermal therapy in liver. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 129:2440, 2011.
Kemmerer, J. P., and M. L. Oelze. Ultrasonic assessment of thermal therapy in rat liver. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 38:2130–2137, 2012.
Kolios, M. C., G. J. Czarnota, M. Lee, J. W. Hunt, and M. D. Sherar. Ultrasonic spectral parameter characterization of apoptosis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 28:589–597, 2002.
Kreitz, S., G. Dohmen, S. Hasken, T. Schmitz-Rode, P. Mela, and S. Jockenhoevel. Nondestructive method to evaluate the collagen content of fibrin-based tissue engineered structures via ultrasound. Tissue Eng. Part C 17:1021–1026, 2011.
Leithem, S. M., R. J. Lavarello, W. D. O’Brien, and M. L. Oelze. Estimating concentration of ultrasound contrast agents with backscatter coefficients: experimental and theoretical aspects. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 131:2295–2305, 2012.
Libgot-Calle, R., F. Ossant, Y. Gruel, P. Lermusiaux, and F. Patat. High frequency ultrasound device to investigate the acoustic properties of whole blood during coagulation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 34:252–264, 2008.
Liu, W., and J. A. Zagzebski. Trade-offs in data acquisition and processing parameters for backscatter and scatterer size estimations. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. 57:340–352, 2010.
Lizzi, F. L., M. Astor, E. J. Feleppa, M. Shao, and A. Kalisz. Statistical framework for ultrasonic spectral parameter imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 23:1371–1382, 1997.
Lizzi, F. L., M. Astor, T. Liu, C. Deng, D. Coleman, and R. Silverman. Ultrasonic spectrum analysis for tissue assays and therapy evaluation. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 8:3–10, 1997.
Lizzi, F. L., M. Greenebaum, E. J. Feleppa, M. Elbaum, and D. J. Coleman. Theoretical framework for spectrum analysis in ultrasonic tissue characterization. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 73:1366–1373, 1983.
Lizzi, F., M. Ostromogilsky, E. Feleppa, M. Rorke, and M. Yaremko. Relationship of ultrasonic spectral parameters to features of tissue microstructure. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. 33:319–329, 1986.
Machado, J. C., and F. S. Foster. Ultrasonic integrated backscatter coefficient profiling of human coronary arteries in vitro. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. 48:17–27, 2001.
McCormick, M. M., E. L. Madsen, M. E. Deaner, and T. Varghese. Absolute backscatter coefficient estimates of tissue-mimicking phantoms in the 5–50 MHz frequency range. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 130:737–743, 2011.
Oe, K., M. Miwa, K. Nagamune, Y. Sakai, S. Y. Lee, T. Niikura, T. Iwakura, T. Hasegawa, N. Shibanuma, Y. Hata, R. Kuroda, and M. Kurosaka. Nondestructive evaluation of cell numbers in bone marrow stromal cell/beta-tricalcium phosphate composites using ultrasound. Tissue Eng. Part C 16:347–353, 2010.
Oelze, M. L., and W. D. O’Brien, Jr. Defining optimal axial and lateral resolution for estimating scatterer properties from volumes using ultrasound backscatter. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 115:3226–3234, 2004.
Pancrazio, J. J., F. Wang, and C. A. Kelley. Enabling tools for tissue engineering. Biosens. Bioelectron. 22:2803–2811, 2007.
Pinkerton, J. M. M. The absorption of ultrasonic waves in liquids and its relation to molecular constitution. Proc. Phys. Soc. 62:129–141, 1949.
Raju, B. I., and M. A. Srinivasan. High-frequency ultrasonic attenuation and backscatter coefficients of in vivo normal human dermis and subcutaneous fat. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 27:1543–1556, 2001.
Raju, B. I., K. J. Swindells, S. Gonzalez, and M. A. Srinivasan. Quantitative ultrasonic methods for characterization of skin lesions in vivo. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 29:825–838, 2003.
Reid, J. M. Standard substitution methods for measuring ultrasonic scattering in tissues. In: Ultrasonic Scattering in Biological Tissues, edited by K. K. Shung, and G. A. Thieme. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 1993, pp. 171–204.
Roberjot, V., S. L. Bridal, P. Laugier, and G. Berger. Absolute backscatter coefficient over a wide range of frequencies in a tissue-mimicking phantom containing two populations of scatterers. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. 43:970–978, 1996.
Saha, R. K., E. Franceschini, and G. Cloutier. Assessment of accuracy of the structure-factor-size-estimator method in determining red blood cell aggregate size from ultrasound spectral backscatter coefficient. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 129:2269–2277, 2011.
Saha, R. K., and M. C. Kolios. Effects of cell spatial organization and size distribution on ultrasound backscattering. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. 58:2118–2131, 2011.
Solorio, L., B. M. Babin, R. B. Patel, J. Mach, N. Azar, and A. A. Exner. Noninvasive characterization of in situ forming implants using diagnostic ultrasound. J. Controlled Release 143:183–190, 2010.
Szabo, T. L. Diagnostic Ultrasound Imaging: Inside Out. Burlington, MA: Elsevier Academic Press, 2004, pp. 243–269, 442–444.
Taggart, L. R., R. E. Baddour, A. Giles, G. J. Czarnota, and M. C. Kolios. Ultrasonic characterization of whole cells and isolated nuclei. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 33:389–401, 2007.
Vlad, R. M., S. Brand, A. Giles, M. C. Kolios, and G. J. Czarnota. Quantitative ultrasound characterization of responses to radiotherapy in cancer mouse models. Clin. Cancer Res. 15:2067–2075, 2009.
Waag, R. C., P. P. K. Lee, R. M. Lerner, L. P. Hunter, R. Gramiak, and E. A. Schenk. Angle scan and frequency-swept ultrasonic scattering characterization of tissue. In: Ultrasound in Medicine, edited by D. White, and E. A. Lyons. New York, NY: Plenum Press, 1978, pp. 563–565.
Wagner, R. F., M. F. Insana, and D. G. Brown. Statistical properties of radiofrequency and envelope-detected signals with applications to medical ultrasound. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 4:910–922, 1987.
Zagzebski, J. A., L. X. Yao, E. J. Boote, and Z. F. Lu. Quantitative backscatter imaging. In: Ultrasonic Scattering in Biological Tissues, edited by K. K. Shung, and G. A. Thieme. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 1993, pp. 451–486.
Zhang, D., X. F. Gong, and S. G. Ye. Acoustic nonlinearity parameter tomography for biological specimens via measurements of the second harmonics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 99:2397–2402, 1996.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Sally Z. Child, M.S., and Stephen McAleavey, Ph.D. (University of Rochester) for technical assistance and helpful discussions. This work was supported, in part, by National Institutes of Health Grant EB008368.
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Scott I Simon oversaw the review of this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mercado, K.P., Helguera, M., Hocking, D.C. et al. Estimating Cell Concentration in Three-Dimensional Engineered Tissues Using High Frequency Quantitative Ultrasound. Ann Biomed Eng 42, 1292–1304 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-0994-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-0994-8