Abstract
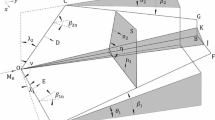
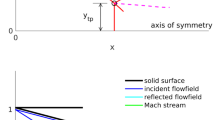
The properties of Mach stems in hypersonic corner flow induced by Mach interaction over 3D intersecting wedges were studied theoretically and numerically. A new method called “spatial dimension reduction” was used to analyze theoretically the location and Mach number behind Mach stems. By using this approach, the problem of 3D steady shock/shock interaction over 3D intersecting wedges was transformed into a 2D moving one on cross sections, which can be solved by shock-polar theory and shock dynamics theory. The properties of Mach interaction over 3D intersecting wedges can be analyzed with the new method, including pressure, temperature, density in the vicinity of triple points, location, and Mach number behind Mach stems. Theoretical results were compared with numerical results, and good agreement was obtained. Also, the influence of Mach number and wedge angle on the properties of a 3D Mach stem was studied.
Graphic abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mach, E.: Uber den verlauf von funkenwellen in der ebene und im raume. Sitzungsbr. Akad. Wiss. Wien. 78, 819–38 (1878)
von Neumann, J.: Oblique reflection of shocks. Explos. Res. Rep. 12, Navy Dept., Bureau of Ordinance, Washington, DC, USA. (1943)
von Neumann, J.: Refraction, intersection and reflection of shock waves. NAVORD Rep. 203-45, Navy Dept., Bureau of Ordinance, Washington, DC, USA (1943)
Kawamura, R., Saito, H.: Reflection of shock waves-1. Pseudo-stationary case. J. Phys. Soc. Japan 11, 584–592 (1956)
Courant, R., Friedrichs, K.O.: Hypersonic Flow and Shock Waves. Willey Interscience, New York (1959)
Liepmann, H.W., Roshko, A.: Elements of Gas Dynamics. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, New York (1957)
Emanuel, G.: Gasdynamics: Theory and Applications, AIAA Education Series. AIAA Inc., New York (1986)
Ben-Dor, G., Takayama, K.: The phenomena of shock wave reflection—a review of unsolved problems and future research needs. Shock Waves 2, 211–223 (1992)
Hornung, H.G., Robinson, M.L.: Transition from regular to MR of shock waves. Part 2: the steady flow criterion. J. Fluid Mech. 123, 155–164 (1982)
Azevedo, D.J., Liu, C.S.: Engineering approach to the prediction of shock patterns in bounded high-speed flows. AIAA J. 31, 83–90 (1993)
Li, H., Ben-Dor, G.: A parametric study of Mach reflection in steady flows. J. Fluid Mech. 341, 101–135 (1997)
Dewey, J.M., McMillin, D.J.: Observation and analysis of the Mach reflection of weak uniform plane shock waves. Part 1. observations. J. Fluid Mech. 152, 49–66 (1985)
Dewey, J.M., McMillin, D.J.: Observation and analysis of the Mach reflection of weak uniform plane shock waves. Part 2. analysis. J. Fluid Mech. 152, 67–81 (1985)
Tan, L.H., Ren, Y.X., Wu, Z.N.: Analytical and numerical study of the near flow field and shape of the Mach stem in steady flows. J. Fluid Mech. 546, 341–362 (2006)
Tan, L.H., Ren, Y.X. and Wu, Z.N.: The shape of incident shock wave in steady axisymmetric conical mach reflection. The 5th Asian-Pacific Conference on Aerospace Technology and Science (2006)
Gao, B., Wu, Z.N.: A study of the flow structure for Mach reflection in steady supersonic flow. J. Fluid Mech. 656, 29–50 (2010)
Marconi, F.: Supersonic, invisid, conical corner flow-fileds. AIAA J. 18, 78–84 (1980)
West, J.E., Korkegi, R.H.: Interaction of the corner of intersecting wedges at a Mach number of 3 and high Reynolds numbers. AIAA J. 10, 652–656 (1972)
Xie, P., Han, Z.Y., Takayama, K.: A study of the interaction between two triple points. Shock Waves 14, 29–36 (2005)
Yang Y.: The investigations on complex flow of three dimensional shock/shock interaction [Ph.D. Thesis], Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (2012) (in Chinese)
Yang, Y., Wang, C., Jiang, Z.L.: Analytical and numerical investigations of the reflection of asymmetric nonstationary shock waves. Shock Waves 22, 435–449 (2012)
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 11372333, 90916028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, G., Wang, C., Teng, H. et al. Study on Mach stems induced by interaction of planar shock waves on two intersecting wedges. Acta Mech. Sin. 32, 362–368 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-015-0498-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-015-0498-2